df.pivot(index='date',
columns='category1',
values='price')
# 에러: ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshapeimport pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{"date" : ["2023-07-01","2023-07-01", "2023-07-01", "2023-07-01", "2023-07-01"] ,
"category1" : ["메인", "메인", "사이드", "음료", "사이드"] ,
"category2" : ["양념치킨", "간장치킨", "치즈볼", "콜라", "감자튀김"],
"count" : [1, 2, 1, 4, 1],
"price" : [20000, 50000, 6000, 8000, 8000]})
df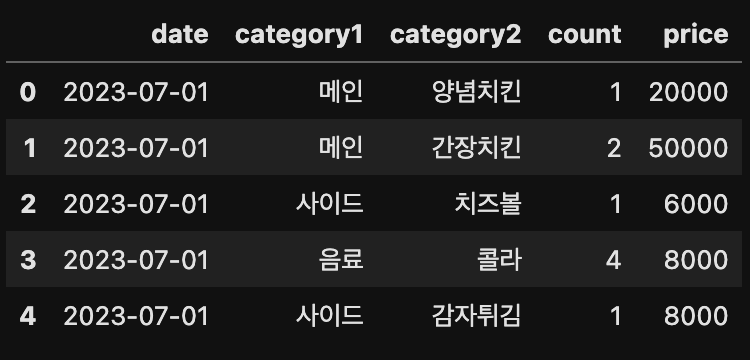
1. pivot()
df.pivot(index='date', columns='category2', values='count')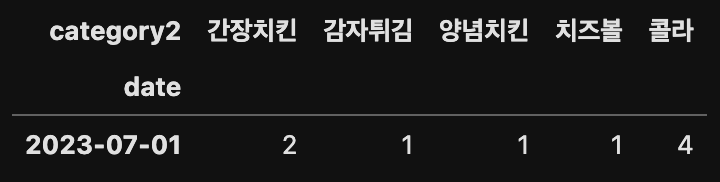
df.pivot(index='category2', columns='date', values='count')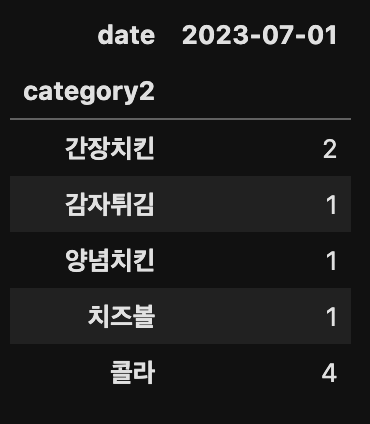
df.pivot(index='category1',
columns='category2',
values=['count', 'price'])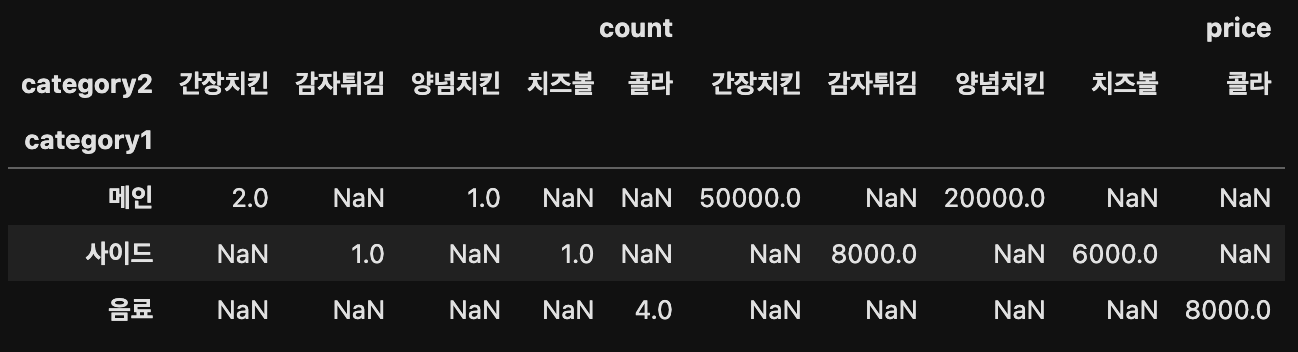
df.pivot_table(index='date',
columns='category1',
values='price')
# 에러: ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape2. pivot_table()
pivot() 메서드는 데이터를 재구조화하는데 사용되며, 중복된 항목이 있는 경우에는 데이터를 재배치할 수 없기 때문에 위와 같이 에러가 발생한다.
하지만 pivot_table() 메서드는 집계 기능을 포함하고 있어 아래와 같이 중복된 항목이 있어도 집계를 할 수 있다.
df.pivot_table(index='date',
columns='category1',
values='price')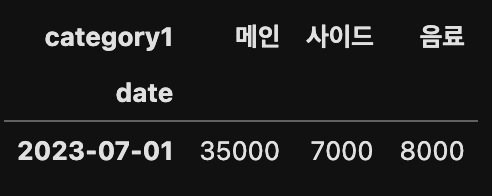
# 일별 총 판매수량과 총 판매금액은?
df.pivot_table(index='date',
values=['count', 'price'],
aggfunc='sum')
# 또는
df.pivot_table(index='date',
values=['count', 'price'],
aggfunc={'count':'sum', 'price':'sum'})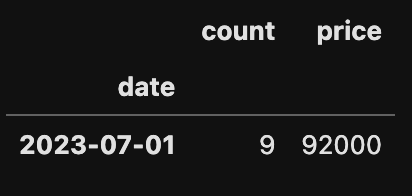
아래와 같이 pivot_table() 메서드는 집계 함수를 사용할 때 여러 개의 집계 함수를 지정할 수 있다.
df.pivot_table(index='date',
values=['count', 'price'],
aggfunc={'count':'sum', 'price':'mean'})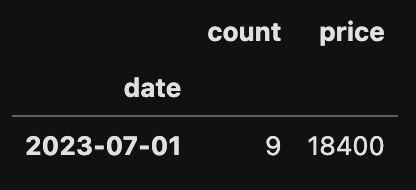
pivot()과 pivot_table() 메서드 모두 데이터프레임을 변형시킬 수 있다. 하지만 pivot() 메서드는 데이터를 재구조화할 때 사용되며, 데이터를 집계하는 옵션이 없다. 그에 반해 pivot_table() 메서드는 데이터를 재구조화할 뿐만 아니라 집계 함수를 사용하여 데이터를 집계할 수 있다. 또한 중복된 값이 있는 경우, 사용자가 지정한 방식에 따라 해당 값을 집계할 수 있다. 이 두 메서드를 적절히 활용하면 데이터를 원하는 형태로 변형하고 분석할 수 있다.
