백준 1753 - 최단경로
문제 파악
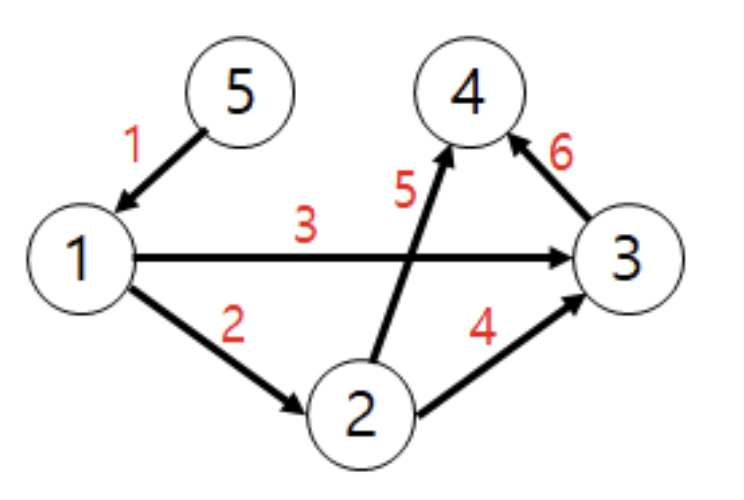
방향 그래프에서 한 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로의 최단 경로를 구하는 문제
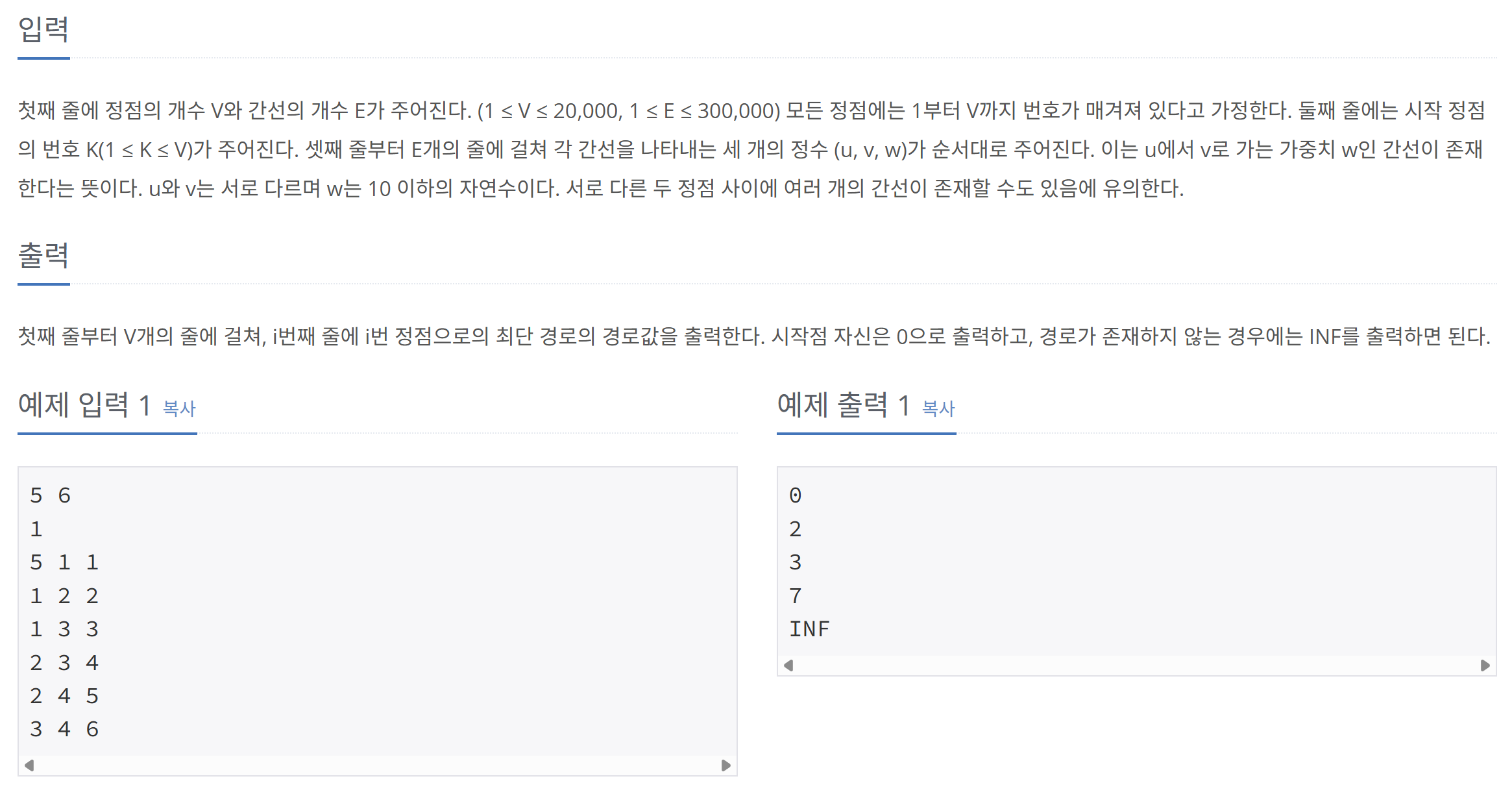
입력
- 첫 줄 : 정점 개수 V, 간선 개수 E
- 둘째 줄 : 시작 정점 K
- 밑에 E개의 줄 : 간선 정보 u, v, w (u에서 v로 가는 가중치 w)
출력
- 시작 정점에서 모든 정점으로의 최단 거리
- 경로가 없으면 INF 출력
다익스트라 알고리즘 : 특정한 하나의 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로 가는 최단 경로를 알려주는 알고리즘
시작 노드에서 가장 가까운 노드에서부터 탐색하면서 각 노드까지의 최단 거리를 구해야 하기 때문에 우선순위 큐를 사용한다.
- 우선 순위 큐 사용 이유 : 일반 큐는 먼저 들어온 순서대로 꺼내기 때문에 가장 가까운 정점인지를 보장할 수 없음
-> 불필요하게 긴 경로를 먼저 탐색하게 될 수 있음
풀이
-
정점 번호와 가중치를 저장하기 위한 노드 클래스 생성
a. Comparable 인터페이스 구현 (compareTo 메소드 구현)
b. 생성자
c. compareTo 메소드 오버라이딩 - 가중치 작은 순서대로우선순위 큐에서 가중치가 작은 순서대로 정렬되게 하고 싶기 때문에 compareTo 메소드 오버라이딩 필요
객체를 정렬할 기준을 정의해야 하기 때문에 comparable 인터페이스 구현이 필요하다!
-> 이런 식으로 하지 않고 람다식 comparator로도 우선순위 큐의 정렬 기준을 작성할 수 있지만, 재사용성과 간결함을 가져가기 위해 comparable을 구현하는 것을 선택 -
도달할 수 없는 거리를 의미하는 상수 선언(INF)
-
노드마다 연결된 간선을 표현하기 위한 인접 리스트 생성
-
각 노드까지의 최단 거리를 저장할 배열 생성
-
버퍼리더와 스트링 토크나이저를 사용해 입력 받기
a. 정점 개수 V와 간선 개수 E
b. 시작 정점 K
c. 입력받은 값들로 인접 리스트 초기화 -
거리 배열을 INF로 모두 초기화
-
다익스트라 함수
a. 우선순위 큐 생성
b. 시작 노드 큐에 넣고 거리는 0으로
c. 큐가 빌 때까지 반복문 실행
d. 가장 가까운 노드 꺼내기
e. 가장 가까운 노드의 정점과 가중치 지정
f. 만약 이미 짧은 거리로 처리된 적이 있으면 무시
g. 이어진 노드들 찾아서 거리 계산 (현재 거리 + 간선 가중치)
h. 새로운 거리가 더 짧으면 갱신하고 큐에 넣기 -
다익스트라 함수 실행
-
거리 배열 출력
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class 최단경로 {
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
//정점
private int vertex;
//가중치
private int weight;
//생성자
public Node(int vertex, int weight) {
this.vertex = vertex;
this.weight = weight;
}
//오버라이딩
public int compareTo(Node other) {
//가중치 작은 순서대로 정렬
return Integer.compare(this.weight, other.weight);
}
}
//도달할 수 없는 거리
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//인접 리스트
static List<Node>[] graph;
//최단 거리 저장 배열
static int[] distance;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
//정점 입력
int V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
//간선 입력
int E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
//시작 정점
int K = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
//인접 리스트 초기화
graph = new ArrayList[V+1];
//정점 번호는 1부터 시작
for (int i=1; i<=V; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
//출발지, 목적지, 가중치 입력
for (int i=0; i<E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
int u = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int v = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int w = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
//u에서 v로 가는 간선을 graph[u]에 추가
graph[u].add(new Node(v, w));
}
//거리 배열 초기화
distance = new int[V+1];
Arrays.fill(distance, INF);
//다익스트라 실행
dijkstra(K);
//각 노드에 대해
for (int i=1; i<=V; i++) {
//만약 거리 배열이 최대면(못가면)
if (distance[i] == INF) {
System.out.println("INF");
}
//도달 가능하면 최단 거리 출력
else {
System.out.println(distance[i]);
}
}
}
//다익스트라 함수
static void dijkstra(int start) {
//우선순위 큐 생성
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
//시작 노드 큐에 넣기
pq.add(new Node(start, 0));
//start는 0으로 거리 넣기
distance[start] = 0;
//큐가 빌 때까지
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
//가장 가까운 노드 꺼내기
Node current = pq.poll();
int curVertex = current.vertex;
int curWeight = current.weight;
//만약 이미 더 짧은 거리로 처리된 적이 있다면
if (curWeight > distance[curVertex]) {
//그 노드는 무시
continue;
}
//현재 노드에서 이어진 이웃 노드 탐색
for (Node next : graph[curVertex]) {
//현재 거리 + 간선 가중치
int newDist = distance[curVertex] + next.weight;
//만약 더 짧은 거리르 발견하면
if (newDist < distance[next.vertex]) {
//거리 갱신
distance[next.vertex] = newDist;
//큐에 넣기
pq.add(new Node(next.vertex, newDist));
}
}
}
}
}