Coroutine(코루틴)
- 동시에 작업하기 위함(비동기)
- 한 태스크를 완전히 완료하지 않아도 다음 태스크를 시작할 수 있으므로 여러 태스크를 동시에 실행할 수 있음
장점
- 여러 테스크들이 동시에 작업되므로 프로그램 동작 시간을 줄여줌
지연 추가
delay()
- 코루틴 라이브러리에서 제공되는 특수 정지 함수
- 이 지점에서 실행이 정지되거나 일시중지되며 지정된 지연 시간이 지나면 다시 시작
measureTimeMillis()
- 이 프로그램을 실행하는 데 얼마나 오래 걸리는지 확인하는 함수
CouroutineScope
- 코루틴의 활동범위
- 내가 원하는 범위의 스코프를 설정하여, 그에 대한 lifeCycle을 가진 코루틴 생성 가능
지원 범위
- Kotlin
- MainScope: Main UI 스레드에서 사용
- GlobalScope: 앱 전체의 생명주기
- Android Jetpack
- LifecycleScope: Activity 생명주기를 따라감
- ViewModelScope: ViewModel 생명주기를 따라감
- LiveData: LiveData 호출 시기에 맞춰 따라감
CoroutineContext
- Job과 Dispatcher, CoroutineExceptionHandler 등이 포함
- 해당 코루틴의 실행되는 환경에 대한 정보 담고 있음
Job
- 코루틴의 실행단위를 관리하는 객체
- 코루틴의 상태를 갖고 있음
- Coroutine Builder의 launch를 사용했을 때 리턴값
역할
- 코루틴 상태 추적
- 코루틴이 현재 어떤 상태에 있는지 확인 가능
- isActive, isCompleted, isCancelled 속성으로 추적
- 코루틴 상태 관리
- start(), join(), cancelAndJoin(), cancel() 메소드 이용해 관리
Dispatcher
- 코루틴이 어느 스레드에서 실행될 지 결정
지원 범위
- Main
- UI업데이트나 사용자 입력처리 등 메인 스레드에서 실행되어야하는 작업에 최적화
- IO
- 네트워크 요청, 파일 입출력 등 I/O 작업에 최적화
- 백그라운드 스레드에서 실행
- Default
- 대기시간이 없는 지속적인 작업에 최적화
- 백그라운드 스레드에서 실행
- Unconfined
- 현재 스레드에서 실행
- 거의 사용 X
CoroutineBuilder
- 비동기적인 작업을 선언하고 실행하기 위한 함수
- 새로운 코루틴을 생성하는 역할
Launch
- 가장 일반적으로 사용
- 코루틴에서 결과를 반환하지 않을 때 사용
- 비동기 작업을 시작하고 블록에서 리턴값을 사용하지 않을 때 사용
코드
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("Weather forecast")
launch {
printForecast()
}
launch {
printTemperature()
}
println("Have a good day!")
}
}
suspend fun printForecast() {
delay(1000)
println("Sunny")
}
suspend fun printTemperature() {
delay(1000)
println("30\u00b0C")
}결과
Weather forecast
Have a good day!
Sunny
30°C
Async
- 코루틴에서 값을 반환하고자 할 때 사용
- 비동기 작업이 완료되면 결과 또는 예외를 포함하는 Defferd 객체를 반환
- await 함수로 결과값 얻기 가능
- 다수의 비동기 작업을 동시에 실행할 때 (병렬실행)
💡 병렬 분해
- 문제를 병렬로 해결할 수 있는 더 작은 하위 태스크로 세분화하는 것
- 하위 태스크의 결과가 준비되면 최종 결과로 결합
fun main() { runBlocking { println("Weather forecast") println(getWeatherReport()) println("Have a good day!") } } suspend fun getWeatherReport() = coroutineScope { val forecast = async { getForecast() } val temperature = async { getTemperature() } "${forecast.await()} ${temperature.await()}" } suspend fun getForecast(): String { delay(1000) return "Sunny" } suspend fun getTemperature(): String { delay(1000) return "30\u00b0C" }
코드
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("Weather forecast")
val forecast: Deferred<String> = async {
getForecast()
}
val temperature: Deferred<String> = async {
getTemperature()
}
println("${forecast.await()} ${temperature.await()}")
println("Have a good day!")
}
}
suspend fun getForecast(): String {
delay(1000)
return "Sunny"
}
suspend fun getTemperature(): String {
delay(1000)
return "30\u00b0C"
}결과
Weather forecast
Sunny 30°C
Have a good day!
runBlocking
- 코루틴을 블로킹하여 실행해 결과를 기다리고자 할 때
withContext
- 코루틴의 실행 컨텍스트를 변경하고자 할 때
- 주로 IO나 Main 디스패처를 변경해 다른 스레드나 메인(UI)에서 코루틴을 실행하고자 할 때
예제 코드
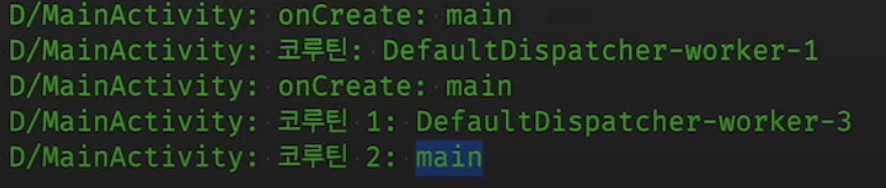
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
delay(3000)
Log.d(TAG, "코루틴 1: ${Thread.currentThread().name}")
withContext(Dispatchers.Main) {
Log.d(TAG, "코루틴 2: ${Thread.currentThread().name}")
}
}
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate: ${Thread.currentThread().name}")
}실행결과