Top Interview 150
66. Plus One
Easy
You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to least significant in left-to-right order. The large integer does not contain any leading 0's.
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.
Example 1:
Input: digits = [1,2,3] Output: [1,2,4] Explanation: The array represents the integer 123. Incrementing by one gives 123 + 1 = 124. Thus, the result should be [1,2,4].
Example 2:
Input: digits = [4,3,2,1] Output: [4,3,2,2] Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321. Incrementing by one gives 4321 + 1 = 4322. Thus, the result should be [4,3,2,2].
Example 3:
Input: digits = [9] Output: [1,0] Explanation: The array represents the integer 9. Incrementing by one gives 9 + 1 = 10. Thus, the result should be [1,0].
Constraints:
1 <= digits.length <= 1000 <= digits[i] <= 9digitsdoes not contain any leading0's.
Code
풀이 1 (2024.04.29)
class Solution(object):
def plusOne(self, digits):
global n
n = ""
for i in digits:
n += str(i)
n = int(n) + 1
return list(map(int, list(str(n))))Time: 18 ms (37.86%), Space: 11.7 MB (39.94%)
풀이 2 (2025.03.07)
class Solution(object):
def plusOne(self, digits):
digits = list(map(str, digits))
num = int(''.join(digits)) + 1
return list(map(int, list(str(num))))Time: 0ms (100.00%), Space: 12.4 MB (52.06%)
풀이 1은 풀이 2에 비해 비효율적이다.
풀이 2는 간단하게 리스트의 요소들을 전부 합치고 1을 더해 변수 num에 저장한다 num을 다시 리스트화해서 반환해준다.
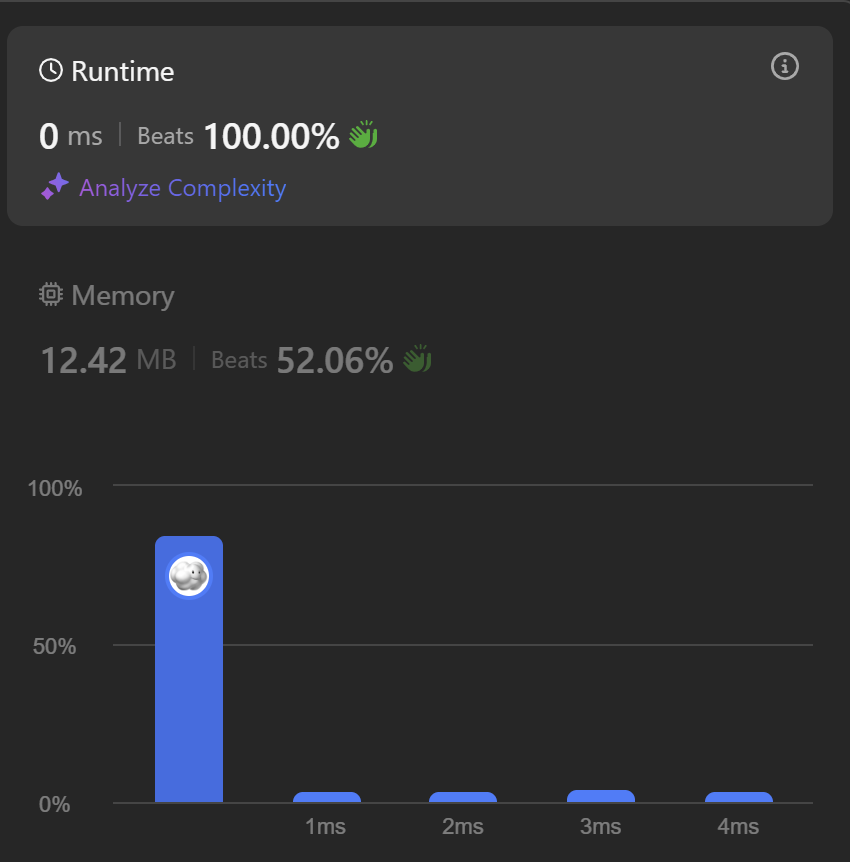
Time Complexity
-
list(map(str, digits)):- N개의 자릿수를 전부 str화시킨다.
-
num = ''.join(digits) + 1: -
list(map(int, list(str(num)))):str(num)-list(str(num))-map(int, list(str(num)))-
