1. Throw
동기함수에서 에러 던지기
// func.js
function someFunc(someParam) {
if (!someParam) {
throw new Error('someError');
}
// ...someFunc의 로직
return someParam;
}
module.exports = { someFunc }someParam이 특정한 값을 가지고 있지 않으면 throw error
비동기함수에서 에러 던지기
// func.js
...someFunc
async function someAsyncFunc(someParam) {
if (!someParam) {
throw new Error('someError');
}
// ...someAsyncFunc의 로직
return someParam;
}
module.exports = { someFunc, someAsyncFunc }동기함수와 에러를 던지는 건 같음
하지만, 비동기함수의 throw는 Promise Rejection 발생시키기 때문에
에러를 잡아내는 곳에선 다른 방식 이용
이러한 비동기식 에러를 해결하기 위해
await을 사용한 try - catch / promise - catch 이용
2. try - catch
동기 방식
// caller.js
const { someFunc } = require('./func');
function caller() {
const someValueWithParam = someFunc(1);
console.log("someValue:", someValueWithParam);
// someValue: 1
try {
const someValueWithoutParam = someFunc();
// 에러가 발생하였으므로 더 이상 실행되지 않습니다.
console.log('someValue', someValueWithoutParam);
}
catch(error) {
console.log(error);
// Error: someError
}
console.log('여기는 실행됩니다.');
}
caller();
// 최종적으로 콘솔에 보이는 것
someValue: 1
Error: someError
여기는 실행됩니다.try - catch를 사용하여 해당 에러를 잡도록 짜여짐
try - catch 문을 제외한 부분은 다시 정상적으로 실행
비동기 방식
1) await
// caller.js
const { someAsyncFunc } = require('./func');
async function caller() {
console.log('첫번째 콘솔');
try {
await someAsyncFunc();
}
catch(error) {
console.log(error);
// Error: someError
}
console.log('두번째 콘솔');
}
caller();
// 최종적으로 콘솔에 보이는 것
첫번째 콘솔
Error: someError
두번째 콘솔await 사용하면 동기 방식에서 사용했던 방법대로 try - catch 구문 사용 가능
하지만 상위 모듈 caller()도 async 함수로 만들어줘야 함
이를 해결하기 위해 promise - catch 방식 이용
2) promise - catch
// caller.js
const { someAsyncFunc } = require('./func');
function caller() {
console.log('첫번째 콘솔');
someAsyncFunc().catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
// Error: someError
});
console.log('두번째 콘솔');
}
caller();
// 최종적으로 콘솔에 보이는 것, 동기적인 작업들 먼저 출력 후 비동기 작업들 출력
첫번째 콘솔
두번째 콘솔
Error: someErrorpromise - catch는 promise를 리턴 받는 상황에서 사용 가능
이는 await를 사용하지 않아서 caller를 동기함수로 유지 가능
3. Express 미들웨어로 에러 핸들링
// app.js
const express = require('express');
const { someFunc, someAsyncFunc } = require('./func');
const app = express();
app.get('/someFunc', (req, res) => {
const { someQuery } = req.query;
const someValue = someFunc(someQuery);
res.json({ result: someValue });
});
app.get('/someAsyncFunc', (req, res) => {
const { someQuery } = req.query;
const someValue = someAsyncFunc(someQuery);
res.json({ result: someValue });
});
// error handling 미들웨어
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
if (err.message === 'someError') {
res.status(400).json({ message: "someQuery notfound." });
return;
}
res.status(500).json({ message: "internal server error" });
});
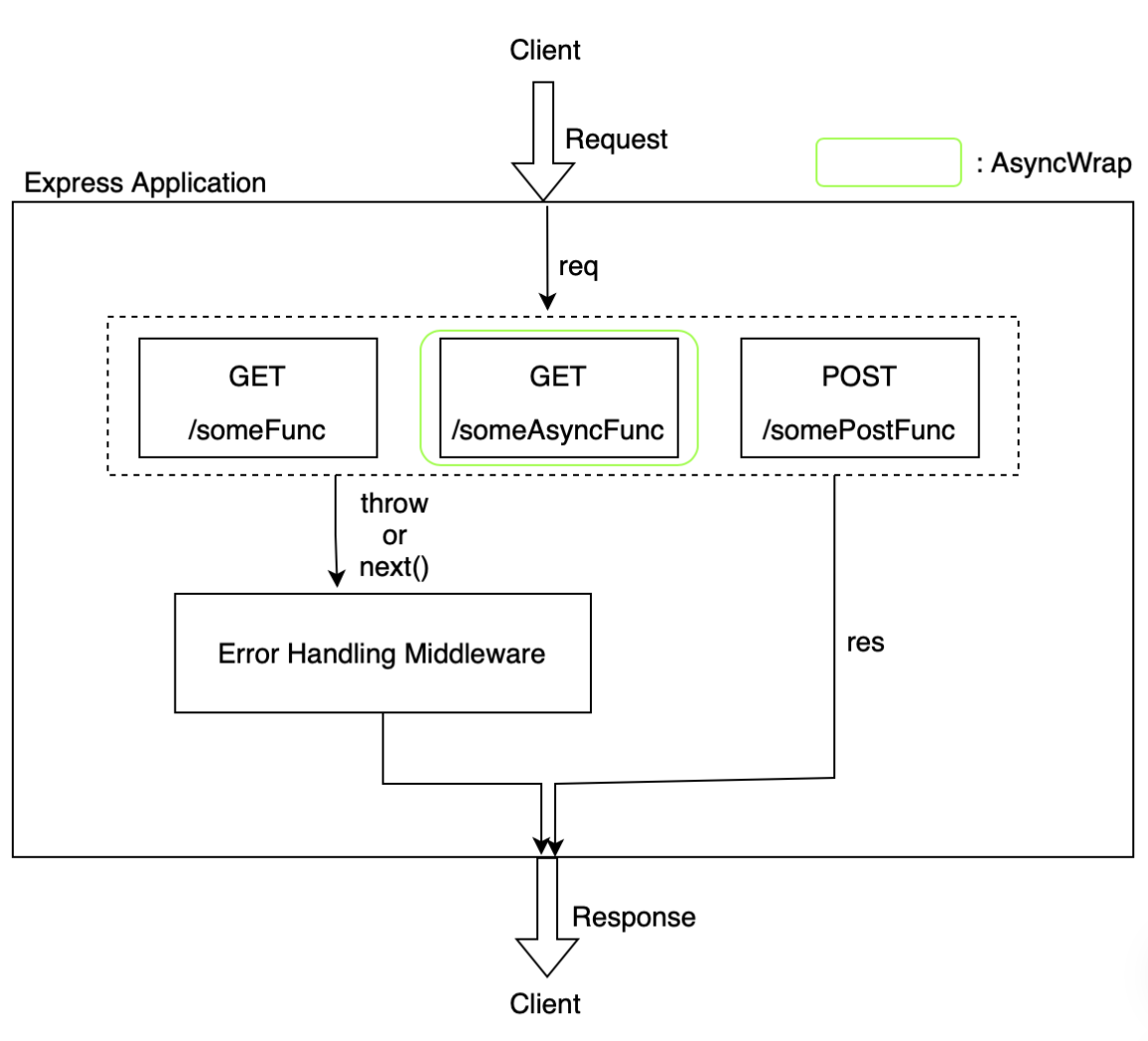
app.listen(3000);에러 핸들링 미들웨어를 추가해서 라우터에서 던지는 에러를 하나로 통일하여 받음
사용자에게 어떤 에러가 갈지 예측 가능
하지만 여전히 비동기 모듈 에러는 잡지 못하므로, 또 다른 모듈인 async wrapping으로 해결
async wrap
컨트롤러를 받아서 비동기 에러를 처리하는 새로운 컨트롤러를 만드는 모듈
next를 통해 에러 핸들링 미들웨어로 넘어감
// async-wrap.js
function asyncWrap(asyncController) {
return async (req, res, next) => {
try {
await asyncController(req, res)
}
catch(error) {
next(error);
}
};
}
module.exports = asyncWrap;
---------------------------------------------------------------
// app.js
const asyncWrap = require('./async-wrap');
app.get('/someAsyncFunc', asyncWrap(async (req, res) => {
const { someQuery } = req.query;
const someValue = await someAsyncFunc(someQuery);
res.json({ result: someValue });
}));asyncWarp을 컨트롤러에 씌워 주게 되면 비동기 컨트롤러에서 생기는 에러를 잡을 수 있음