
해시 테이블 (Hash Table)
- 키(Key), 값(Value)을 대응시켜 저장하는 데이터 구조
- 키를 통해 해당 데이터에 빠르게 접근 가능
- 해싱
- 키를 특정 계산식에 넣어 나온 결과를 사용하여 값에 접근하는 과정
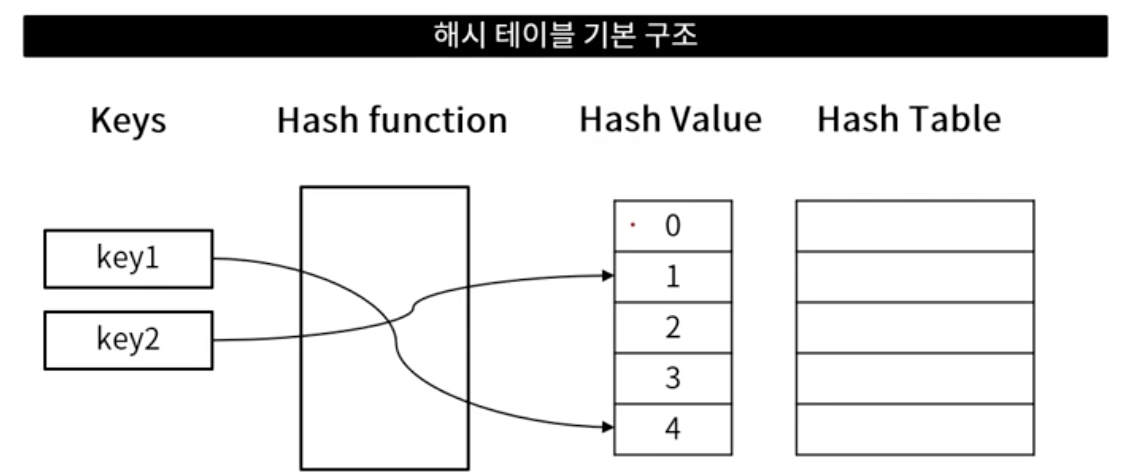
해시 테이블 구조
- 키: 해시 테이블 접근을 위한 입력 값
- 해시 함수: 키를 해시 값으로 매핑하는 연산
- 해시 값: 해시 테이블의 인덱스
- 해시 테이블: 키-값을 연관시켜 저장하는 데이터 구조
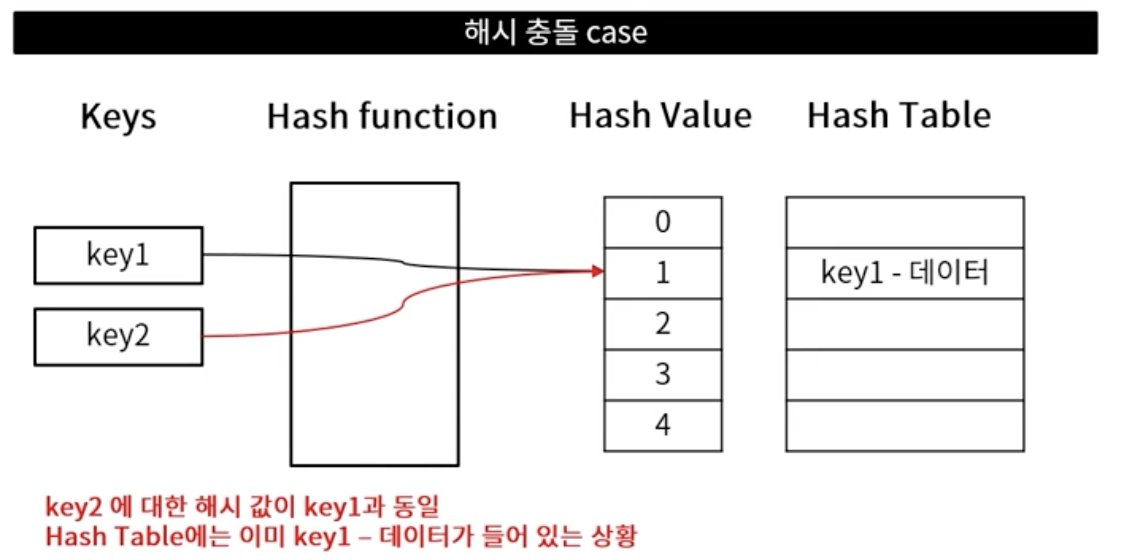
해시 충돌
- 해시 테이블의 같은 공간에 서로 다른 값을 저장하려는 경우
- 서로 다른 키의 해시 함수를 통한 해시 값이 동일한 경우
- 해시 충돌 해결 방법으로는 크게 개방 주소법과 분리 연결법이 있음
해시 충돌 해결 방법(1)
- 개방 주소법 (Open Address)
- 충돌 시, 테이블에서 비어 있는 공간의 hash를 찾아 데이터를 저장
- hash와 value가 1:1 관계 유지
- 비어 있는 공간 탐색 방법에 따라 분류
- 선형 탐사법, 제곱 탐사법, 이중해싱
개방 주소법 - 선형 탐사법
- Linear Probing
- 빈 공간을 순차적으로 탐사하는 방법
- 충돌 발생 지점부터 이후의 빈 공간을 순서대로 탐사
- 일차 군집화 문제 발생
- 반복된 충돌 발생시 해당 지점 주변에 데이터가 몰리는 경우 발생
개방 주소법 - 제곱 탐사법
- Quadratic Probing
- 빈 공간을 n제곱만큼의 간격을 두고 탐사하는 방법
- 충돌 발생 지점 부터 이후의 빈 공간을 n제곱 간격으로 탐사
- 일차 군집화 문제 일부 보완
- 이차 군집화 문제 발생 가능성
개발 주소법 - 이중 해싱
- Double Hashing
- 해싱 함수를 이중으로 사용
- 해시 함수1: 최초 해시를 구할 때 사용
- 해시 함수2: 충돌 발생 시, 탐사 이동 간격을 구할 때 사용
- 선형탐사, 제곱탐사에 비해 데이터가 골고루 분포됨
해시 충돌 해결 방법 (2)
- 분리 연결법 (Separate Chaining)
- 해시 테이블을 연결 리스트로 구성
- 충돌 발생 시, 테이블 내의 다른 위치를 탐색하는 것이 아닌 연결 리스트를 이용하여 해당 테이블에 데이터를 연결
// 선형 자료구조 - 해시 테이블
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
// 해시 함수
public static int getHash(int key) {
return key % 5;
}
// 해시 테이블의 사이즈를 만들어줌
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 기본 해시 테이블 사용 방법
Hashtable<String, Integer> ht = new Hashtable();
ht.put("key1", 10);
ht.put("key2", 20);
ht.put("key3", 30);
// ht.put("key3", 40); >> 해당 키에 대한 데이터가 바뀜.
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> item: ht.entrySet()) { // ht 안에 있는 key 값에 대응되는 entry 값을 뽑아주는데, 그걸 for 문에서 받아줌
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
System.out.println(ht.get("key1"));
System.out.println(ht.get("key2"));
ht.remove("key1");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> item: ht.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
// 해시 충돌 케이스 (해시 함수 사용)
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht2 = new Hashtable();
ht2.put(getHash(1), 10);
ht2.put(getHash(2), 20);
ht2.put(getHash(3), 30);
ht2.put(getHash(4), 40);
ht2.put(getHash(5), 50);
System.out.println("== 충돌 전 ==");
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> item: ht2.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
System.out.println("== 충돌 후 ==");
ht2.put(getHash(6), 60); // key 값이 1이 된다!, 충돌. 따라서 1이라는 위치에 60으로 바뀐다. 기존의 데이터가 없어짐.
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> item: ht2.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
}
}<실행 결과>
key3 - 30
key2 - 20
key1 - 10
10
20
key3 - 30
key2 - 20
== 충돌 전 ==
4 - 40
3 - 30
2 - 20
1 - 10
0 - 50
== 충돌 후 ==
4 - 40
3 - 30
2 - 20
1 - 60
0 - 50// Practice1
// 해시 테이블 배열로 직접 구현
class MyHashTable {
Integer[] table;
int elemCnt;
MyHashTable() {}
MyHashTable(int size) {
this.table = new Integer[size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public int getHash(int key) {
return key % this.table.length;
}
// key 값에 따라서 테이블의 인덱스가 뱅글뱅글 ..
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key); // hash 값을 뽑아낸다.
this.table[idx] = data; // hash 값에다가 데이터를 넣어준다.
this.elemCnt++;
}
public int getValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
return this.table[idx]; // 인덱스에 있는 값 리턴
}
public void removeValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
this.table[idx] = null; // 해당 hash에 해당하는 데이터를 지워준다.
this.elemCnt--;
}
public void printHashTable() {
System.out.println("== Hash Table ==");
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + ": " + this.table[i]);
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable ht = new MyHashTable(7);
ht.setValue(1, 1);
ht.setValue(2, 2);
ht.setValue(3, 3);
ht.setValue(4, 4);
ht.setValue(5, 5);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(8, 6);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}<실행 결과>
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 1
2: 2
3: 3
4: 4
5: 5
6: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 6
2: 2
3: 3
4: 4
5: 5
6: null// Practice2
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (선형 탐사법)
class MyHashTable2 extends MyHashTable { // MyHashTable 상속 받음
MyHashTable2(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
if (this.elemCnt == this.table.length) { // 테이블이 꽉 차있다면
System.out.println("Hash table is full!");
return;
} else if (this.table[idx] == null) { // 공간이 남아있는 상황에서 해당 hash에 데이터가 할당이 안 된 상태라면
this.table[idx] = data;
} else { // 해당 hash에 어떤 데이터가 들어가 있는 경우 (충돌이 일어난 경우)
int newIdx = idx;
while (true) {
newIdx = (newIdx + 1) % this.table.length; // 인덱스 하나씩 증가
if (this.table[newIdx] == null) { // 빈공간을 찾았다!
break;
}
}
this.table[newIdx] = data; // 해당 위치에다가 데이터를 넣어줌. (빈공간 찾은)
}
elemCnt++;
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable2 ht = new MyHashTable2(5);
ht.setValue(1, 1);
ht.setValue(3, 3);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 20);
ht.setValue(1, 30);
ht.setValue(1, 40);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}<실행 결과>
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 1
2: null
3: 3
4: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 1
2: 10
3: 3
4: null
Hash table is full!
== Hash Table ==
0: 30
1: 1
2: 10
3: 3
4: 20// Practice3
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (제곱 탐사법)
class MyHashTable3 extends MyHashTable {
MyHashTable3(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
if (this.elemCnt == this.table.length) { // 해시테이블의 데이터 공간이 꽉 찬 상황
System.out.println("Hash table is full!");
return;
} else if (this.table[idx] == null) { // 데이터를 넣을 수 있는 상황
this.table[idx] = data;
} else { // 충돌이 일어난 경우 -> 제곱 탐사법 이용!
int newIdx = idx; // 기존의 충돌 난 지점으로 초기화
int cnt = 0; // 충돌이 몇 번 발생하는 지 세기 위한 변수
while (true) {
newIdx = (newIdx + (int)Math.pow(2, cnt)) % this.table.length;
// 2의 제곱 수를 더해줌. (해시 테이블의 길이만큼 나누어 준 나머지를 출력하여 뱅글 뱅글 돌도록 ..)
if (this.table[newIdx] == null) { // 빈 공간 찾음
break;
}
cnt++; // 충돌 +1
}
this.table[newIdx] = data; // 빈 공간에다가 데이터 넣어줌
}
elemCnt++;
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable3 ht = new MyHashTable3(11);
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.setValue(2, 20);
ht.setValue(4, 40);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 100);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 200);
ht.setValue(1, 300);
ht.setValue(1, 400);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}<실행 결과>
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: null
4: 40
5: null
6: null
7: null
8: null
9: null
10: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: null
4: 40
5: null
6: null
7: null
8: 100
9: null
10: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: null
4: 40
5: 200
6: null
7: null
8: 100
9: 400
10: 300// Practice4
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (이중 해싱)
class MyHashTable4 extends MyHashTable {
int c;
MyHashTable4(int size) {
super(size);
this.c = this.getHashC(size);
}
public int getHashC(int size) { // 해쉬 테이블에 사이즈보다 조금 작은 소수를 구하는 메소드
int c = 0;
if (size <= 2) { // 사이즈가 2보다 작거나 같으면?
return size;
}
for (int i = size - 1; i > 2; i--) { // 2보다 큰 수 일때
boolean isPrime = true; // 소수 판별 변수
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) { // 1과 자기 자신으로만 나누어지는 수 구한다.
if (i % j == 0) { // 나누어 떨어지면 소수가 아니다.
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPrime) { // 소수다!
c = i;
break;
}
}
return c;
}
public int getHash2(int key) { // 두번째 해시 함수를 구하기 위한 메소드
int hash = 1 + key % this.c; // 새롭게 얻는 해쉬, 해쉬 테이블에 사이즈보다 조금 작은 소수로 나눠줌
return hash;
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
if (this.elemCnt == this.table.length) { // 해시 테이블이 꽉 차있다면
System.out.println("Hash table is full!");
return;
} else if (this.table[idx] == null) { // 데이터를 넣을 수 있다면
this.table[idx] = data;
} else { // 충돌이 일어난 상황
int newIdx = idx;
int cnt = 1;
while (true) {
newIdx = (newIdx + this.getHash2(newIdx) * cnt) % this.table.length; // 충돌이 발생할 때마다 곱셈으로 가중
if (this.table[newIdx] == null) { // 빈 공간 찾음
break;
}
cnt++; // 충돌 횟수 +1
}
this.table[newIdx] = data; // 데이터 넣어줌
}
elemCnt++;
}
}
public class Practice4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable4 ht = new MyHashTable4(11);
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.setValue(2, 20);
ht.setValue(3, 30);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 100);
ht.setValue(1, 200);
ht.setValue(1, 300);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}<실행 결과>
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: 30
4: null
5: null
6: null
7: null
8: null
9: null
10: null
== Hash Table ==
0: 100
1: 10
2: 20
3: 30
4: null
5: null
6: null
7: 300
8: 200
9: null
10: null// Practice5
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 분리 연결법
class Node {
int key;
int data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(int key, int data, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void addData(int key, int data) {
if (this.head == null) { // 해당 헤드 값이 비어 있다
this.head = new Node(key, data, null); // 그곳에다가 값 넣어줌
} else { // 비어 있지 않다
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) { // 해당 연결 리스트의 끝까지 이동 (비어있는 곳을 찾을 때 까지)
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(key, data, null); // 그 곳에다가 데이터 넣어줌
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == data) { // 노드의 key와 비교
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public Integer findData(int key) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return null;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == key) { // key 값 기준
return cur.data; // 찾은 데이터 리턴
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
return null;
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class MyHashTable5 { // 분리 연결법으로 해결
LinkedList[] table; // LinkedList 배열로 만든다
MyHashTable5(int size) {
this.table = new LinkedList[size]; // 연결 리스트 공간 만듬
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
this.table[i] = new LinkedList(null); // 각각의 객체를 생성
}
}
public int getHash(int key) {
return key % this.table.length;
}
// 해쉬 값 구하는 메소드
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key); // key 값을 기준으로 해시값 가져옴
this.table[idx].addData(key, data);
}
// 데이터 세팅하는 메소드
public int getValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key); // key 값을 기준으로 해시값 가져옴
int data = this.table[idx].findData(key);
return data;
}
// 데이터를 얻어오는 메소드
public void removeValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
this.table[idx].removeData(key);
}
// 데이터를 지우는 메소드
public void printHashTable() {
System.out.println("== Hash Table ==");
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
System.out.print(i + ": ");
this.table[i].showData();
}
}
}
public class Practice5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable5 ht = new MyHashTable5(11);
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.setValue(2, 20);
ht.setValue(3, 30);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(12, 11);
ht.setValue(23, 12);
ht.setValue(34, 13);
ht.setValue(13, 21);
ht.setValue(24, 22);
ht.setValue(35, 23);
ht.setValue(5, 1);
ht.setValue(16, 2);
ht.setValue(27, 3);
ht.printHashTable();
System.out.println("== key 값으로 해당 데이터 가져오기 ==");
System.out.println(ht.getValue(1));
System.out.println(ht.getValue(12));
System.out.println("== 데이터 삭제 ==");
ht.removeValue(1);
ht.removeValue(5);
ht.removeValue(16);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}<실행 결과>
== Hash Table ==
0: List is empty!
1: 10
2: 20
3: 30
4: List is empty!
5: List is empty!
6: List is empty!
7: List is empty!
8: List is empty!
9: List is empty!
10: List is empty!
== Hash Table ==
0: List is empty!
1: 10 11 12 13
2: 20 21 22 23
3: 30
4: List is empty!
5: 1 2 3
6: List is empty!
7: List is empty!
8: List is empty!
9: List is empty!
10: List is empty!
== key 값으로 해당 데이터 가져오기 ==
10
11
== 데이터 삭제 ==
== Hash Table ==
0: List is empty!
1: 11 12 13
2: 20 21 22 23
3: 30
4: List is empty!
5: 3
6: List is empty!
7: List is empty!
8: List is empty!
9: List is empty!
10: List is empty!// Practice1
// 해시 테이블을 이용한 수 찾기
// 주어진 첫 번째 배열을 이용하여 해시 테이블을 초기화 한 후
// 두 번째 배열이 주어졌을 때 해당 배열 내 데이터가 해시 테이블에 있는지 확인하는 코드를 작성하세요.
// 입출력 예시)
// 배열1: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
// 배열2: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
// 출력: True, False, True, False, True
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht = new Hashtable<>();
// 해시 테이블 구성
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
ht.put(arr1[i], arr1[i]);
}
// 포함하고 있으면 true, 없으면 false 출력
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
if(ht.containsKey(arr2[i])) {
System.out.print("True ");
} else {
System.out.print("False ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr1 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
solution(arr1, arr2);
}
}// Practice2
// 정수형 배열 nums 와 target 이 주어졌을 때,
// nums 에서 임의의 두 수를 더해 target 을 구할 수 있는지 확인하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 두 수 의 합으로 target 을 구할 수 있으면 해당 값의 index 를 반환하고,
// 없는 경우 null 을 반환하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// nums: 7, 11, 5, 3
// target: 10
// 출력: 0, 3
// nums: 8, 3, -2
// target: 6
// 출력: 0, 2
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Practice2 {
public static int[] solution(int[] numbers, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht = new Hashtable<>();
// 해시 테이블을 full 로 구성하고 시작 x
// 현재 값이 해시테이블에 있는지 검사
// 있으면 구간 result 에 설정 후 break
// 없으면 target - 현재 값 을 해시 테이블에 추가
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (ht.containsKey(numbers[i])) {
result[0] = ht.get(numbers[i]); // 해당 index
result[1] = i; // 지금 index
return result;
}
ht.put(target - numbers[i], i);
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {7, 11, 5, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(nums, 10)));
nums = new int[]{8, 3, -2};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(nums, 6)));
nums = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(nums, 12)));
}
}// Practice3
// 참고 - Hashtable? HashMap?
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Hashtable
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht = new Hashtable<>(); // 객체 만들기
ht.put(0, 10); // key와 값을 넣어줌
System.out.println(ht.get(0)); // 10 출력
// HashMap
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hm = new HashMap<>(); // 객체 만들기
hm.put(0, 10); // key와 값을 넣어줌
System.out.println(hm.get(0)); // 10 출력
// Map 인터페이스 (다형성)
Map<Integer, Integer> map1 = ht;
Map<Integer, Integer> map2 = hm;
System.out.println(map1.get(0)); // 10 출력
System.out.println(map2.get(0));// 10 출력
// ht.put(null, -999); ---> 에러 발생. null을 이용한 key 값 출력 불가능(해시 테이블)
// System.out.println(ht.get(null));
hm.put(null, -999);
System.out.println(hm.get(null)); // null을 이용한 key 값 출력 가능(해시 맵)
// Hashtable 과 HashMap 차이
// 공통: 둘 다 Map 인터페이스를 구현한 것
// 차이:
// Thread-safe
/* ( 컴퓨터 cpu에는 프로세서가 있다.
프로세서에는 작업을 처리하는 단위인 쓰레드가 있다.
멀티 쓰레드라고 하는 것은 프로세서가 일을 할 수 있는 시간 안에서
어떤 시간대에는 스레드1을 돌리고, 어떤 시간대에서는 스레드2를 돌리는 것이다.
이들의 델타 시간이 균일 하진 않지만 빠르게 스위칭 하면서 돌린다.
-> 우리가 볼때는 동시에 진행하는 것처럼 보인다.
--> 잘못된 결과가 출력될 수도 있다. (10, 5, 10, 5... 반복될때 5가 출력 되어야 하는데 10이 출력)
해결 방법 중 하나는 우리가 공유 메모리인 a를 사용할 때 쓰레드 1이 잠깐 lock을 걸고
사용한 후에 unlock을 해준다. 따라서 그 사이에는 침범을 할 수 없다.
자세한 내용은 나중에 ..)
*/
// Hashtable: O (멀티 스레드 환경에서 우수)
// HashMap: X (싱글 스레드 환경에서 우수) --> 요새 자주 사용!
// 참고) synchronizedMap, ConcurrentHashMap
// Key 에 Null 사용 여부
// Hashtable: X
// HashMap: O
}
}