🌿 sstream
sstream은 C++ 표준 라이브러리의 헤더 파일로,
문자열(string)을 스트림(Stream)처럼 다룰 수 있게 해주는 도구이다.
문자열을 마치 파일이나 콘솔 입출력처럼 읽고 쓰는 통로로 사용할 수 있도록 해준다.
🔷 헤더파일
#include <sstream>대표적으로 세 가지 클래스가 있다.
| 클래스 | 특징 |
|---|---|
std::stringstream | 문자열에 대해 입력과 출력을 모두 지원한다. |
std::istringstream | 문자열 입력만 지원한다. |
std::ostringstream | 문자열 출력만 지원한다. |
🔷 멤버함수
| 함수 | 설명 |
|---|---|
str() | 현재 문자열 가져오기 |
str(string) | 문자열 새로 지정하기 |
clear() | 상태 플래그(EOF 등) 초기화입력 ↔ 출력이 오갈 때는 필수완전 새로운 문자를 할당할 때 권장 |
eof() | 스트림이 끝에 도달했는지 확인 |
good() | 스트림이 정상 상태인지 확인 |
🔷 활용 예시
-
생성자에 문자열을 넣으면 내부 버퍼에 문자열을 담는다.
string str = "10 + 20 - 5" stringstream ss(str); -
>>연산자를 사용하면 공백 기준으로 문자열을 잘라 하나씩 읽어온다.string token; ss >> token; // token == "10" ss >> token; // token == "+" ss >> token; // token == "20" while (ss >> temp) { vec.push_back(temp); } -
숫자 문자열을 읽을 때는 바로
int나double에 담으면 된다.int num; ss >> num; // num == 10
🔷 활용법
대표적인 활용법 나누기 / 합치기
✅ istringstream
- 문자열을 쉽게 분해(parsing)할 수 있다
-
문자열을 공백이나 구분자로 잘라서 토큰화하기 편리하다.
-
공백이나 구분자 단위로 문자열을 자르고 각 토큰을 변수에 읽어올 수 있다.
-
마치
cin으로 입력 받듯이 사용 가능.string str = "123 456 789"; istringstream iss(str); int a, b, c; iss >> a >> b >> c; // 123, 456, 789를 각각 변수에 저장
-
✅ ostringstream
- 숫자나 문자열을 문자열 버퍼에 출력할 수 있다
-
마치
cout처럼 여러 값을 이어 붙일 수 있다. -
str()로 값을 가져온다.
ostringstream oss; oss << "Value: " << 42; string result = oss.str(); // "Value: 42"
-
🌿 공백이 포함된 문자열 자르기
✅ 예제 코드
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int solution(string str)
{
stringstream ss(str);
vector<string> vec;
string temp;
// 공백 기준으로 토큰 분리
while (ss >> temp) {
vec.push_back(temp);
}
int answer = stoi(vec[0]);
// i = 1부터 시작해 연산자와 숫자를 순서대로 처리
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i += 2) {
if (vec[i] == "+")
answer += stoi(vec[i + 1]);
else
answer -= stoi(vec[i + 1]);
}
return answer;
}✅ 사용 예
solution("3 + 5 - 2"); // 6
solution("10 - 4 + 1"); // 7🌿 stringstream + getline()
공백이 아닌 쉼표나 탭으로 구분하려면 getline()을 사용해야 한다.
stringstream ss("apple,banana,cherry");
string token;
while(getline(ss, token, ','))
{
cout << "단어: " << token << endl;
}출력:
단어: apple
단어: banana
단어: cherrygetline()은 공백뿐만 아니라 반점(,)이나 세미콜론(;) 같은 다른 문자를 구분자로 사용할 수도 있다.
' ' 대신 ','이나 ';' 등을 세 번째 인자로 넘겨주면 된다.
| 항목 | ss >> temp | getline(ss, temp, ' ') |
|---|---|---|
| 구분자 | 공백(space, tab, newline 등 모든 공백 문자) | 지정한 문자 하나만 (예: ' ' 하나만) |
| 연속된 구분자처리 | 연속된 공백은 건너뜀 (→ 빈 문자열 안 생김) | 연속된 구분자는 빈 문자열 포함 가능 |
| 줄바꿈 처리 | 줄바꿈(\n)에서 멈추지 않음 | 기본적으로 \n을 만나면 종료 (또는 지정 문자까지) |
| 않은 경우 | 공백만 있으면 읽지 않음 | 공백만 있어도 빈 문자열로 읽음 |
✅ 숫자를 문자열로 변환
ostringstream객체 생성이to_string()보다 살짝 무겁다.- 정밀도 제어가 필요없는 단순 변환이라면
to_string()이 더 간단.
int n = 123;
ostringstream oss;
oss << n;
string s = oss.str(); // "123"✅ 소수점 자리수 제어
fixed, setprecision과 같이 쓰면 숫자 포맷을 쉽게 바꿀 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double pi = 3.1415926535;
ostringstream oss;
oss << fixed << setprecision(3) << pi;
// fixed: 소수점 아래 자릿수를 고정
// setprecision(3): 소수점 3자리까지 출력
cout << oss.str() << endl; // 3.142
return 0;
}📌 프로그래머스 모스부호 Lv.0 문제
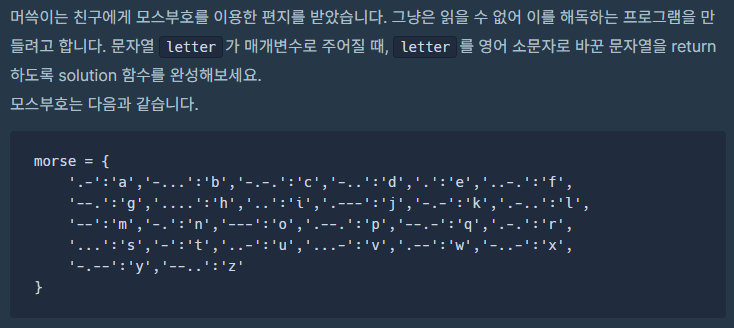
stringstream을 사용하면 공백을 기준으로 자를 수 있다.
<sstream>선언- 모스 부호의 키와 벨류값을 담기 위한 map 선언 후 할당
- stringstream 이름(문자열); ➡ 문자열을 스트림으로 만든다.
- while(stream >> code) ➡ 공백을 기준으로 문자열을 하나씩 읽는다.
- result += morse[code]; ➡ 키 값code로 벨류값을 찾고 result에 추가
✅ >> 연산자는 스트림에서 데이터를 "추출"하는 연산자
cin >> x→ 표준 입력에서 값을 추출stream >> x→ 문자열 스트림에서 값을 추출
즉, stream은 실제로는 stringstream 타입 객체이기 때문에, 내부에 담긴 문자열에서 값을 읽는 역할을 한다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
string solution(string letter)
{
string code;
string result;
map <string, char> morse =
{
{".-", 'a'}, {"-...", 'b'}, {"-.-.", 'c'}, {"-..", 'd'}, {".", 'e'}, {"..-.", 'f'},
{"--.", 'g'}, {"....", 'h'}, {"..", 'i'}, {".---", 'j'}, {"-.-", 'k'}, {".-..", 'l'},
{"--", 'm'}, {"-.", 'n'}, {"---", 'o'}, {".--.", 'p'}, {"--.-", 'q'}, {".-.", 'r'},
{"...", 's'}, {"-", 't'}, {"..-", 'u'}, {"...-", 'v'}, {".--", 'w'}, {"-..-", 'x'},
{"-.--", 'y'}, {"--..", 'z'}
};
stringstream stream(letter);
while(stream >> code)
{
result += morse[code];
}
return result;
}
