1. readlines()
readlines() 함수는 파일의 모든 데이터를 읽어서 각 줄을 리스트 형태로 반환한다.
url = '/Users/kimye/Downloads/pythonTxt/'
with open(url + 'language.txt', 'r') as f:
lanList = f.readlines()
print(f'lanList: {lanList}')
print(f'lanList type: {type(lanList)}')
2. readline()
readline() 함수는 파일에서 한 줄을 읽어서 문자열로 반환한다.
url = 'kimye/Downloads/pythonTxt'
with open(url + 'lans.txt', 'r') as f:
line = f.readline()
while line != '':
print(f'line: {line}', end='')
line = f'readline()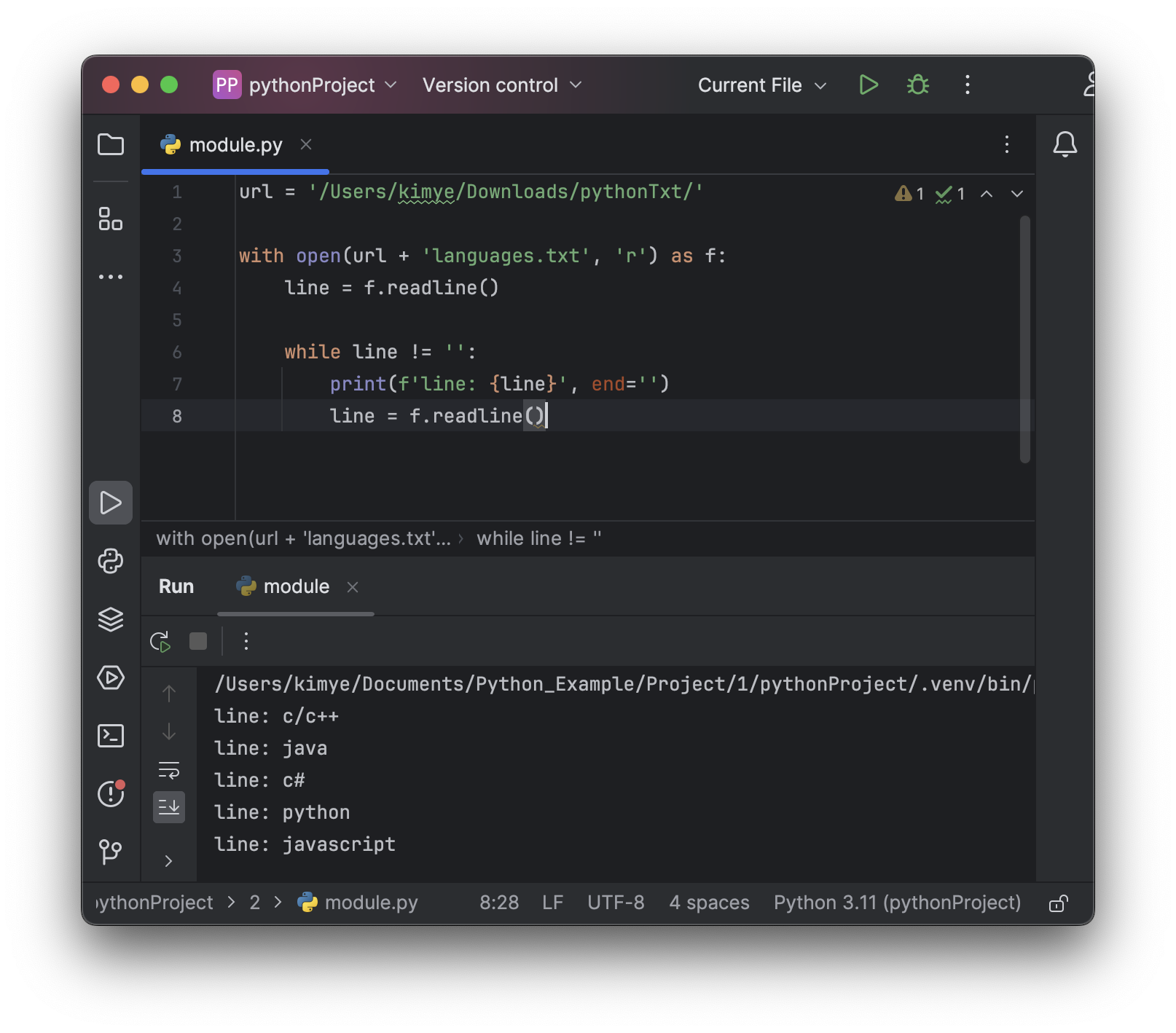
Example: 파일에 저장된 과목별 점수를 파이썬에서 읽어, dictionary에 저장하는 코드 만들기
scoresDic: {'kor': 85, 'eng': 90, 'math': 92, 'sic': 79, 'his': 82}
scoresDic = {}
url = '/Users/kimye/Downloads/pythonTxt/'
with open(url + 'scores.txt', 'r') as f:
line = f.readline()
while line != '':
tempList = line.split(':')
scoresDic[tempList[0]] = int(tempList[1].strip('\n'))
line = f.readline()
print(f'scoresDic: {scoresDic}')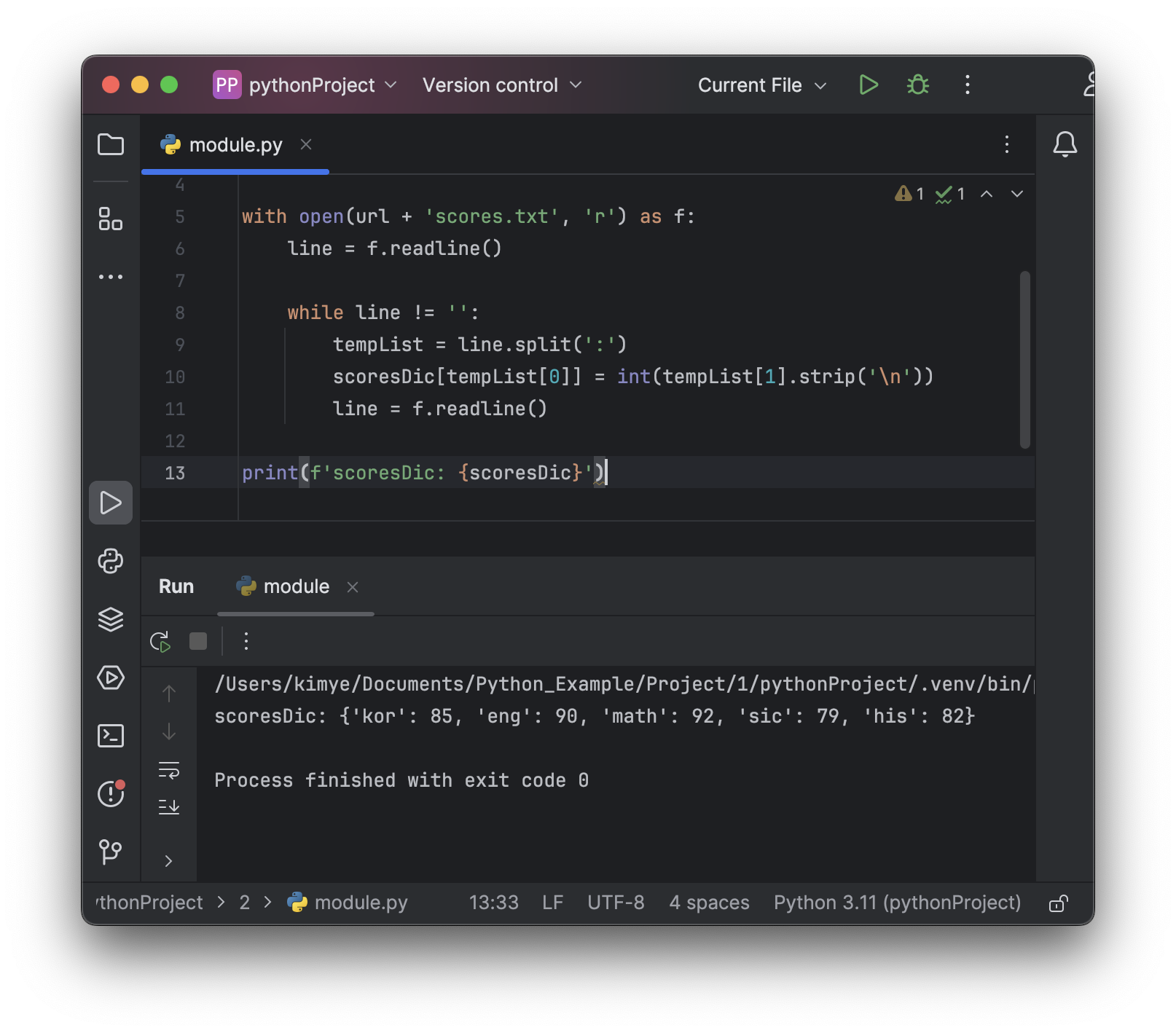
-
while line != '':은 파일의 끝에 도달할 때까지 반복한다. 파일의 끝에 도달하면 line 변수에 빈 문자열('')이 할당되어 루프를 종료한다. -
tempList = line.split(':')은 line 문자열을 콜론(':')을 기준으로 나누어 리스트로 만든다. 이 리스트는 키와 값으로 구성된다. -
scoresDic[tempList[0]] = int(tempList[1].strip('\n'))은 리스트의 첫 번째 요소를 키로, 두 번째 요소를 값으로 사용하여 딕셔너리 scoresDic에 저장합니다. 값은 정수로 변환한 후 개행 문자('\n')를 제거한다. -
line = f.readline()을 통해 다음 줄을 읽어온다. 이 과정을 파일의 끝까지 반복한다.
