실습
- ansible-server, ansible-node1~3, ansible-server2(box: generic/ubuntu1804)
-> cpu : 2 -> memory : 2048 -> public_network -> br0, private_network: 10.10.10.20
- 모두 다 완성됐다면 vagrant halt 종료
- 해결
############ Server2 ############ config.vm.define "server2" do |cfg4| cfg4.vm box = "generic/ubuntu1804" cfg4.vm.provider :libvirt do |resource| resource.cpus = 2 resource.memory = 2048 end cfg4.vm.host_name = "server2" cfg4.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :mode => "bridge", :type =>"bridge" cfg4.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.20" cfg4.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60014, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh" cfg4.vm.synced_folder "../data", "vagrant", disabled: true # /vagrant 공유 비활성화 end
net-autostart 활성화
virsh net-list --all Name State Autostart Persistent ---------------------------------------------------------- default active yes yes project20 active no yes vagrant-libvirt active no yes
- net-autostart 활성화
virsh net-autostart project20virsh net-list --all Name State Autostart Persistent ---------------------------------------------------------- default active yes yes project20 active yes yes vagrant-libvirt active no yes
ubuntu 이미지 인스턴스 추가하기
# -*- mode: ruby -*- # # vi: set ft=ruby : Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| ############ node01 ############ config.vm.define "node1" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "centos/7" cfg.vm.host_name = "node1" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :mode => "bridge", :type =>"bridge" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.11" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60011, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "mykey.pem.pub", destination: "/home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "cat /home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys" end ############ node02 ############ config.vm.define "node2" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "centos/7" cfg.vm.host_name = "node2" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :mode => "bridge", :type =>"bridge" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.12" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60012, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "mykey.pem.pub", destination: "/home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "cat /home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys" end ############ node03 ############ config.vm.define "node3" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "centos/7" cfg.vm.host_name = "node3" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :mode => "bridge", :type =>"bridge" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.13" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60013, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "mykey.pem.pub", destination: "/home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "cat /home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys" end ############ Server ############ config.vm.define "server" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "centos/7" cfg.vm.provider :libvirt do |resource| resource.cpus = 2 resource.memory = 1024 end cfg.vm.host_name = "server" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :mode => "bridge", :type =>"bridge" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.10" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install -y epel-release" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "yum install -y ansible" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "mykey.pem", destination: "/home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "chmod 600 /home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "ssh_config_mykey", destination: "/home/vagrant/ssh_config_mykey" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "cat /home/vagrant/ssh_config_mykey >> /etc/ssh/ssh_config" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo '10.10.10.11' >> /etc/ansible/hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo '10.10.10.12' >> /etc/ansible/hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo '10.10.10.13' >> /etc/ansible/hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo '10.10.10.15' >> /etc/ansible/hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo '10.10.10.16' >> /etc/ansible/hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "sudo ssh-keyscan 10.10.10.11 >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/known_hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "sudo ssh-keyscan 10.10.10.12 >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/known_hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "sudo ssh-keyscan 10.10.10.13 >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/known_hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "sudo ssh-keyscan 10.10.10.15 >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/known_hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "sudo ssh-keyscan 10.10.10.16 >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/known_hosts" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "chown vagrant.vagrant /home/vagrant/.ssh/known_hosts" end ############ Server2 ############ config.vm.define "server2" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "generic/ubuntu1804" cfg.vm.provider :libvirt do |resource| resource.cpus = 2 resource.memory = 2048 end cfg.vm.host_name = "server2" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :mode => "bridge", :type =>"bridge" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.14" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60014, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "vagrant", disabled: true # /vagrant 공유 비활성화 end ############ ubuntu1 ############ config.vm.define "node4" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "generic/ubuntu1804" cfg.vm.host_name = "ubuntu1" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :type => "bridge" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60015, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.15" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "mykey.pem.pub", destination: "/home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "cat /home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys" end ############ ubuntu2 ############ config.vm.define "node5" do |cfg| cfg.vm.box = "generic/ubuntu1804" cfg.vm.host_name = "ubuntu2" cfg.vm.network "public_network", :dev => "br0", :type => "bridge" cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60016, id: "ssh" cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "10.10.10.16" cfg.vm.provision "file", source: "mykey.pem.pub", destination: "/home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub" cfg.vm.provision "shell", inline: "cat /home/vagrant/.ssh/mykey.pem.pub >> /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys" end end
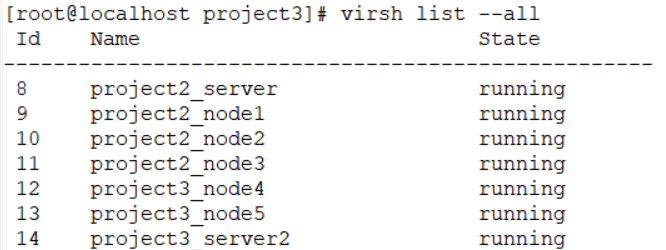
- 생성 확인
virsh list --all
1. 데이터센터 그룹 이름을 통한 인벤토리 작성
- 서버 접속
vagrant ssh server
- 연결된 호스트 정보
cat /etc/ansible/hosts | tail -7ansible all -m ping --list-hosts
- Instance의 Private Network Ip 추가
sudo vi /etc/ansible/hosts [centos] centos1 ansible_host=10.10.10.11 centos2 ansible_host=10.10.10.12 centos3 ansible_host=10.10.10.13 [ubuntu] ubuntu1 ansible_host=10.10.10.14 ubuntu2 ansible_host=10.10.10.15 [koreaeast] centos1 centos2 ubuntu1 [koreawest] centos3 ubuntu2
2. when조건과 facts
2.1 facts
- httpd 설치하기
touch httpdinstall.yaml--- - name: HTTPD 설치 hosts: koreaeast gather_facts: false become: true tasks: - name: httpd installation yum: name: httpd state: present - name: httpd start service: name: httpd enable: yes state: started
- 실행
ansible-playbook httpdinstall.yaml
- ubuntu1의 경우 yum 모듈을 이용할 수 없으므로 설치가 되지 않는 문제가 발생한다.
when
--- - name: httpd installation hosts: koreaeast gather_facts: true become: true tasks: - name: httpd install yum: name: httpd state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: httpd start service: name: httpd enable: yes state: started
- 다음과 같이 when을 사용하여 조건을 걸었다.
- server는 gather_facts를 통해서 Node의 facts 를 사용해 조건에 해당하는 Node에게 명령을 전달한다.
[quiz]
- 배포판 CentOS 는 yum 을 이용하여 httpd 를 설치하고, 배포판 버전 Ubuntu 또는 Debian 이라면 apt 이용하여 nginx 설치해 주세요
cat httpdinstall.yaml --- - name: HTTPD 설치 hosts: koreaeast gather_facts: true become: true tasks: - name: httpd installation yum: name: httpd state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: nginx installation apt: pkg: nginx state: present update_cache: yes # nginx 패키지에 대한 의존성을 갖는 목록을 리스트업 when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'apt' # centos 에는 yum, ubuntu 에서는 apt 를 이용하여 각각 httpd 와 nginx 를 설치하게 할 수 있다 # update_cache 를 yes 로 하면, nginx 패키지에 대한 의존성을 갖는 목록을 리스트업 해준다
- 배포하기
[vagrant@server ~]$ ansible-playbook httpdinstall.yaml
3. 플레이북 내에서 처리 결과를 변수 담고 이를 debug로 확인하기
- name: test shell: ls /home
- 위의 결과는 playbook이 실행될때 출력되지 않는다.
- 따라서 해당 결과를 별도의 변수에 담고 이를 debug를 통해 출력시켜보자
[quiz]
- CentOS 만 별도로 골라서 httpd 를 실행하고 처리결과를 실시간으로 화면에 디버그로 띄우세요
[vagrant@server ~]$ cat ethinfo.yaml --- - name: VM interface check gather_facts: true hosts: all tasks: - name: PRINT IP ADDRESS debug: msg: - "NodeName : {{ ansible_nodename }}" - "eth0 : {{ ansible_eth0.ipv4.address }}" - "eth1 : {{ ansible_eth1.ipv4.address }}" - "eth2 : {{ ansible_eth2.ipv4.address }}"[vagrant@server ~]$ cat httpdinstall.yaml --- - name: HTTPD 설치 hosts: koreaeast gather_facts: true become: true tasks: - name: httpd installation yum: name: httpd state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' register: resulth - debug: var: resulth - name: start httpd on CentOS VMs service: name: httpd state: started when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'yum' - name: nginx installation apt: pkg: nginx state: present update_cache: yes when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'apt'[quiz]
- github으로 부터 초기에 파일을 클론하였다.
- 이후 update: yes 를 통해 변경된 부분에 대해서는 pull 을 하기로 yml 파일에 작성해 두었다. 이 경우 멱등성이 적용되지 않음로 changed 된다.
- changed 가 될때마다 지정된 작업이 시작되도록 하고 싶다
- 우리의 경우 github 에서 pull 할 때마다 자동으로 httpd 를 재실행 시키고싶다면??
- '트리거를 걸자'
- Question. 아래의 주소로 부터 get_url 을 하세요!!!
- http://192.168.1.97/test.html
- 해당 내용은 CentOS 의 기본 페이지(/var/www/html/index.html)로 보내세요
- 페이지가 보이면 ansible-playbook 을 다시한번 실행했을 때 변경된 페이지를 다시 덮어 씌고 httpd 가 재 실행되어야 한다.
- 이때, httpd 의 재실행 결과를 debug 를 통해 화면에서 볼 수 있어야 한다.
- name: HTTPD 설치 hosts: koreaeast gather_facts: true become: true tasks: - name: httpd installation yum: name: httpd state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: start httpd on CentOS VMs service: name: httpd state: started when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'yum' - name: nginx installation apt: pkg: nginx state: present update_cache: yes when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'apt' - name: curl -X GET http://192.168.1.97/test.html -> local/index.html get_url: url: http://192.168.1.97/test.html dest: /var/www/html/index.html mode: 0644 when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'yum' notify: - triggers1 handlers: - name: triggers1 service: name: httpd state: restarted register: resultd notify: - result - name: result debug: var: resultd
message를 이용하여 출력하기
- cat ethinfo.yaml
--- - name: VM interface check gather_facts: true hosts: all tasks: - name: PRINT IP ADDRESS debug: msg: - "NodeName : {{ ansible_nodename }}" - "eth0 : {{ ansible_eth0.ipv4.address }}" - "eth1 : {{ ansible_eth1.ipv4.address }}" - "eth2 : {{ ansible_eth2.ipv4.address }}"
- debug - msg를 사용하면 message로 처리 결과를 확인할수 있다.
- 모든 Node에서 자신의 facts에서의 Ip 정보를 출력한다.
handler
- 전 단계가 정상적으로 이루어지거나, 변경 사항이 발생했을 때 동작한다.
Question. 아래의 주소로 부터 get_url 하기
- 해당 내용은 CentOS 의 기본 페이지(/var/www/html/index.html) 로 보내라
- 페이지가 보이면 ansible-playbook 을 다시한번 실행했을 때 변경된 페이지를 다시 덮어 씌고 httpd 가 재 실행되어야 한다.
- 이때, httpd 의 재실행 결과를 debug 를 통해 화면에서 볼 수 있어야 한다
--- - name: httpd installation hosts: koreaeast gather_facts: true become: true tasks: - name: httpd install yum: name: httpd state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: httpd start service: name: httpd state: started when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: nginx installation apt: pkg: nginx state: present update_cache: yes when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'apt' - name: get it get_url: url: http://192.168.1.97/test.html dest: /var/www/html/index.html mode: 644 when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' notify: - trigger1 register: resulth
- debug:
var: resulthhandlers:
- name: trigger1
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
register: triggerre
- debug:
var: triggerre- get_url 을 할 때, changed 가 발생하면, handler 를 호출한다