Mitigating Object Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models through Visual Contrastive Decoding
Abstract
- The proposed VCD effectively reduces the over-reliance on statistical bias and unimodal priors, two essential causes of object hallucinations.
- This adjustment ensures the generated content is closely grounded to visual inputs, resulting in contextually accurate outputs.
Introduction
- Several recent studies address this issue by proposing hallucination-targeted datasets for finetuning, training a post-hoc revisor to reconstruct less hallucinatory outputs or adapting factually augmented Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF).
- In this work, we analyze the effect of visual uncertainty on the twoprimary causes of object hallucinations in LVLMs, namely statistical bias and unimodal priors.
- Visual Contrastive Decoding (VCD), a training-free technique designed to mitigate object hallucination in LVLMs
- VCD is grounded in the principle of contrasting output distributions from original and distorted visual inputs.
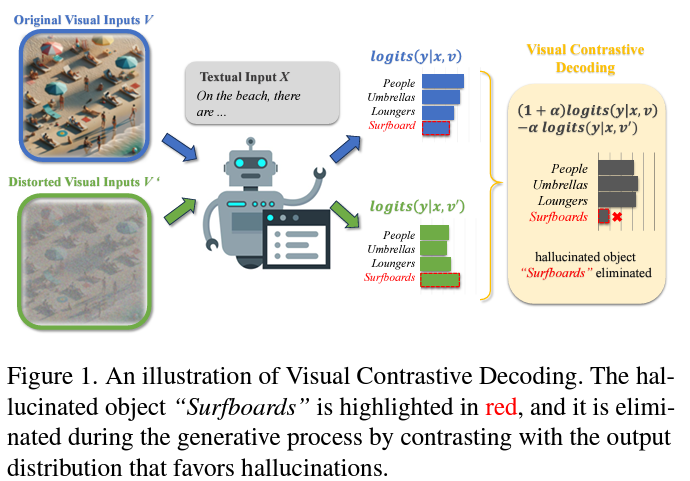
Method
Decoding of Vision-Language Models
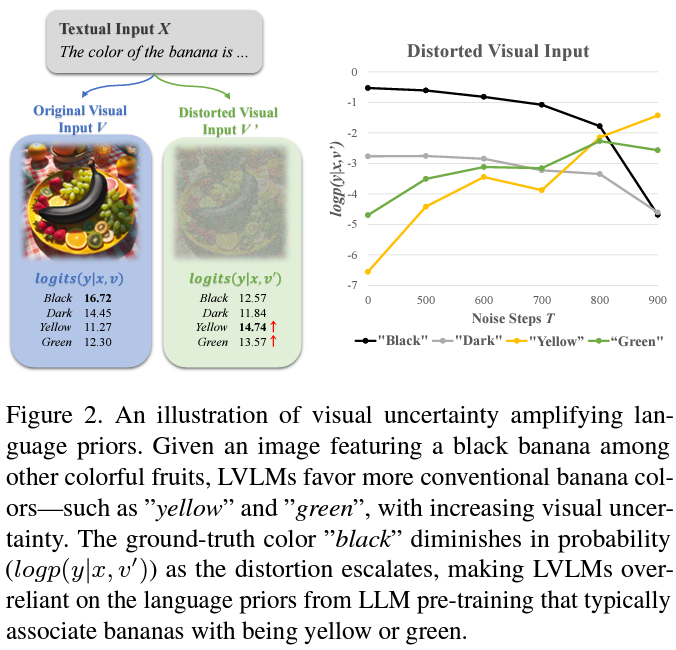
Visual Uncertainty amplifies hallucination
- applying a gaussian noise mask to the original image
- Visual Uncertainty amplifies language priors
- Visual Uncertainty amplifies statistical bias
Visual contrastive decoding
- visual uncertainty not only amplifies reliance on language priors but also makes LVLMs more likely to be biased by superficial object correlations present in pretraining datasets, leading to more severe hallucinations.
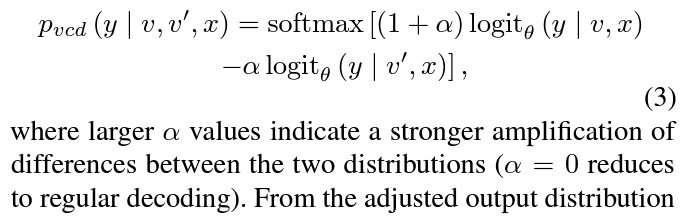
Adaptive Plausibility Constraints
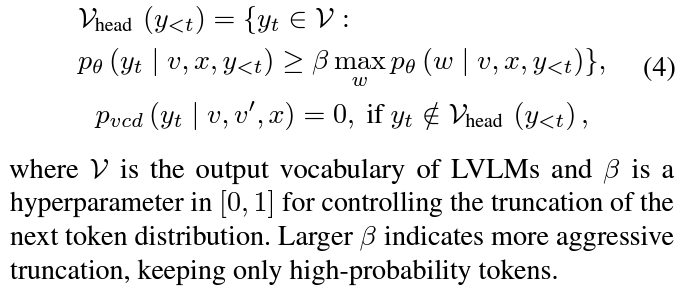
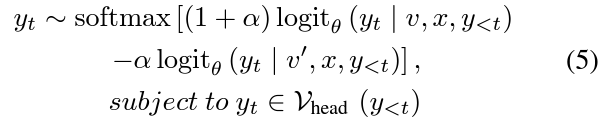
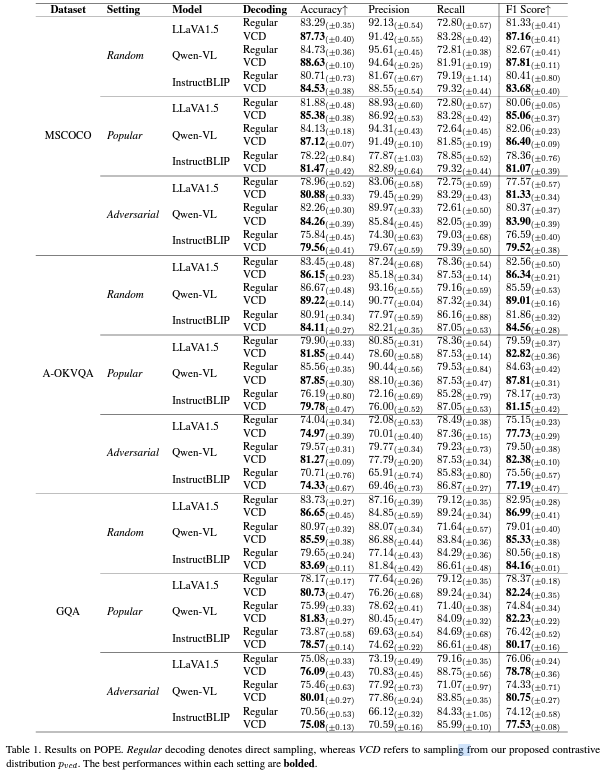
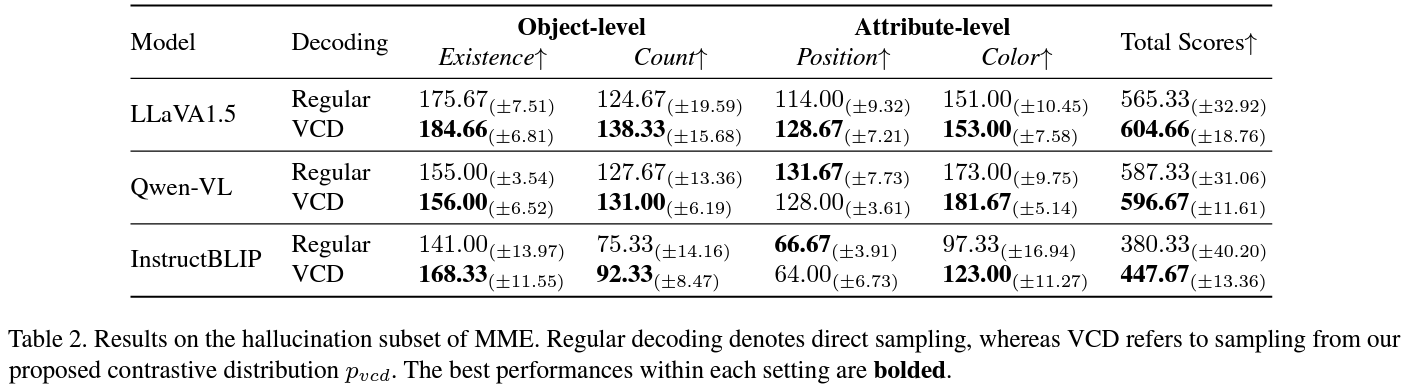
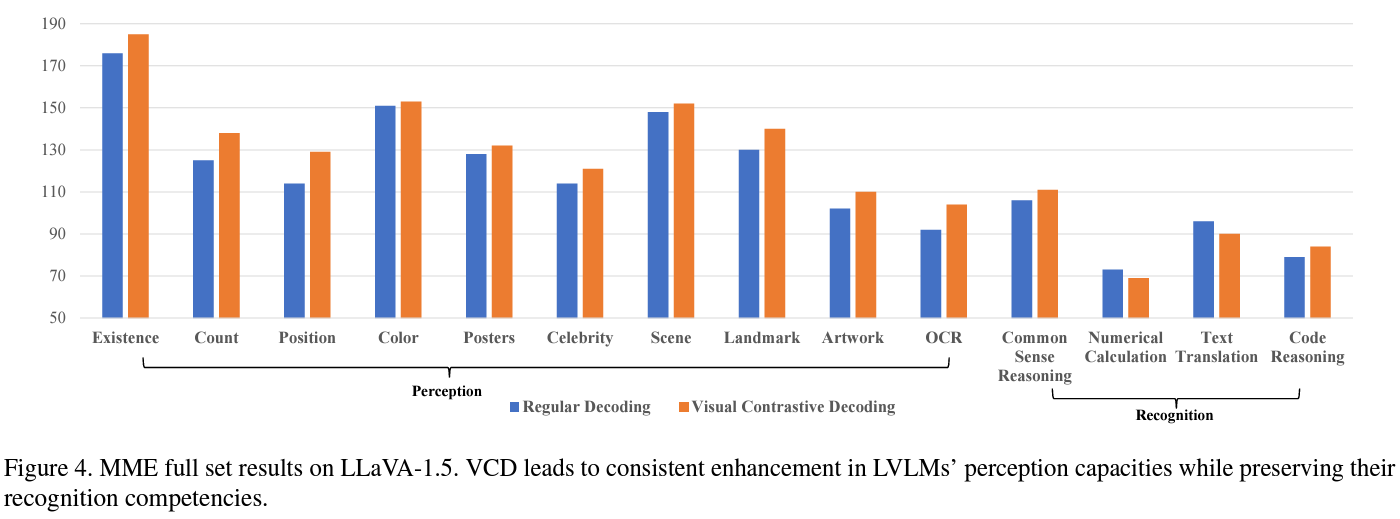
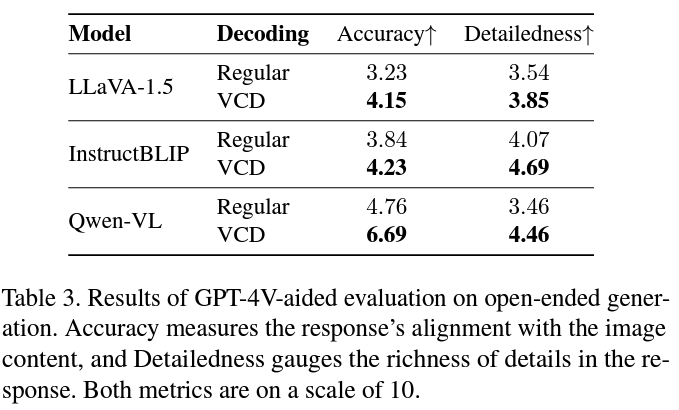
Experiment