Module #5: Algorithms
1. Property of Algorithms
알고리즘 : 계산을 하거나, 문제를 풀기 위한 정확한 명령의 유한한 서열
- 프로그램은 알고리즘을 구현한다.
Properties
- Input : 특정한 집합으로부터의 입력값
- Output : 입력한 값에 대한 출력값
- Definiteness : 알고리즘의 단계는 명확히 정의되어야 함
- Correctness : 어떠한 입력값에 대해서도 항상 정답을 구해야 함
- Finiteness : 유한한 횟수의 단계를 거쳐 답을 도출해야 함
- Effectiveness : 정확하고 유한한 시간 내에 수행해야 함
- Generality : 조건을 만족하는 모든 입력에 대해 적용 가능해야 함
- Efficiency : 최소한의 시간 & 공간을 사용 해야 함
Pseudocode
- 의사 코드, 알고리즘을 표현하는 방법
procedure
이름(인자: 타입)
ex) procedure maximum(L: list of integers)
변수 := 표현
- 의사 코드에선 정형화 되지 않은 표현도 허용된다.
v := 3x + 7
x := the largest integer in the list L
swap x and y
→ 실제 프로그래밍 언어에선 사용 불가
begin
statements
endif condition
then statement
→ 프로그래밍 언어의 ifwhile condition
statement
→ 프로그래밍 언어의 whilefor var := initial to final
statement
→ 프로그래밍 언어의 for
{comment}
→ 주석, 설명을 덧붙이기 위해 사용
-
example
procedure
max( : intergers)
max := {largest element so far}
for i := 2 to n {go thru rest of elems}
if max < then max := {found bigger?}
{이 지점에서 max는 list의 원소 중 가장 큰 정수와 같다}
return max {max is the largest element} -
example
procedure
sum( : intergers)
s := 0 {sum of elems so far}
for i := 1 to n {go thru all elems}
s := s + ai {add current item}
{이 지점에서 s는 모든 list 안의 값의 합}
return s
2. Algorithms for Searching and Sorting
Search Algorithm
Linear Search
- 선형 탐색 : 차례대로 x를 다음 원소와 비교하며 일치하는지 확인하는 알고리즘
procedure
linear search(x : integer, : distinct integers)
i := 1
while (i ≤ n and x ≠ )
i := i+1
if i ≤ n then location := i
else location := i
return location {location is the subscript of the term that equal x, or is 0 if x is not found}
→ 시간 복잡도 : O(n)
Binary Search
- 이진 탐색 : 리스트 중간 원소 조사, 두 구간으로 나눠 어느 쪽에 있는지 판단하고 범위를 줄이는 알고리즘
procedure
binary search(x : integer, : increasing integers)
i := 1 {i is left endpoint of search interval}
j := n {j is right endpoint of search interval}
while i < j
m :=
if then i := m + 1
else j := m
if x = then location := i
else location := 0
return location {location is the subscript of the term equal to x, or 0 if x is not found
→ 시간 복잡도 : O(log n)
Sort Algorithm
Bubble Sort
- 버블 정렬 : 인접한 원소를 차례대로 비교, 순서가 잘못되어 있으면 서로 교환해 정렬하는 알고리즘
procedure
bubble sort( : real numbers with n ≥ 2)
for i := 1 to n-1
for j := 1 to n-i
if then interchange and
{ is in increasing order}
→ 시간 복잡도 : O(n2
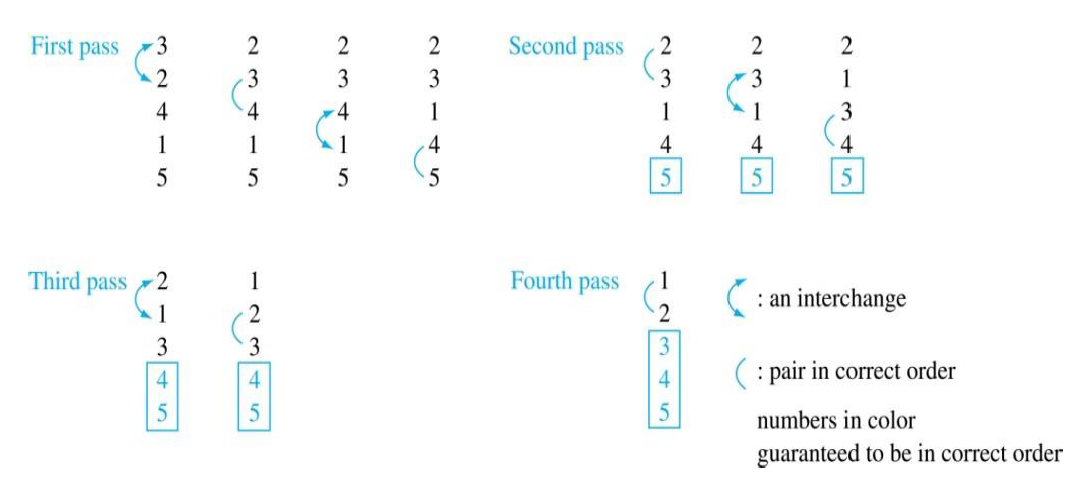
Insertion Sort
- 삽입 정렬 : - 두 번째 원소 부터 시작, 첫 원소와 비교해 앞/뒤 정해, 점점 뒤로가고, 앞쪽에서 정렬이 되는 알고리즘
procedure
insertion sort(: real numbers with n ≥ 2)
for j := 2 to n
i := 1
while
i := i + 1
m :=
for k := 0 to j - i - 1
:= m
{ is in increasing order}
→ 시간 복잡도 : O(n2

3. Greedy Algorithms
욕심쟁이 알고리즘(greedy algorithm) : 각 단계마다 가장 좋은 선택을 하는 알고리즘
-
계산원 알고리즘 : 동전으로 거스름돈을 주는 방법을 계산하는 알고리즘
procedure
change(: values of denominations of coins, where , n : a positive integer
for i := 1 to r
:= 0 { counts the coins of denomination used}
while n ≥
:= + 1 {andd a coin of denomination
n := n -
{ is the number of coins of denomination in the change for i = 1, 2, …, r} -
greedy 알고리즘이 모든 알고리즘에 대한 답인 것은 아니다.
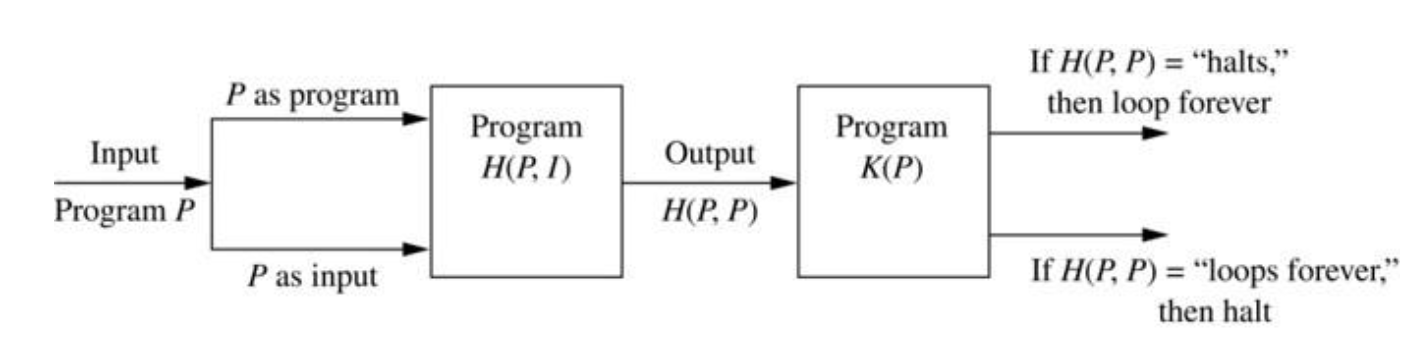
4. Halting Problem
- Halting Problem : 주어진 프로그램과 그 입력값에 대해 프고르갬이 유한한 시간 안에 종료될지, 아니면 무한 루프에 빠져 종료되지 않을지 판별하는 알고리즘은 존재하지 않는다.
- 입력으로 프로그램 P와 그 프로그램의 입력값 I를 받는 절차 H(P, I)가 있다고 가정.
- H는 프로그램 P가 입력 I로 실행되었을 때, P가 멈출지 멈추지 않을지 판정하는 절차.
→ 해결할 수 없다는 것 증명
1. 가정 : 만약 H(P, I)라는 절차가 존재한다고 가정
2. 만약 프로그램이 멈추면 "halt", 멈추지 않으면 "loops forever" 출력
3. 프로그램 K(P) 정의
- 만약 H(P, P) 가 "loops forever" 출력할 시 K(P)는 멈춤.
- 만약 H(P, P) 가 "halt" 출력할 시 K(P)는 무한 루프.
- K(K)를 호출한다면
-
K(K)가 "loops forever" 라면 K(K)는 멈춘다 → 모순
-
K(K)가 "halt" 라면 K(K)는 무한 루프에 빠진다 → 모순
-
따라서, Halting 문제를 해결할 수 있는 일반적인 알고리즘은 존재하지 않는다.