10. standard and applications - Basic Security Protocols (operational security : firewall, intruders)
🌙 CS_security
목록 보기
20/24
index
- firewall
- (IDS) intrusion detection system
firwall
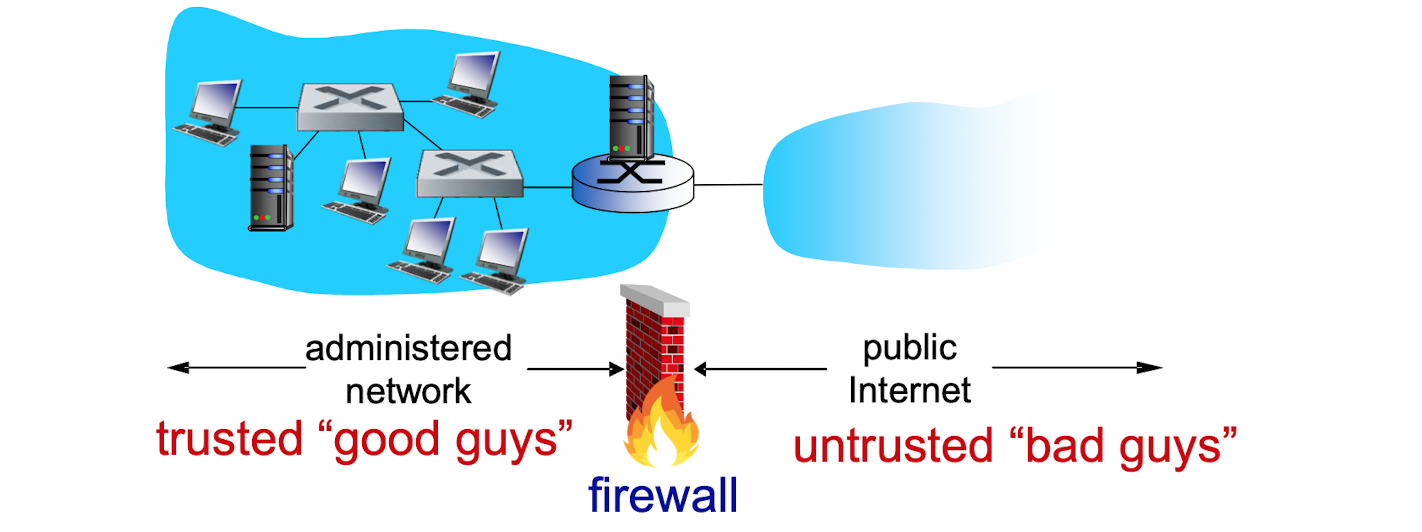
- what firewall can do
- define a 'single choke point'
- keeps unauthorized users out of the protected ntework
- prohibits potentially vunerable services from entering or leaving the network
- provides protection from various kinds of IP spoofing and routing attacks
- firewall itself must be immune to penetration!
- cannot do
- cannot protect from attacks bypassing it
- cannot protect against internal threats
- cannot protect against transfer of virus infected programs or files.
- types
- packet filter
- application-level gateways
- circuit-level gateways
packet filter
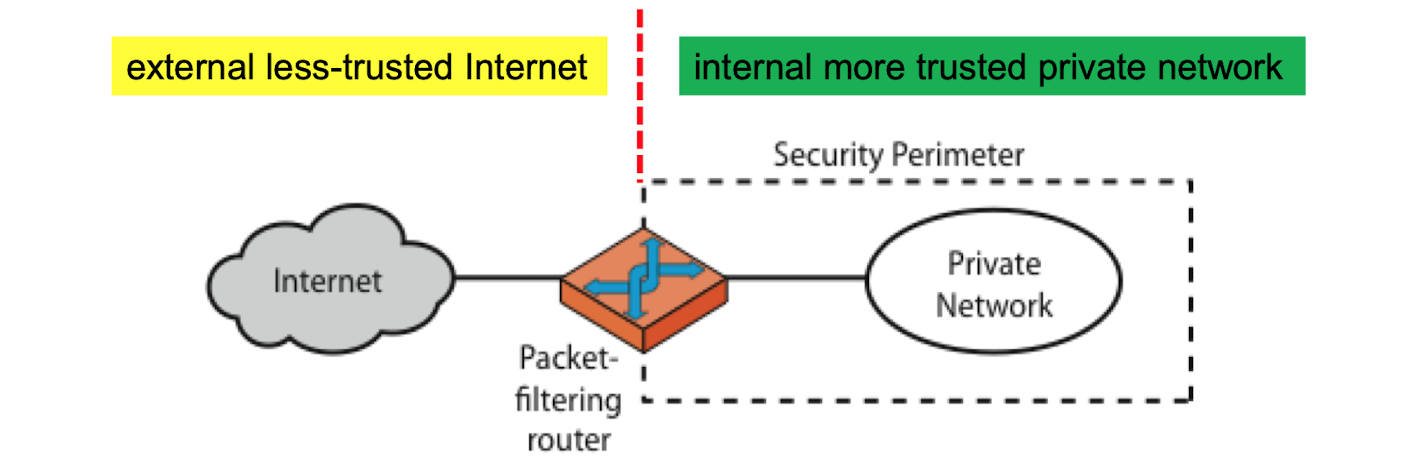
-
OSI 3,4 계층, 네트워크계층 (IP프로토콜)과 전송계층(TCP프로토콜)의 패킷을 필터링
-
패킷 필터링 라우터 (border router)에 의해 TCP 포트와 IP주소 패킷을 필터링
-
simplest & fastes
-
ACL : access control list 라는 테이블 내용에 따라 액션정함.
-
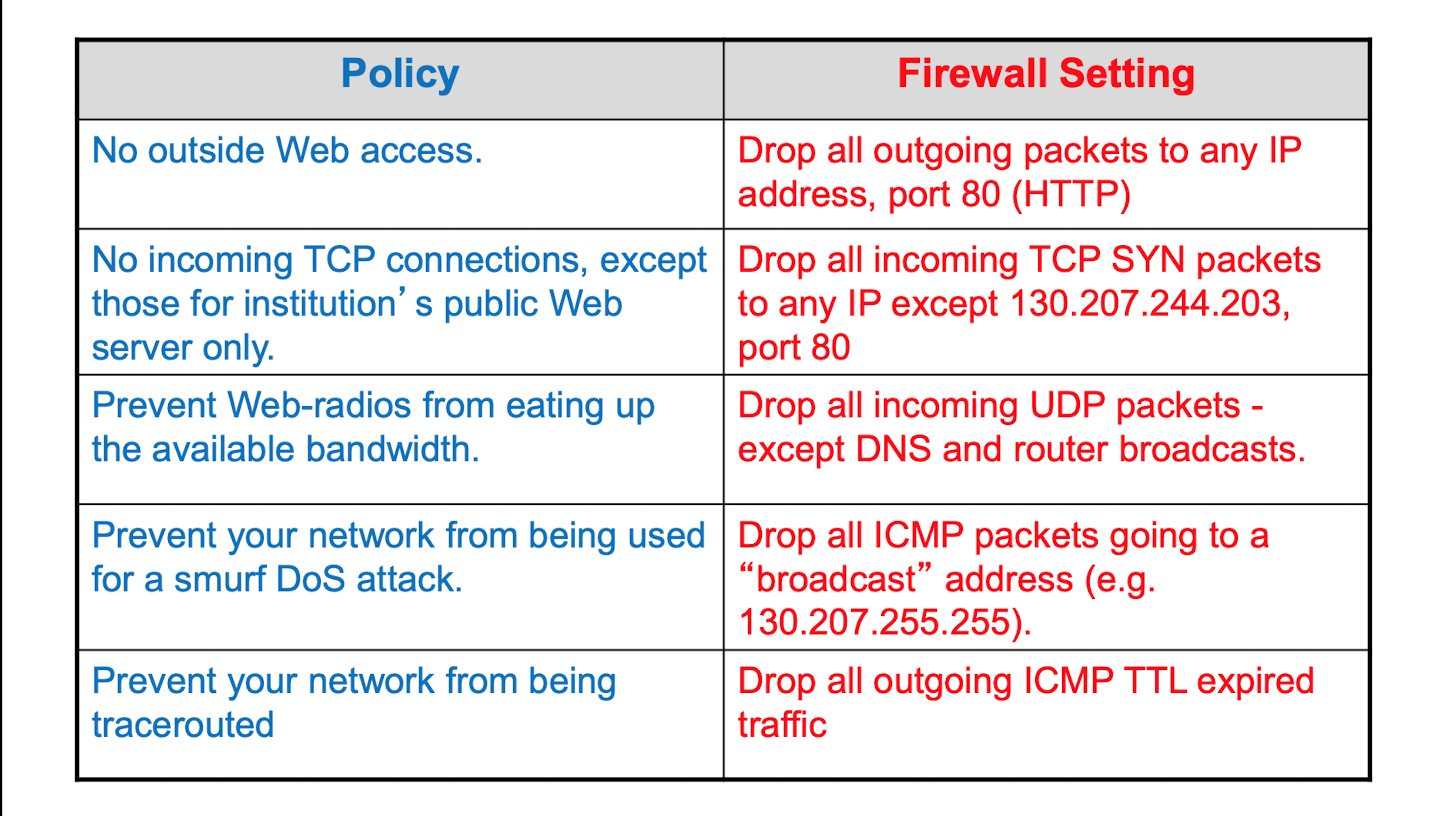
state less packet 일 경우
- heavy haded tool needed.
-
statefull packet 일 경우
- track status of every TCP connection
- Augmented ACL 사용하여 판단
-
Possible attacks
- 내부의 Ip인척 IP address spoofing
- source routing attacks
- tiny fragment attacks
application-level gateways
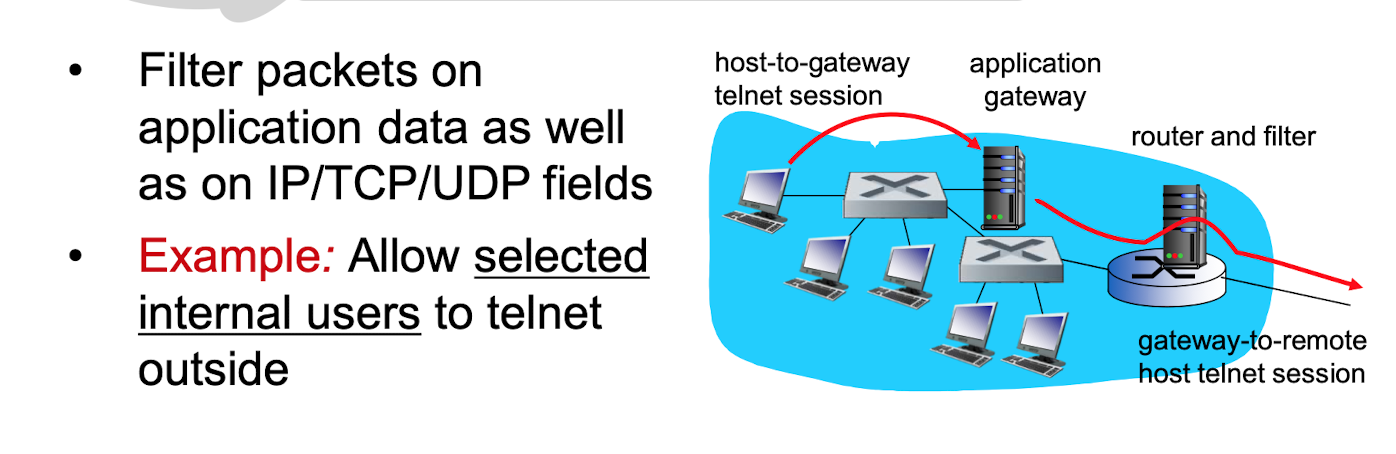
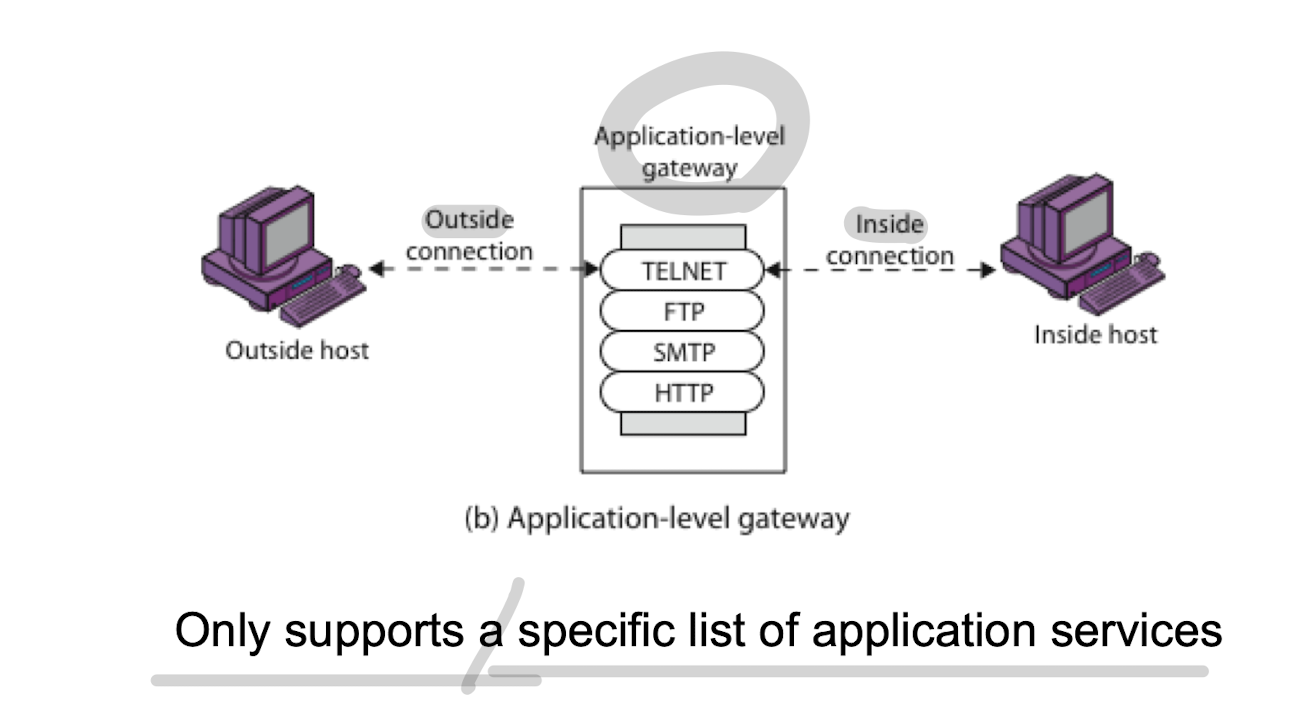
- 설명
- OSI 모델 중 7계층, Application Layer 에서 동작
- 서비스 별로 Proxy 서버가 존재할 수 있어 프락시 게이트웨이라고도함. 프락시 서버가 트래픽 보안 검사 실시
~~ - IP주소, TCP 포트로 NW 보안 설정, 사용자 인증 실시 - 보안성 우수(내부, 외부 NW이 프락시 서버 통해서만 연결)
- 매우 높은 보안정책 실현(로그인, 감시기능) 및 바이러스 검사 등 부가기능 제공
- 프록시 서버를 활용하여 확장성이 우수
- 속도 느림, 일부 서비스의 투명도가 떨어짐, 프락시 사용으로 새로운 서비스에 대한 유연성 부족(전용 Gateway 에 따른 어플리케이션의 유연성 부족하며 하드웨어에 의존적)
~~
circuit-level gateways
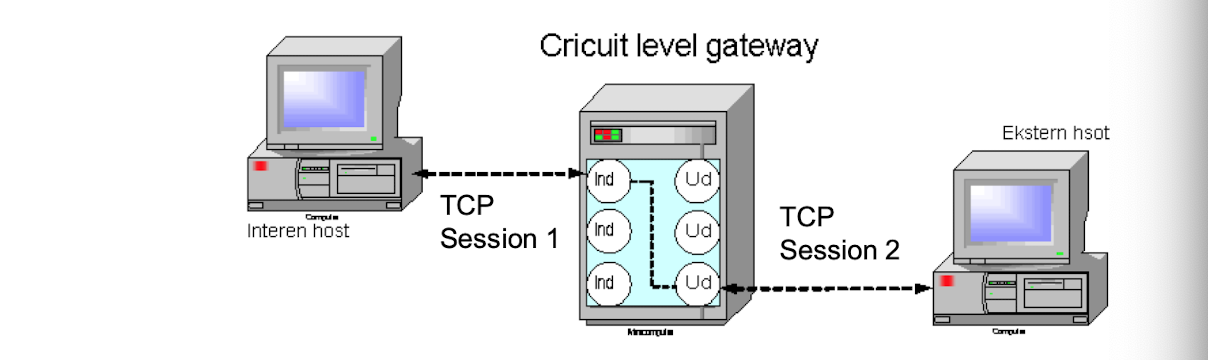
- 근래 거의 쓰이지 않음 (typcally used when trust internal user by allowing general outbound connections)
- once created, usually relays traffic wihtout examining contents
intruders
inturder 종류
- masquereader : an individaul who is not authorized to use the computer (outsider)
- misfeasor : a legitimate user who access unauthorized data, programs, or resources (insider)
- clandestine user : an individual who seizes supervisory control of the system and uses this control to evade auditing and access controls or to suppress audit collection (either)
level of attacks
- benign : simply exploring net to see what is ther
- serious : who atempt to read privileged data, perform unauthorized modification or disrupt system
대부분 Password를 얻고자 함
- password guessing
- password capture
intrusion detection systems
-
packet filtering
- operates on TCP/IP의 헤더 only
- no correlation check
-
IDS : intrusion detection system
- deep packet insepction
- look at packet contents
- examine correlation among multiple packets
- 각자 다른 위치에 각자 다른 종류를 체크한다
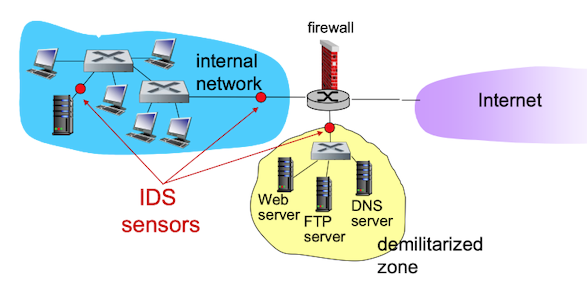
- deep packet insepction
-
분류
-
rule-based detection
- intruder인지 판단할때 사용하는 set of rules
- anomaly detection
- penetration identification
- 예시
- Rule-based anomaly detection : 이전 HIstorical audit records를 분석하여 usage pattern을 identify하고 그에 따른 rule을 auto-generate
- rule-based penetration identification : experts가 known penetration을 분석하여 생성한 rule 사용
- intruder인지 판단할때 사용하는 set of rules
-
statistical anomaly detection
-
statistical test to determine with a high level of confidence
- threshold (한계점)
- specific event occurence를 Count한다.
- profile based
- 사용자의 past behavior를 characterize
- threshold (한계점)
-
-
aduit records
- fundemental tool for intrusion detection
- 종류
- Native audit records
- user activity전부를 Os가 수집 (과다수집가능성 :()
- detection-specific audit records
- custom audit records를 생성 (system에 extra overhead :()
- Native audit records
-
distributed intrusion detection
-
network system에 intrusion detect가 distuributed & working togethr할 수록 효율적이다.
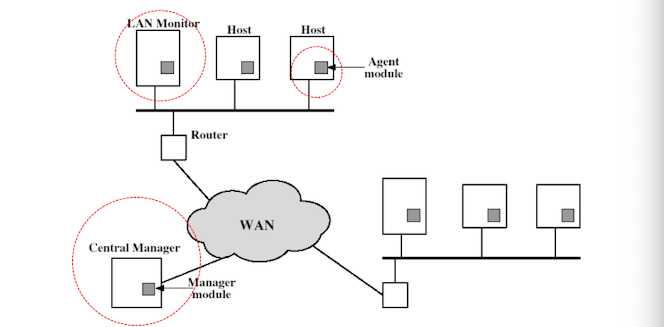
-
honeypots
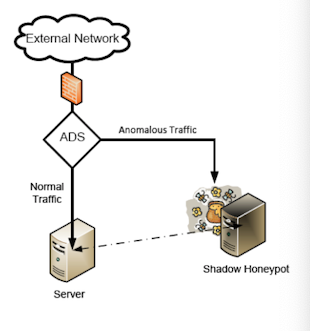
- 진짜 서버인척 shadow honeypot (fabricated information)으로 anomalous traffic을 lure한다
-
snort
- lightweight IDS
- open source
-
