연결 리스트 (Linked List)
- 데이터를 링크로 연결해서 관리하는 구조
- 자료의 순서는 정해져 있지만, 메모리상 연속상이 보장되지는 않음
연결 리스트의 장점
- 데이터 공간을 미리 할당할 필요 없음
- 즉, 리스트의 길이가 가변적이라 데이터 추가/삭제 용이
연결 리스트의 단점
- 연결 구조를 위한 별도 데이터 공간 필요
- 연결 정보를 찾는 시간이 필요 (접근 속도가 상대적으로 느림)
- 데이터 추가, 삭제 시 앞뒤 데이터의 연결을 재구성하는 작업 필요
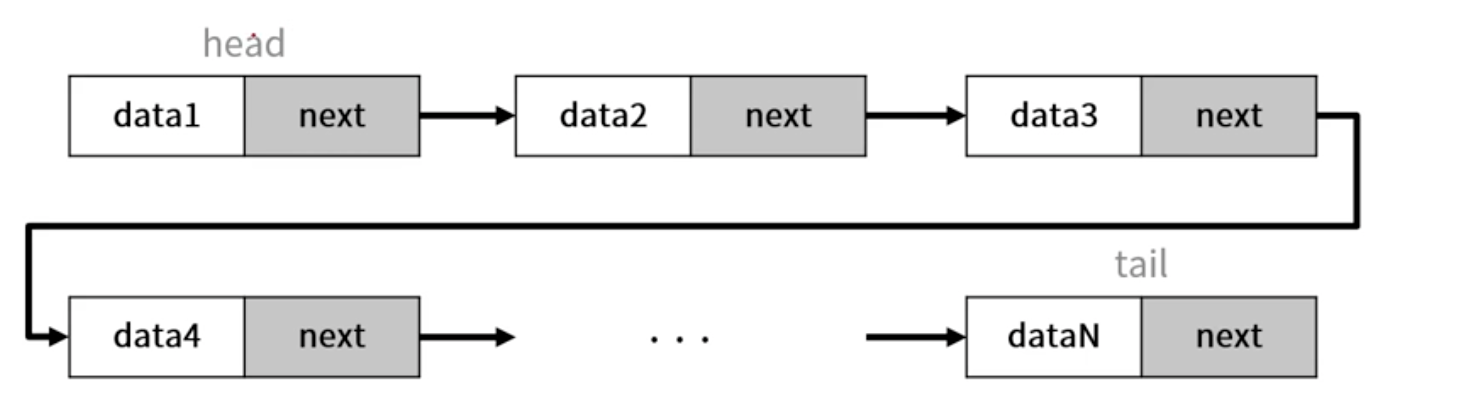
연결리스트 기본 구조
노드 (Node)
- 데이터 저장 단위로, 값과 포인터로 구성
- 포인터 : 다음 노드나 이전 노드의 연결 정보
연결 리스트 기본 연산
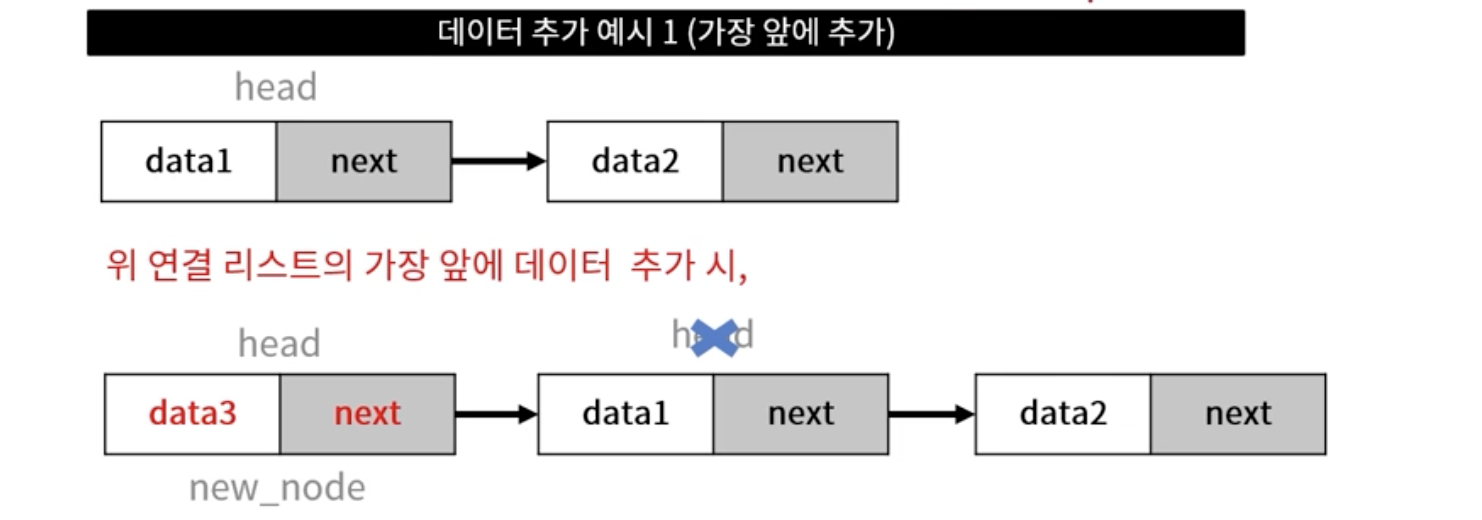
데이터 추가
- 데이터 추가 위치 (head, 중간, tail)에 따른 연결 작업 필요
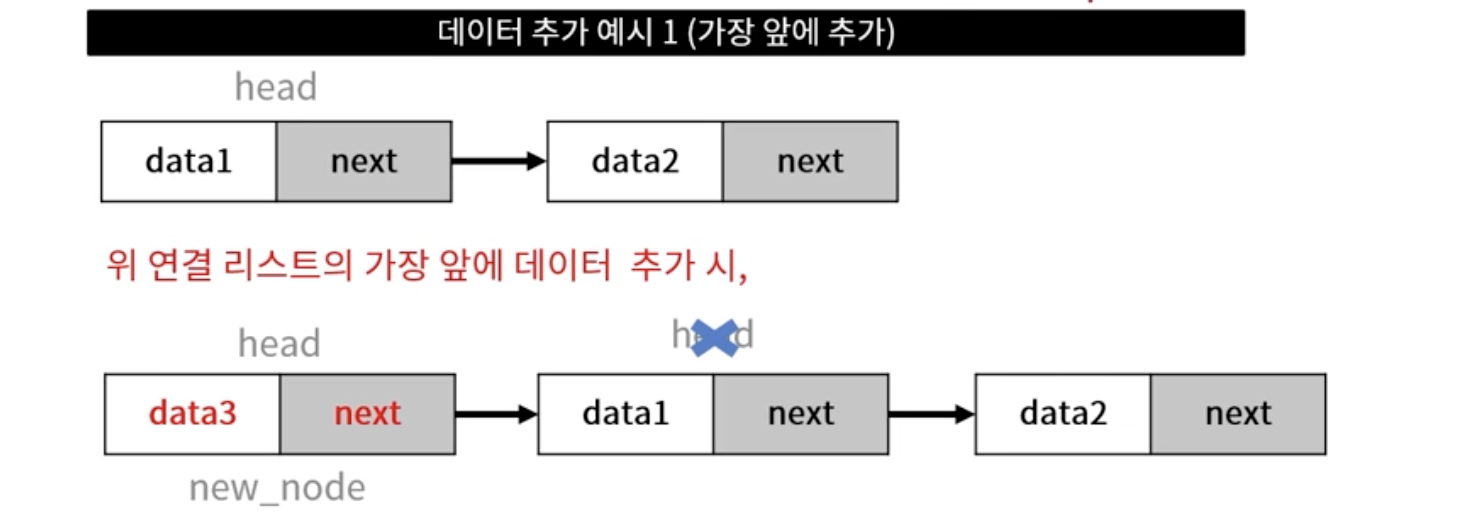
- 추가할 데이터를 담을 노드 생성
- 링크 연결 작업
- head 이전 작업
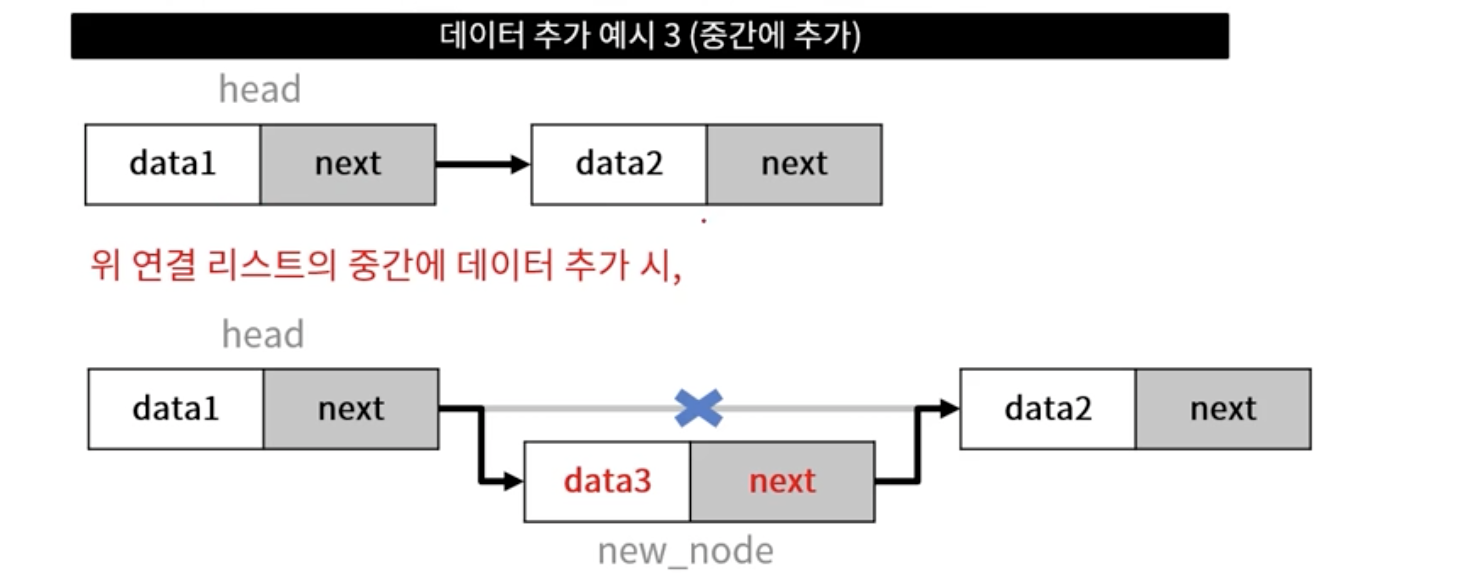
- 추가할 데이터를 담을 노드 생성
- head로부터 끝 노드까지 순회
- 링크 연결 작업
- 추가할 데이터를 담을 노드 생성
- head로부터 데이터 추가 위치 직전 노드까지 순회
- 링크 연결 작업
데이터 삭제
- 데이터 삭제 위치(head, 중간, tail)에 따른 연결 작업 필요
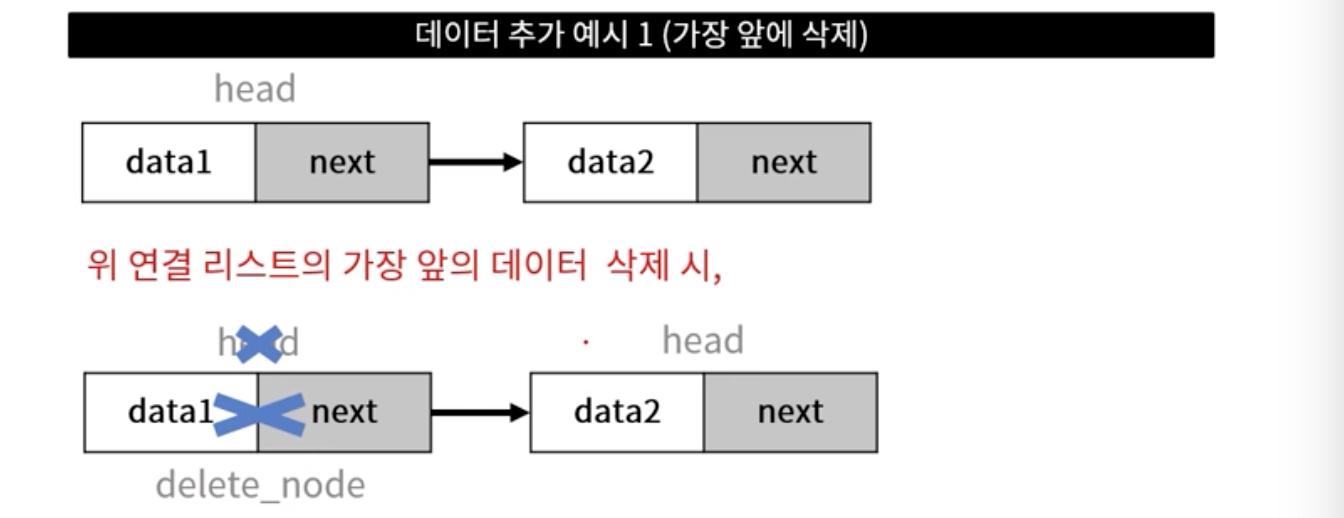
- 삭제 대상 노드 지정 (delete_node)
- head 이전 작업
- delte_node 삭제
- head로부터 가장 끝까지 순회
- 끝 노드 삭제
- 삭제 이전 노드의 링크 처리
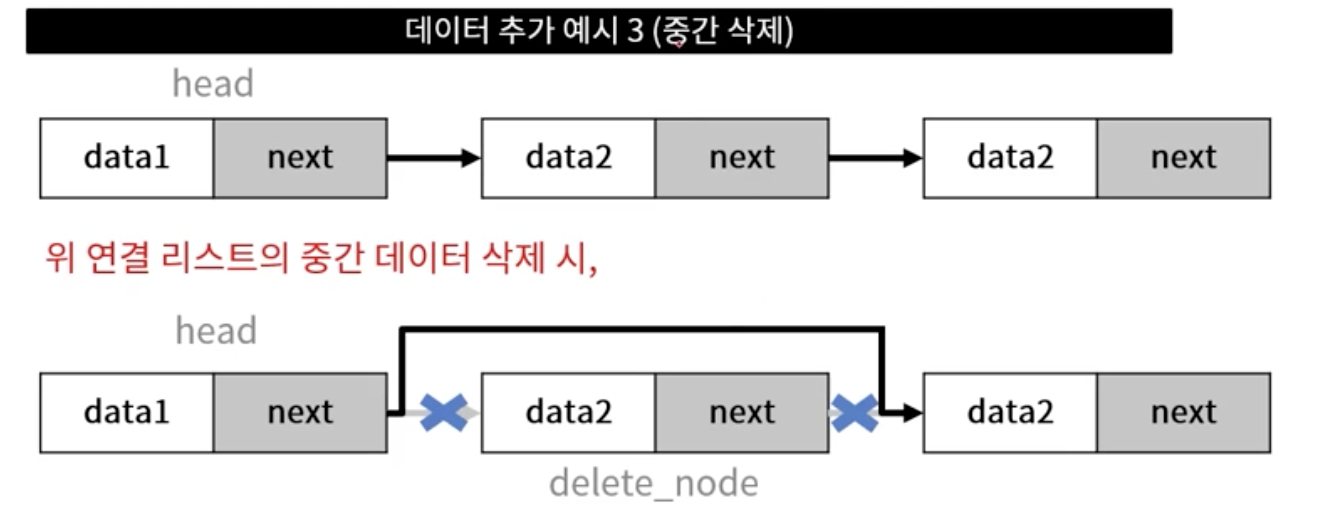
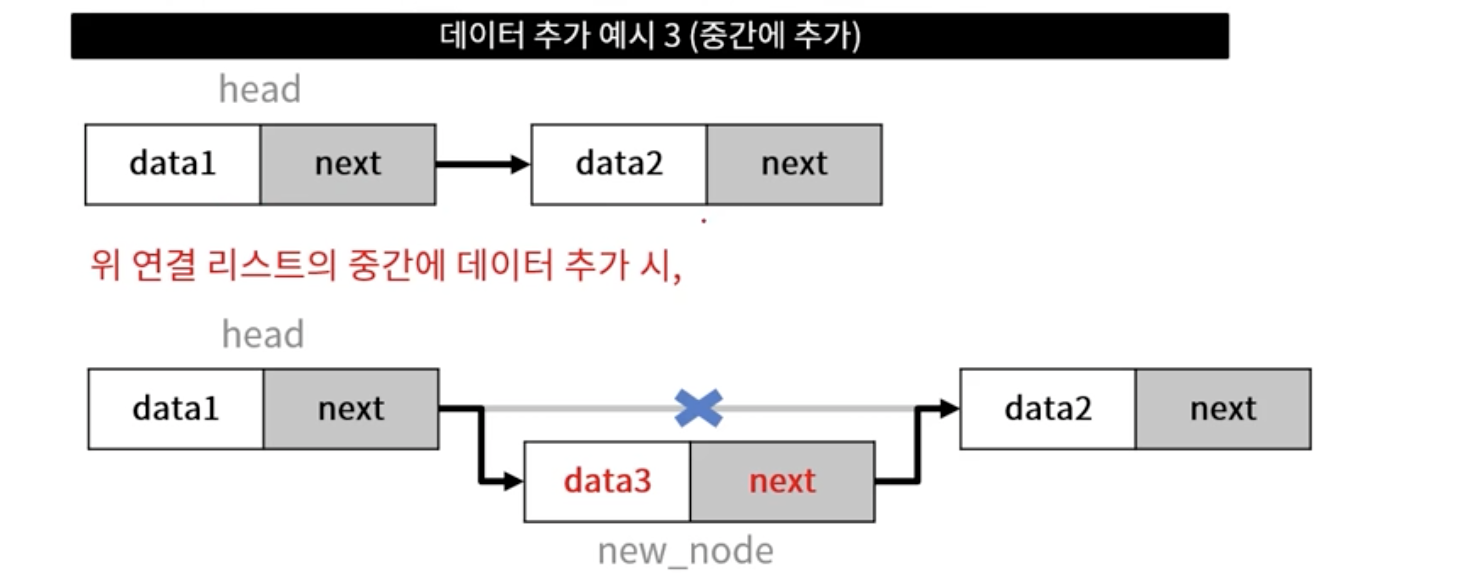
- head로부터 삭제 대상 노드까지 순회 및 해당 노드 지정 (delete_node)
- 삭제 대상 이전/이후 노드의 링크 연결 작업
- delete_node 삭제
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void addData(int data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
}
}
public void removeData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node prev = cur;
while (cur.next != null) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = null;
} else {
prev.next = null;
}
}
public void findData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
System.out.println("Data exist!");
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList myList = new LinkedList(new Node(1, null));
myList.showData();
myList.addData(2);
myList.addData(3);
myList.addData(4);
myList.addData(5);
myList.showData();
myList.findData(3);
myList.findData(100);
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
myList.showData();
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
}
}
class LinkedList2 extends LinkedList {
LinkedList2(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else if (beforeData == null) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
} else {
pre.next = new Node(data, cur);
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList2 myList = new LinkedList2(new Node(1, null));
myList.showData();
myList.addData(2);
myList.addData(3);
myList.addData(4);
myList.addData(5);
myList.showData();
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData();
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData();
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData();
}
}
class LinkedList2 extends LinkedList {
LinkedList2(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else if (beforeData == null) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
} else {
pre.next = new Node(data, cur);
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList2 myList = new LinkedList2(new Node(1, null));
myList.showData();
myList.addData(2);
myList.addData(3);
myList.addData(4);
myList.addData(5);
myList.showData();
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData();
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData();
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData();
}
}
class NodeBi {
int data;
NodeBi next;
NodeBi prev;
NodeBi(int data, NodeBi next, NodeBi prev) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
NodeBi head;
NodeBi tail;
DoublyLinkedList(NodeBi node) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new NodeBi(data, null, null);
this.tail = this.head;
} else if (beforeData == null) {
this.tail.next = new NodeBi(data, null, this.tail);
this.tail = this.tail.next;
} else {
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = new NodeBi(data, this.head, null);
this.head.next.prev = this.head;
} else {
pre.next = new NodeBi(data, cur, pre);
cur.prev = pre.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head && cur == this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
this.head.prev = null;
} else if (cur == this.tail) {
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = pre;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void showDataFromTail() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.prev;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList myList = new DoublyLinkedList(new NodeBi(1, null, null));
myList.showData();
myList.addData(2, null);
myList.addData(3, null);
myList.addData(4, null);
myList.addData(5, null);
myList.showData();
myList.showDataFromTail();
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData();
myList.showDataFromTail();
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData();
myList.showDataFromTail();
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData();
myList.showDataFromTail();
}
}
class CircularLinkedList {
NodeBi head;
NodeBi tail;
CircularLinkedList(NodeBi node) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
node.next = this.head;
node.prev = this.head;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, null, null);
this.head = newNodeBi;
this.tail = newNodeBi;
newNodeBi.next = newNodeBi;
newNodeBi.prev = newNodeBi;
} else if (beforeData == null) {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, this.head, this.tail);
this.tail.next= newNodeBi;
this.head.prev = newNodeBi;
this.tail = newNodeBi;
} else {
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
do {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, this.head, this.tail);
this.tail.next = newNodeBi;
this.head.prev = newNodeBi;
this.head = newNodeBi;
} else {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, cur, pre);
pre.next = newNodeBi;
cur.prev = newNodeBi;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
} while (cur != this.head);
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head && cur == this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else if (cur == this.head) {
cur.next.prev = this.head.prev;
this.head = cur.next;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else if (cur == this.tail) {
pre.next = this.tail.next;
this.tail = pre;
this.head.prev = this.tail;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = pre;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != this.head) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(cur.data);
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularLinkedList myList = new CircularLinkedList(new NodeBi(1, null, null));
myList.addData(2, null);
myList.addData(3, null);
myList.addData(4, null);
myList.addData(5, null);
myList.showData();
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData();
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData();
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData();
}
}
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == null;
}
public void addData(int data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public boolean findData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return false;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
System.out.println("Data exist!");
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
return false;
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static LinkedList removeDup(LinkedList listBefore) {
LinkedList listAfter = new LinkedList();
Node cur = listBefore.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (listAfter.findData(cur.data) == false) {
listAfter.addData(cur.data);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return listAfter;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(4);
linkedList.addData(2);
linkedList.addData(4);
linkedList.addData(2);
linkedList.showData();
linkedList = removeDup(linkedList);
linkedList.showData();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static boolean checkPalindrome(LinkedList list) {
Node cur = list.head;
Node left = list.head;
Node right = null;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
right = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
Node prevRight = right;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt / 2; i++) {
if (left.data != right.data) {
return false;
}
left = left.next;
right = left;
while (right.next != prevRight) {
right = right.next;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(5);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(1);
System.out.println(checkPalindrome(linkedList));
LinkedList linkedList2 = new LinkedList();
linkedList2.addData(3);
linkedList2.addData(5);
linkedList2.addData(5);
linkedList2.addData(3);
System.out.println(checkPalindrome(linkedList2));
LinkedList linkedList3 = new LinkedList();
linkedList3.addData(1);
linkedList3.addData(3);
linkedList3.addData(5);
linkedList3.addData(1);
System.out.println(checkPalindrome(linkedList3));
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static LinkedList reverseList(LinkedList list, int left, int right) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node pre1 = null;
cur1 = list.head;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre1 = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
Node cur2 = cur1;
Node pre2 = pre1;
Node after = null;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
after = cur2.next;
cur2.next = pre2;
pre2 = cur2;
cur2 = after;
}
pre1.next = pre2;
cur1.next = cur2;
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(2);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(4);
linkedList.addData(5);
linkedList.showData();
linkedList = reverseList(linkedList, 2, 4);
linkedList.showData();
LinkedList linkedList2 = new LinkedList();
linkedList2.addData(1);
linkedList2.addData(2);
linkedList2.addData(3);
linkedList2.addData(4);
linkedList2.addData(5);
linkedList2.addData(6);
linkedList2.addData(7);
linkedList2.showData();
linkedList2 = reverseList(linkedList2, 3, 5);
linkedList2.showData();
}
}
package P4;
import java.util.HashSet;
class Node {
String data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(String data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
char alphabet;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node, char alphabet) {
this.head = node;
this.alphabet = alphabet;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == null;
}
public void addData(String data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
}
}
public void removeData(String data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data.equals(data)) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public boolean findData(String data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return false;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data.equals(data)) {
System.out.println("Data exist!");
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
return false;
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice4 {
public static void dataCollect(String[] data) {
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet();
for (String item: data) {
set.add(item.toCharArray()[0]);
}
System.out.println(set);
Character[] arr = set.toArray(new Character[0]);
LinkedList[] linkedList = new LinkedList[set.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.length; i++) {
linkedList[i] = new LinkedList(null, arr[i]);
}
for (String item: data) {
for (LinkedList list: linkedList) {
if (list.alphabet == item.toCharArray()[0]) {
list.addData(item);
}
}
}
for (LinkedList list: linkedList) {
System.out.print(list.alphabet + ": ");
list.showData();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] input = {"apple", "watermelon", "banana", "apricot", "kiwi", "blueberry", "cherry", "orange"};
dataCollect(input);
System.out.println();
String[] input2 = {"ant", "kangaroo", "dog", "cat", "alligator", "duck", "crab", "kitten", "anaconda", "chicken"};
dataCollect(input2);
}
}







