클래스 상속 / 접근지정자
!!! 동적 할당할때
Person* p = new Person;
Person* p = new Person();의 차이는 괄호가 있으면 생성자 호출하라는 뜻이다.
- 상속
-
상속이란 어떤 개념을 확장해 새로운 개념을 만들어내는 것입니다. 추상화된 데이터들을 이용해 더 복잡한 개념을 만들어내는 것 이죠.
-
예시를 들었던 프로토스 유닛이라는 개념을 확장해서 질럿 이라는 세부개념을 만들어내는 것과 같습니다.
// 참고사항 동적 할당은 ->로 표현 정적 할당은 .으로 표현
- 상속 방법
- 상속을 받을 땐 : 콜론을 입력하고 상속을 해줄 부모 클래스를 public 키워드와 함께 입력합니다.
3.멤버변수와 멤버 함수
-
자식클래스는 부모클래스의 상속받은 모든 멤버 변수와 멤버함수를 활용할 수 있으며
-
외부에서도 접근이 가능합니다 (public 한정)
- 생성자의 실행 순서
-
생성자가 실행이 되는 순서를 알아봅시다.
-
클래스의 생성자는 부모클래스가 있을 경우 부모클래스의 기본생성자를 자동으로 먼저 호출하게 됩니다.
-
부모클래스가 없다면 자연스럽게 자신의 생성자만 실행하고 끝나게 됩니다.
5.파라미터가 있는 생성자
- 부모클래스가 파라미터를 받는 생성자가 있다면,자식클래스는 부모클래스의 생성자를 꼭 명시적으로 호출을 해 줘야 합니다. 자식클래스에서 어떻게 부모 클래스의 생성자가 초기화될지 알 수 없기 때문입니다.
- 다형성
- 다형성을 통해 클래스 인스턴스를 관리하게 되면 여러 가지 이점이 있습니다. 예를 들어 코드상의 Animal* animals[10] 이라는 배열을 만들어서 해당 배열 안의 실제 값은 Person, 혹은 Dog 등 여러 가지 객체가 들어갈 수 있기 때문이죠. 집합의 개념으로 생각하면 이게 왜 좋은지 알 수 있습니다.
//여기까지 예시 코드 작성
#include "Header.h"
//부모 클래스
class Animal {
public:
int legs;
char name[50];
Animal(int legs, const char* name) {
this->legs = legs;
strcpy(this->name, name);
}
~Animal() {
delete[] name;
}
void printAnimalInfo() {
printf("다리의 갯수: %d\n", legs);
printf("이름 : %s\n", name);
}
};
// 자식 클래스
class Person : public Animal{
public:
char regist_no[30];
Person(const char* regist_no) :Animal(2, "사람") {
strcpy(this->regist_no, regist_no);
}
};
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
Dog() : Animal(4, "강아지") {
printf("Dog 생성자가 실행 됨\n");
}
};
int main() {
Person* p = new Person("1234-9921");
p->printAnimalInfo();
Dog* s = new Dog();
s->printAnimalInfo();
return 0;
}- public, protected, private
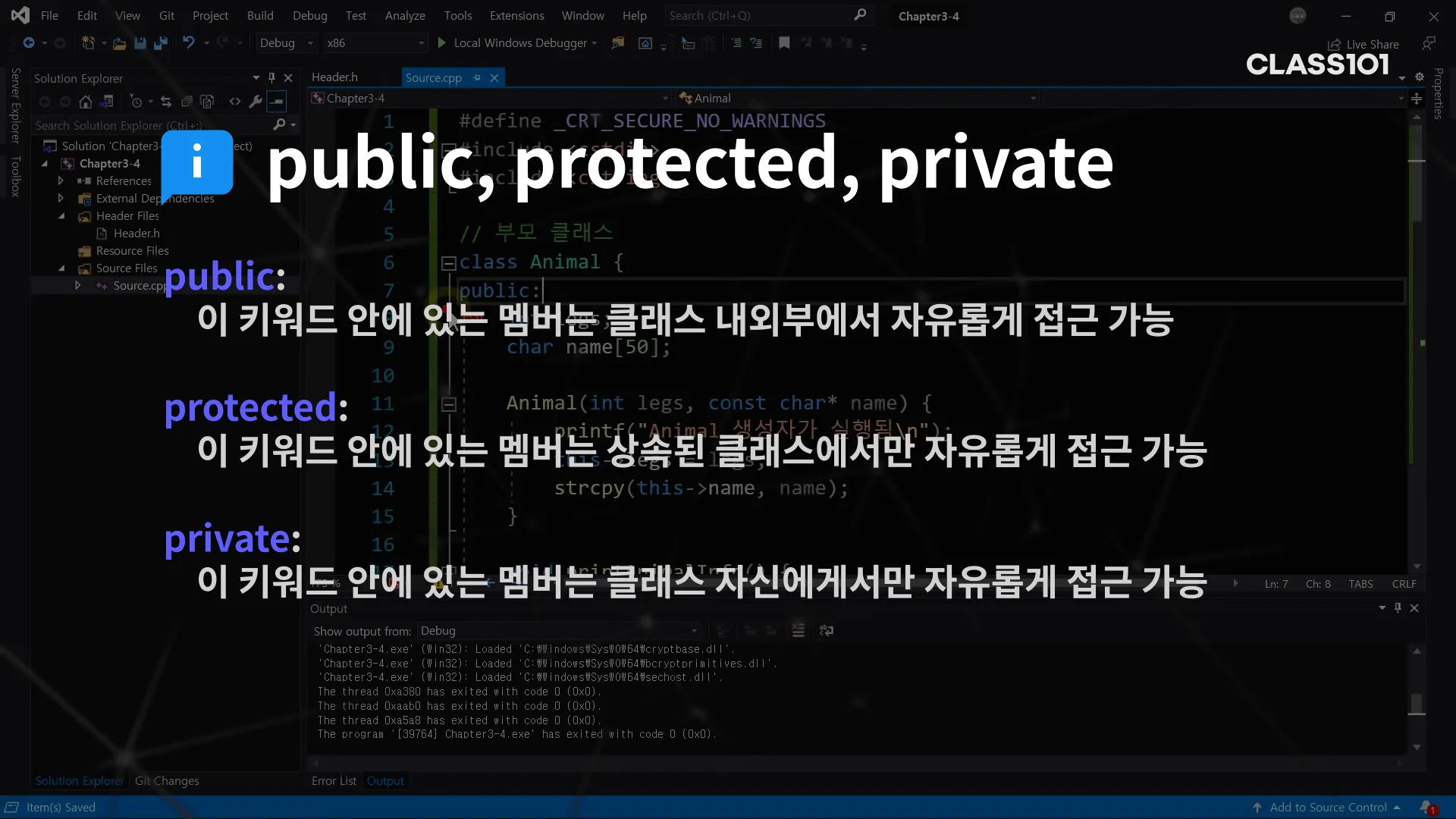
- 접근 지정자를 통해 클래스 멤버의 접근 위치를 강제할 수 있습니다. public의 경우 자유로운 접근을 허용하며 protected의 경우 자신과 상속된 클래스에서만 접근을 허용하고 private의 경우 자신에게서만 접근을 허용합니다.
- 상속에서의 접근 지정자
- 상속에서의 접근 지정자는 개념만 간단히 알아두시면 됩니다. 현대 프로그래밍에서 접근지정을 통한 상속은 거의 사용되지 않습니다.
연습문제 )
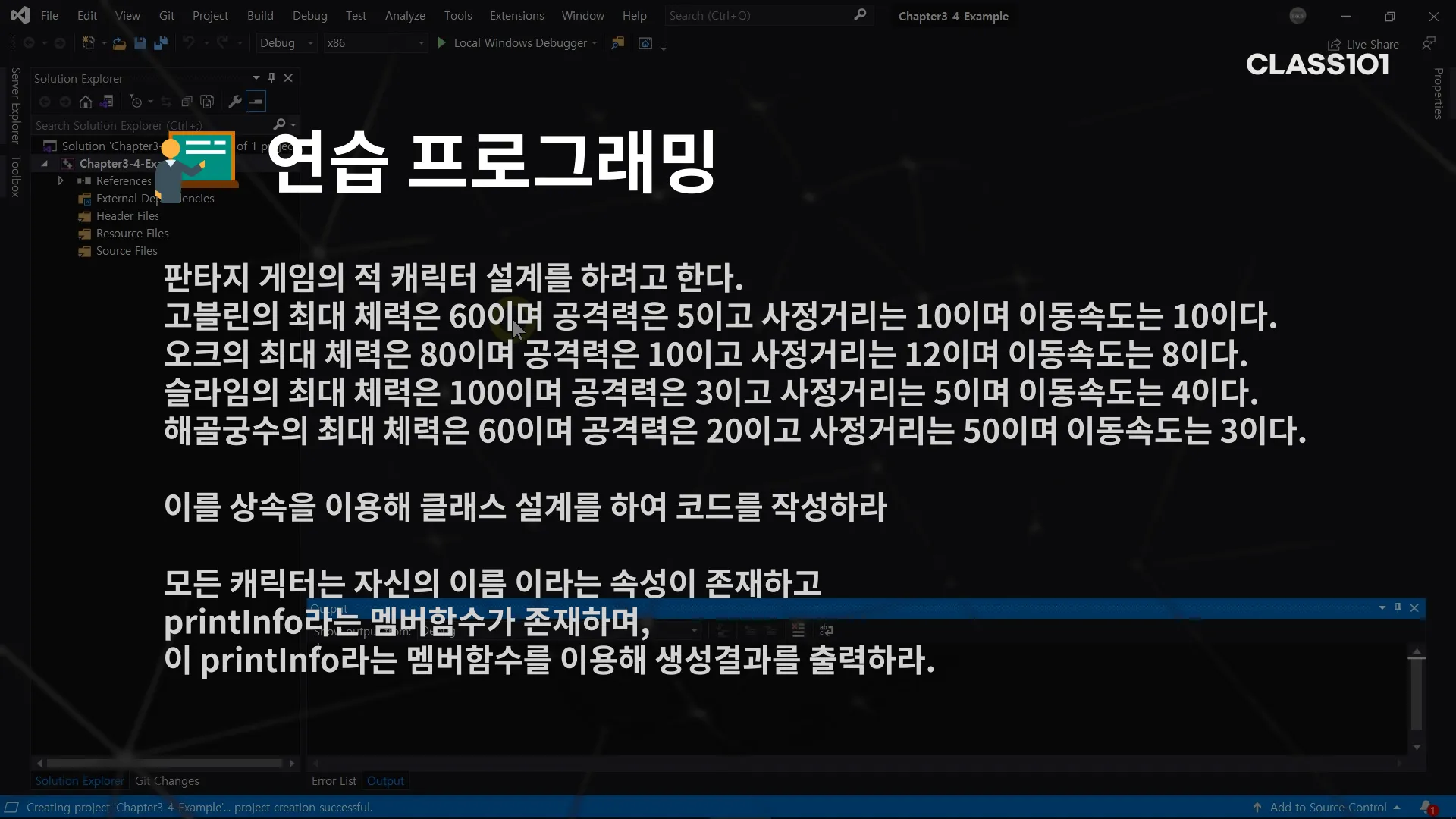
sol)
헤더파일)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
class Characters {
public:
char name[50];
int maxHp;
int atk;
int range;
int speed;
void printINfo() {
printf("%s의 능력치\n", name);
printf("최대체력 : %d\n", maxHp);
printf("공격력 : %d\n", atk);
printf("사정거리 : %d\n", range);
printf("이동속도 : %d\n", speed);
}
};
class Goblin : public Characters {
public:
Goblin() {
strcpy(name, "고블린");
maxHp = 60;
atk = 5;
range = 10;
speed = 10;
}
};
class Ork : public Characters {
public:
Ork() {
strcpy(name, "오크");
maxHp = 80;
atk = 10;
range = 12;
speed = 8;
}
};
class Slime : public Characters {
public:
Slime() {
strcpy(name, "슬라임");
maxHp = 100;
atk = 3;
range = 5;
speed = 4;
}
};
class SkeletonArcher : public Characters {
public:
SkeletonArcher() {
strcpy(name, "해골궁수");
maxHp = 60;
atk = 20;
range = 50;
speed = 3;
}
};소스파일)
#include "Header.h"
int main() {
Characters* units[10] = {nullptr,};
for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++) {
switch (rand() % 4) {
case 0:
units[i] = new Goblin();
case 1:
units[i] = new Ork();
case 2:
units[i] = new Slime();
case 3:
units[i] = new SkeletonArcher();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
units[i]->printINfo();
}
return 0;
}sol2)
헤더파일)
efine _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
class Characters {
public:
char name[50];
int maxHp;
int atk;
int range;
int speed;
Characters(int maxHp, int atk, int range, int speed) {
this->maxHp = maxHp;
this->atk = atk;
this->range = range;
this->speed = speed;
}
void printINfo() {
printf("%s의 능력치\n", name);
printf("최대체력 : %d\n", maxHp);
printf("공격력 : %d\n", atk);
printf("사정거리 : %d\n", range);
printf("이동속도 : %d\n", speed);
}
};
class Goblin : public Characters {
public:
Goblin() : Characters(60, 10, 12, 10) {
strcpy(name, "고블린");
}
};
class Ork : public Characters {
public:
Ork() : Characters(80, 10, 12, 8) {
strcpy(name, "오크");
}
};
class Slime : public Characters {
public:
Slime() : Characters(100, 3, 5, 4) {
strcpy(name, "슬라임");
}
};
class SkeletonArcher : public Characters {
public:
SkeletonArcher() : Characters(60, 20, 50, 3) {
strcpy(name, "해골궁수");
}
};소스파일
#include "Header.h"
int main() {
Characters* units[10] = {nullptr,};
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++) {
switch (rand() % 4) {
case 0:
units[i] = new Goblin();
break;
case 1:
units[i] = new Ork();
break;
case 2:
units[i] = new Slime();
break;
case 3:
units[i] = new SkeletonArcher();
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
units[i]->printINfo();
}
return 0;
}과제형 문제)
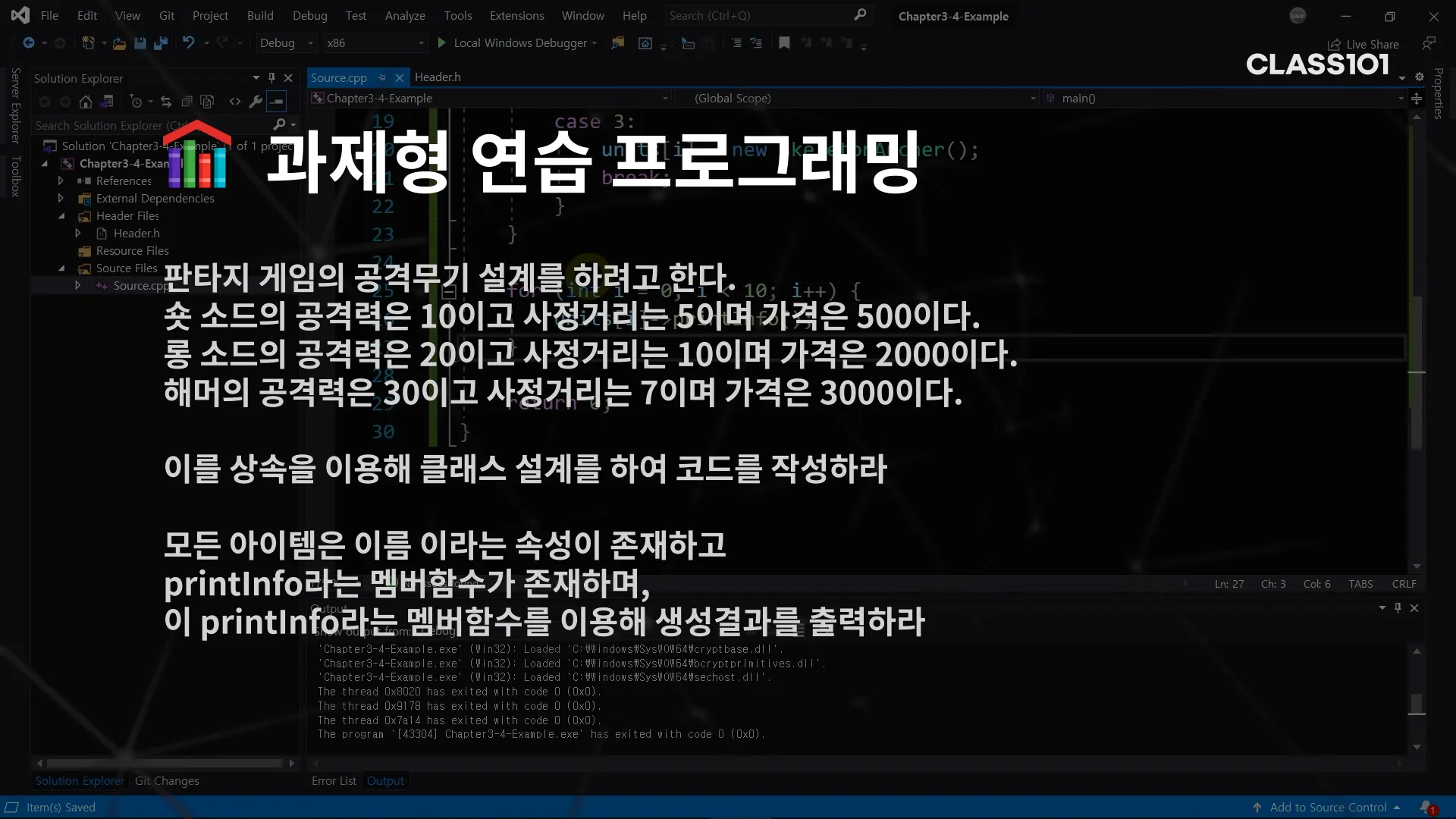
sol)
해더파일)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
class Weapon {
public:
char name[50];
int atk;
int gold;
int range;
Weapon(const char* name,int atk, int range, int gold){
strcpy(this->name, name);
this->atk = atk;
this->range = range;
this->gold = gold;
}
void printInfo() {
printf("%s의 능력치 : \n", name);
printf("공격력 : %d\n", atk);
printf("사정거리 : %d\n", range);
printf("가격(gold) : %d\n", gold);
}
};
class shortSword : public Weapon {
public:
shortSword() : Weapon("숏 소드", 10, 5, 500) {
}
};
class longSword : public Weapon {
public:
longSword() : Weapon("롱 소드", 20, 10, 2000) {
}
};
class Hammer : public Weapon {
public:
Hammer() : Weapon("해머", 30, 7, 3000) {
}
};소스파일)
#include "Header.h"
int main() {
Weapon* units[10] = {nullptr,};
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
switch (rand() % 3) {
case 0:
units[i] = new shortSword();
break;
case 1:
units[i] = new longSword();
break;
case 2:
units[i] = new Hammer();
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
units[i]->printInfo();
}
return 0;
}
