1. Introdunction to GUI Programming
GUI(Graphical User Interface)
- 유저가 직접 정보를 볼 수 있는 화면
- 유저와 상호작용 하는 방식. 개발을 모르더라도 사용 가능하도록 함.
ex) button, text fields, menus, windows
Java Swing
- GUI를 위해 미리 정의해놓은 class들의 모음
- Platform Independent : 특정 OS에 국한되지 않음
- Rich and Customizable Component : 대부분의 component와 기능 제공 + 개발자가 커스텀 가능
Key Concept of Swing
- Component-Based Model
- 다양한 Component 조합해서 화면 구성
- container ⊃ butten, text field
- Event-Driven Model
- Event 를 통해 유저와 상호작용 함
ex) button 클릭 / text 입력 - Component 가 이벤트를 생성하면 event listener 가 들음.
- Event 를 통해 유저와 상호작용 함
- Hierarchical Organization
- Component 들은 위계 질서를 가지고 정렬되어 있음
- 복잡하게 구성된 유저 인터페이스 생성 가능.
2. Components & Containers
Containers
-
Component를 가지고 구성하는 도화지.
-
GUI 레이아웃을 구성할 때 필수적
Top level
JFrame: main 창. 이 아래 panel(⊃ component) 배치JDialog: 팝업창. 경고, 알림용JApplet: 보안 이슈로 잘 사용하지 않음
Intermidiate level → 공간 구분 시 사용
JPanel: component끼리 모아두는 곳- layout manager 통해 요소 정렬
- Container 내부에 또 다른 Container 넣을 수 있음.
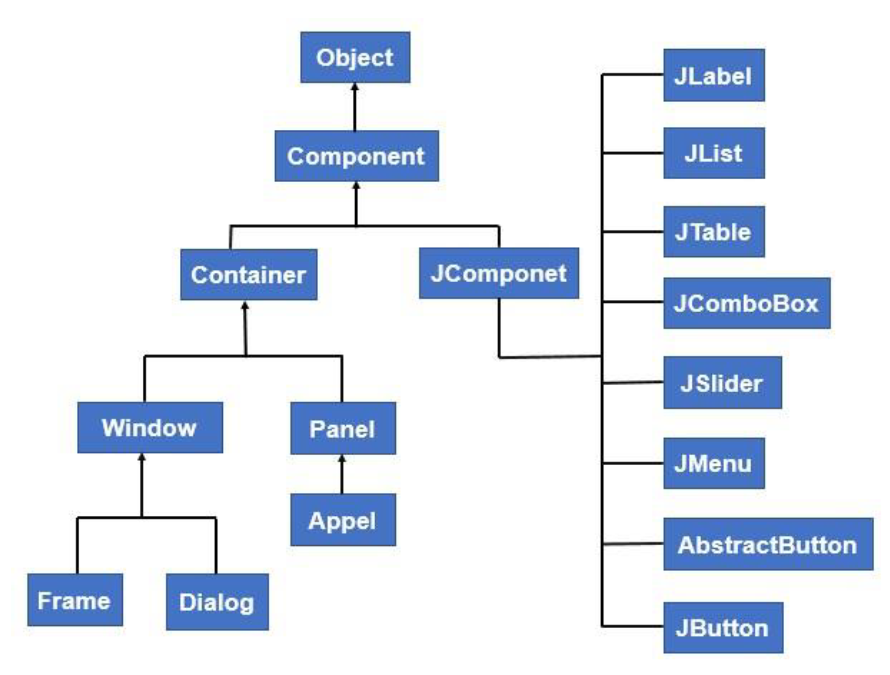
Basic Components
- GUI 를 만들 때 기본 클래스
- 모든 Component는
java.swing.JComponent클래스를 상속 받음- 기본 값 : size, position, color
- 기본 행동 : responsing user input
- 한계
- Lack of Sophistication : 복잡한 구조를 만들기엔 부족함.
- Limited Customization : 실시간 업데이트가 안됨. 한 번 만든 후에는 변화 불가
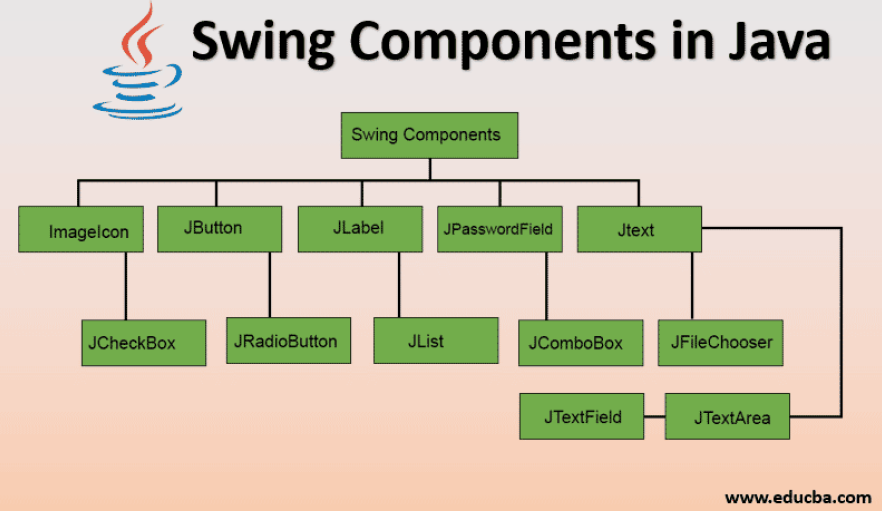
종류
JButton: 클릭될 수 있는 버튼JLabel: 텍스트나 이미지를 보여줌 (이후 수정 불가)JTextField: 한 줄짜리 유저가 입력 가능한 입력 공간JPasswordField: 입력한 값이 보이지 않는 입력 공간
3. Advanced Components
JTree
- 계층적인 데이터 구조를 나타낼 때 사용
- node는 확장하거나 나눠질 수 있음
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.tree.DefaultMutableTreeNode;
public class BasicJTreeExample extends JFrame {
public BasicJTreeExample() {
setTitle("Basic JTree Example");
setSize(300, 300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Create a root node
DefaultMutableTreeNode root = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Root");
// Ad first level child nodes
DefaultMutableTreeNode child1 = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Child 1");
DefaultMutableTreeNode child2 = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Child 2");
// Add second level child nodes to child 1
DefaultMutableTreeNode grandChild1 = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("grandChild 1");
DefaultMutableTreeNode grandChild2 = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("grandChild 2");
child1.add(grandChild1);
child1.add(grandChild2);
// Construct the tree structure
root.add(child1);
root.add(child2);
// Create a JTree
JTree tree = new JTree(root);
// Add the tree to the frame
JScrollPane TreeView = new JScrollPane(tree);
add(TreeView);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BasicJTreeExample();
}
}
JScrollPane에서만 사용 가능- 기본 Panel은 사이즈가 고정. 그렇지만 Tree는 얼마나 길지 모르므로 ScrollPane 사용.
JTree⊂JScrollPane⊂JPanel가능
JTable
- 표 형식의 데이터 구조를 나타낼 때 사용
- 열 정렬, cell 수정, custom cell rendering 지원
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.DefaultTableModel;
public class BasicJTableExample extends JFrame {
public BasicJTableExample() {
setTitle("Basic JTable Example");
setSize(400, 300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
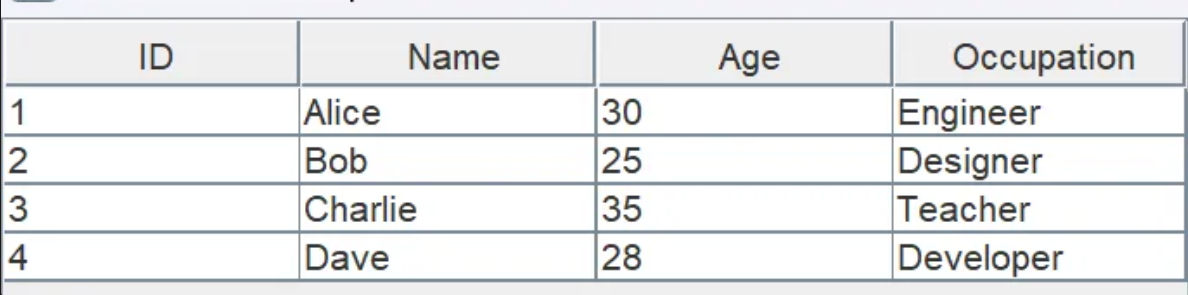
// Define column names for the table
String[] columnNames = {"ID", "Name", "Age", "Occupation"};
// Define data for the table (2D array)
Object[][] data = {
{1, "Alice", 30, "Engineer"},
{2, "Bob", 25, "Designer"},
{3, "Charlie", 35, "Teacher"},
{4, "Dave", 28, "Developer"}
};
// Create table model with the specified data and column names
DefaultTableModel model = new DefaultTableModel(data, columnNames);
// Create JTable with the model
JTable table = new JTable(model);
// Add the table to a scroll pane
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(table);
add(scrollPane);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BasicJTableExample();
}
}
JTree와 마찬가지로JScrollPane에서만 사용 가능
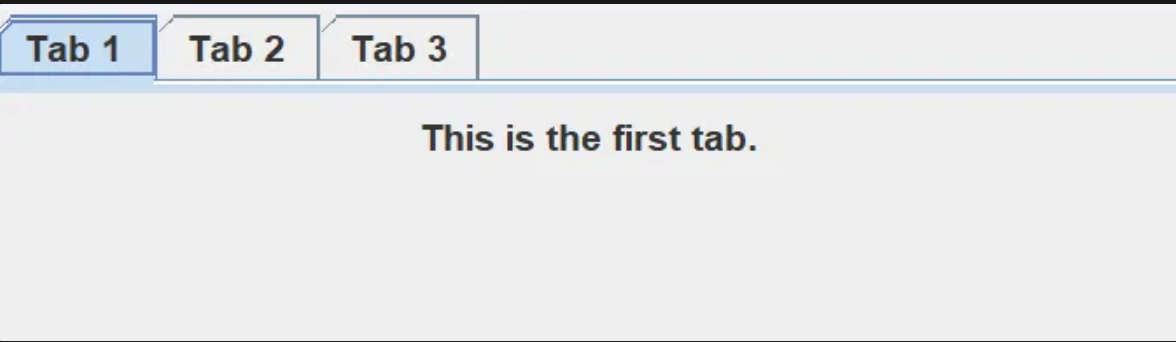
JTappedPane
- 여러 탭의 인터페이스를 가능하게 함. 여러 패널 & 섹션이 한 화면에 나올 수 있음
JTappedPane안에Panel넣기
import javax.swing.*;
public class BasicJTabbedPaneExample extends JFrame {
public BasicJTabbedPaneExample() {
setTitle("Basic JTabbedPane Example");
setSize(400, 300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Create JTabbedPane
JTabbedPane tabbedPane = new JTabbedPane();
// Create panels for each tab
JPanel panel1 = new JPanel();
panel1.add(new JLabel("This is the first tab."));
JPanel panel2 = new JPanel();
panel2.add(new JLabel("This is the second tab."));
JPanel panel3 = new JPanel();
panel3.add(new JLabel("This is the third tab."));
// Add panels to JTabbedPane with titles
tabbedPane.addTab("Tab 1", panel1);
tabbedPane.addTab("Tab 2", panel2);
tabbedPane.addTab("Tab 3", panel3);
// Add the tabbed pane to the frame
add(tabbedPane);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BasicJTabbedPaneExample();
}
}
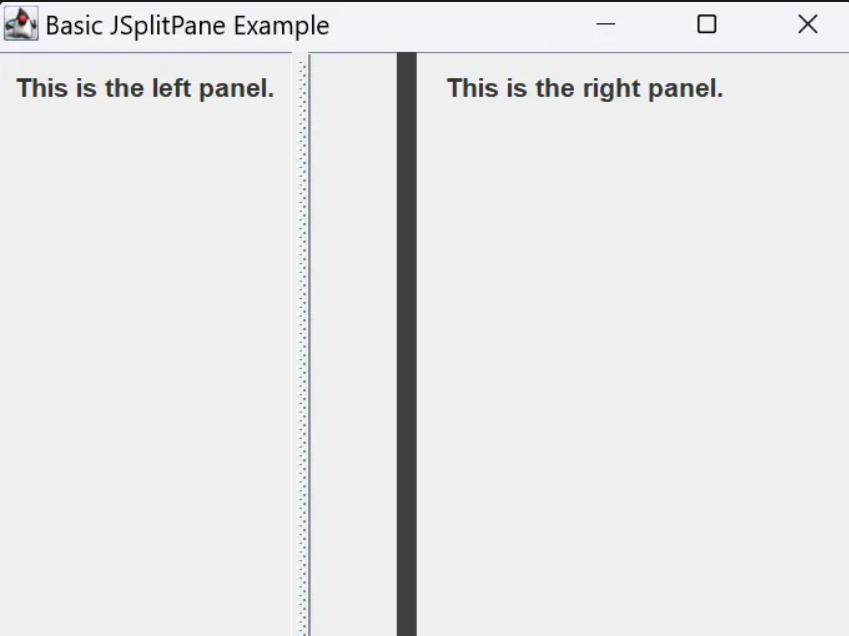
JSplitPane
- 컨테이너를 두 개의 크기 재지정 가능한 패널로 나눔. 유저가 드래그해 사이즈 조절 가능
JTappedPane안에 어떻게 나눌건지 넣고, 각각 위치할Panel넣기
import javax.swing.*;
public class BasicJSplitPaneExample extends JFrame {
public BasicJSplitPaneExample() {
setTitle("Basic JSplitPane Example");
setSize(400, 300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Create two panels to split
JPanel leftPanel = new JPanel();
leftPanel.add(new JLabel("This is the left panel."));
JPanel rightPanel = new JPanel();
rightPanel.add(new JLabel("This is the right panel."));
// Create JSplitPane with the two panels
JSplitPane splitPane = new JSplitPane(JSplitPane.HORIZONTAL_SPLIT, leftPanel, rightPanel);
splitPane.setDividerLocation(150); // Initial divider position
// Add the split pane to the frame
add(splitPane);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BasicJSplitPaneExample();
}
}
Extra
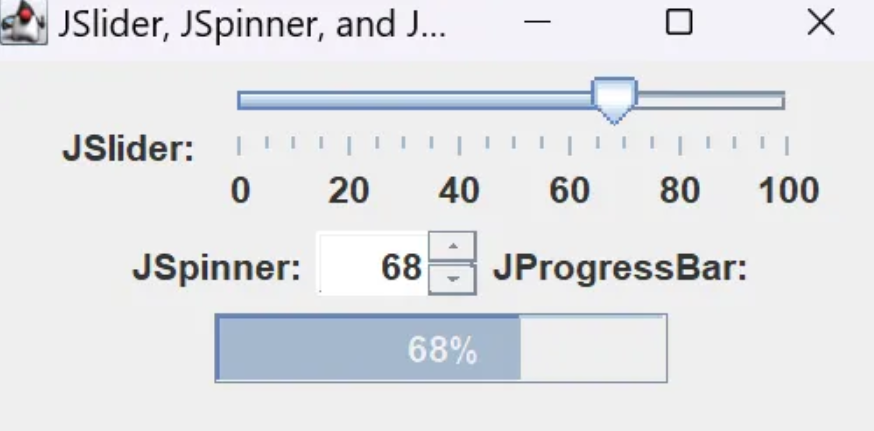
JSlider: 유저가 슬라이더로 값을 조절할 수 있게 함 (ex. 볼륨 조절)slider = new JSlider(최소, 최대, 초기값);
JSpinner: 유저가 여러 값 중 선택할 수 있도록 함spinner = new JSpinner(new SpinnerNumberModel(초기값, 최소, 최대, 증가량));
JProgressBar: 작업률을 보여줌progressBar = new JProgressBar(초기값, 최대);
4. Layout Manager
-
기본적인 레이아웃들
-
component들을 알아서 크기 조절 & 배치해줌
-
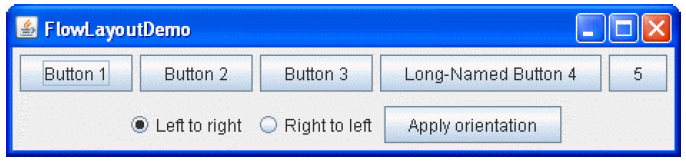
FlowLayout- component를 한 줄에 배치, 줄이 모두 차면 다음 줄로 넘김(반응형,
- 간단한 왼 → 오른쪽 레이아웃
-
BorderLayout- component 들을 나눠진 다섯 영역으로 나눔
- North, South, East, West, Center
JFrame frame = new JFrame("BorderLayout");
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
frame.add(new JButton("North"), BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(new JButton("South"), BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(new JButton("West"), BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(new JButton("East"), BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(new JButton("Center"), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(400, 300);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);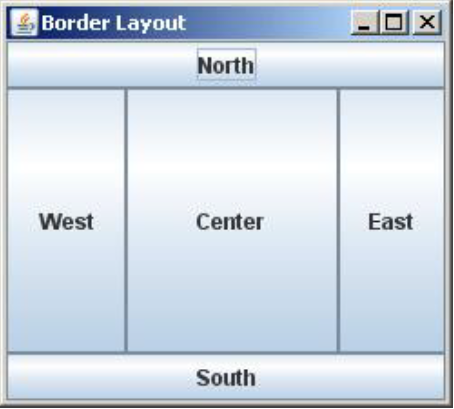
-
GridLayout- 특정한 행과 열로 나뉜 그리드에 Component 배치
- 각 칸마다의 크기가 같음
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); // 2 * 2 행렬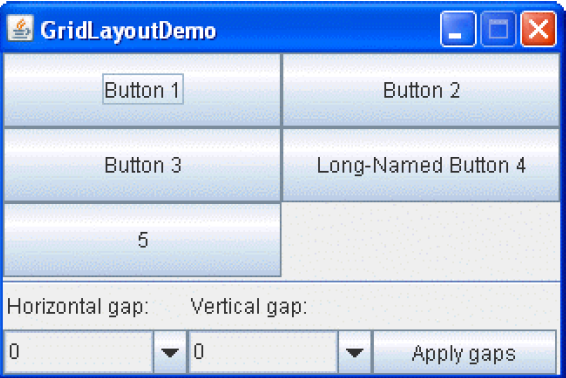
5. Event Handling
Event Handling
-
GUI component 들로 유저 상호작용을 관리하는 과정
- 클릭, 키입력, 마우스 움직임 등
Event Listener
- component 에서 발생시킨 특정한 타입의 event를 듣는 interface
ActionListener: 버튼 클릭 같은 액선 이벤트를 들음MouseListener: 마우스 클릭이나 움직임 같은 마우스 이벤트를 들음KeyListener: 키 입력이나 떼기 같은 키보드 이벤트를 들음
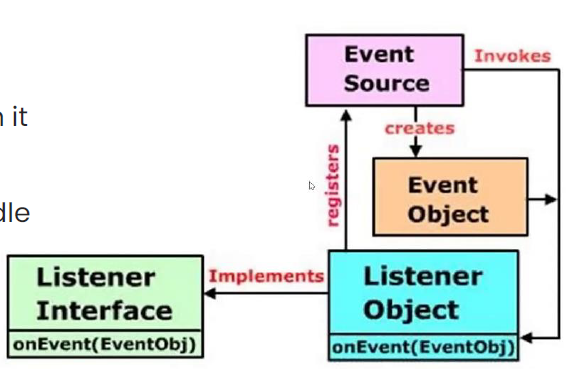
Process of Event Handling
-
Event Source : 이벤트를 만드는 Component
-
Event Listener
- 특정한 이벤트를 듣는 인터페이스
- Event Source와 붙어있음
-
Event Object : 이벤트의 타입, 소스에 대한 캡슐화 된 정보
-
Event Source가 이벤트를 생성하면 Event Listener 가 그것을 듣고 Event Object를 생성함.