https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11660
우선, 이중배열을 제대로 짚고 넘어가야 이 문제를 이해하기 쉽다.
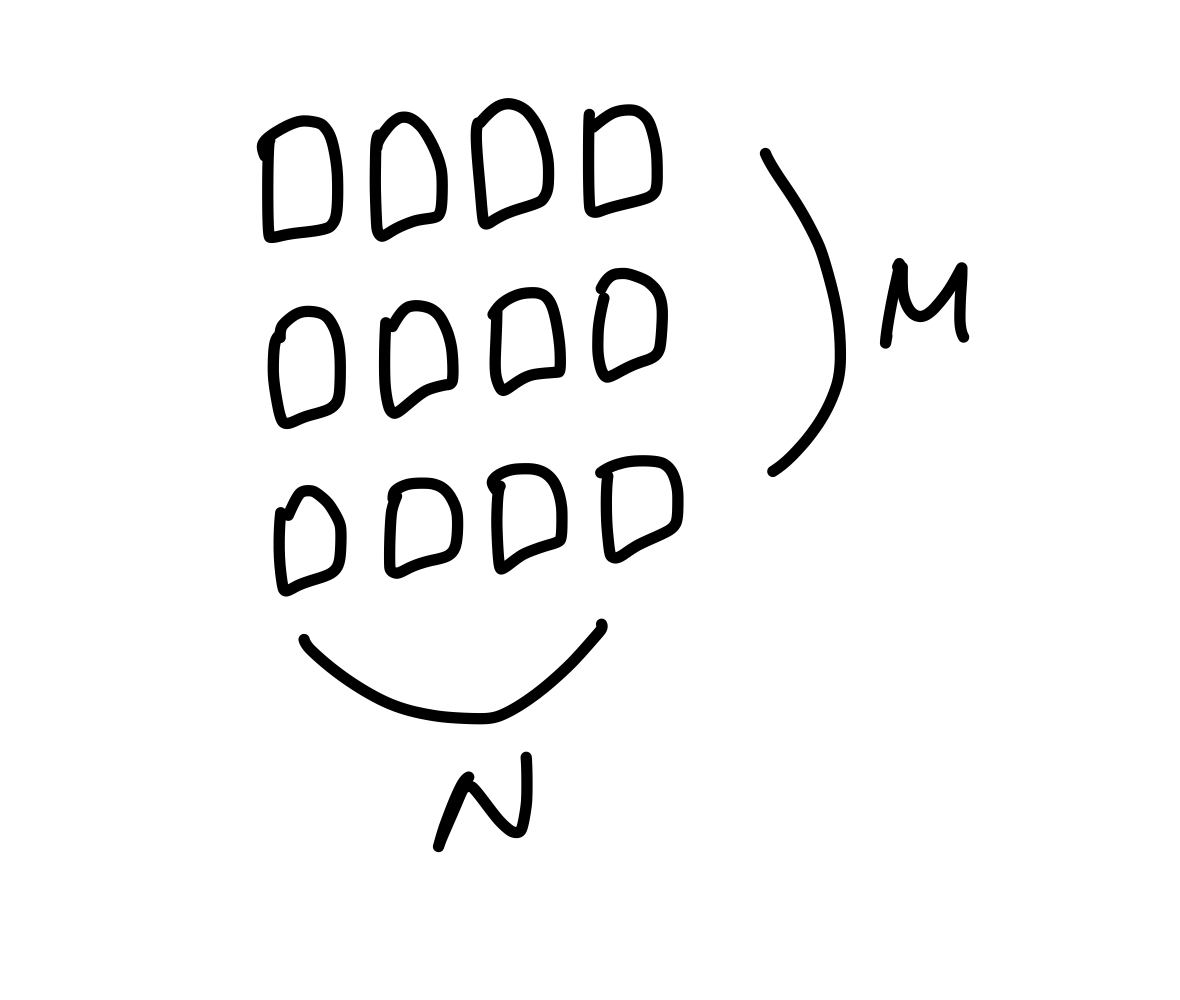
int[M][N]의 경우, M개의 행과 N개의 열 이라는 뜻이다.
즉, 다음과 같은 모양인 것이다.
초반, 내가 생각한 프로세스는 다음과 같았다.
- M과 N을 입력받음
- N * N의 표를 이중배열로 입력받음
- M만큼 반복하여 4개의 수를 입력받음(x,y좌표)
- startX, startY, endX, endY값을 구한 후 for문을 돌려 배열을 차근차근 더해준다
그래서 구현한 코드는 다음과 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] inputNM = br.readLine().split(" ");
int N = Integer.parseInt(inputNM[0]); //표의 크기
int M = Integer.parseInt(inputNM[1]); //합을 구해야 하는 횟수
int[][] table = new int[N][N]; //표. [x][y]는 (x,y)를 의미
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { //표를 입력받음
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
table[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(input[j]);
}
}
int[][] xy = new int[M][4]; //x,y좌표를 저장할 배열
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { //M만큼 반복해서 입력받음
String[] inputXY = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { //N만큼 쪼개서 배열에 저장
xy[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(inputXY[j]);
}
}
int startX = 0;
int startY = 0;
int endX = 0;
int endY = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
startX = xy[i][0] - 1;
startY = xy[i][1] - 1;
endX = xy[i][2] - 1;
endY = xy[i][3] - 1;
int sum = 0;
for (int a = startX; a <= endX; a++) {
for (int j = startY; j <= endY; j++) {
sum = sum + table[a][j];
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
br.close();
}
}

하지만, 시간초과가 발생하였고 인터넷을 찾아보니 DP, 즉 누적합을 이용해야 하는 문제였다. DP는 이전 계산 결과를 재사용하기 때문에 반복적인 덧셈 연산을 피할 수 있고, 그래서 속도가 더 빠르다.
예시로 [a,b,c,d]의 값을 구하려면 'a + b', '(a + b) + c', '((a + b) + c) + d'의 과정이 필요하지만 dp를 사용하면 a+b+c가 누적된 dp값 + d만 해주면 되므로 단 한번의 덧셈을 통해 구현할 수 있다.
이후 dp를 사용하여 문제를 해결하였다. dp를 사용하는 것을 넘어 초반에는 입력을 받는 로직과 배열에 저장하는 로직을 따로 구현해 주었었다. 하지만, 한번에 해결할 수 있는 방법이 떠올라 코드를 더 간소화시켰다.
아래는 정답 코드이다.
package silver1;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num11660 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] inputNM = br.readLine().split(" ");
int N = Integer.parseInt(inputNM[0]); //표의 크기
int M = Integer.parseInt(inputNM[1]); //합을 구해야 하는 횟수
int[][] table = new int[N + 1][N + 1]; //표. [x][y]는 (x,y)를 의미
int[][] sum = new int[N + 1][N + 1]; //누적합을 저장할 배열
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { //표를 입력받음
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
table[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(input[j - 1]);
sum[i][j] = table[i][j] + sum[i - 1][j] + sum[i][j - 1] - sum[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
String[] inputXY = br.readLine().split(" ");
int startX = Integer.parseInt(inputXY[0]);
int startY = Integer.parseInt(inputXY[1]);
int endX = Integer.parseInt(inputXY[2]);
int endY = Integer.parseInt(inputXY[3]);
int result = sum[endX][endY] - sum[endX][startY - 1] - sum[startX - 1][endY] + sum[startX - 1][startY - 1];
System.out.println(result);
}
br.close();
}
}

7월 10일에 모의 코테가 있다. 그 전까지 매일 하나씩 풀도록 노력할 예정이다.
