Chap7 스프링 AOP 구현
스프링 AOP를 이용해서 공통 기능을 구현, 적용하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
- Aspect로 사용할 클래스에 @Aspect 어노테이션 적용
- @Pointcut 어노테이션으로 공통 기능을 적용할 Pointcut 정의
- 공통 기능을 구현한 메서드에 @Around 어노테이션 적용
@Aspect, @Pointcut, @Around로 AOP 구현
@Aspect
public class ExeTimeAspect{
@Pointcut("execution(public * chap07..*(..))")
private void publicTarget(){}
@Around("publicTarget()")
public Object measure(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
long start=System.nanoTime();
try{
Object result=joinPoint.proceed();
reutrn result;
}finally{
long finish=System.nanoTime();
Signature sig=joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("%s.%s(%s) 실행시간: %d ns",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
sig.getName(),
Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()),
(finish-start)
);
}
}
}@Aspect 어노테이션을 적용한 클래스는 Advice와 Pointcut을 함께 제공한다.
@Pointcut은 공통 기능을 적용할 대상을 설정한다. execution으로 chap07 패키지와 그 하위 패키지에 위치한 타입의 public 메서드를 Pointcut으로 설정한다.
@Around 어노테이션은 Around Advice를 설정한다. @Around 어노테이션의 값이 "publicTarget()"인데 이는 publicTarget() 메서드에 정의한 Pointcut에 공통 기능을 적용한다는 것을 의미한다.
publicTarget() 메서드는 chap07 패키지와 그 하위 패키지에 위치한 public 메서드를 Pointcut으로 설정하고 있으므로, @Around가 붙은 measure() 메서드를 적용한다.
measure() 메서드의 ProceedingJoinPoint 타입 파라미터는 프록시 대상 객체의 메서드를 호출할 때 사용한다. preceed() 메서드를 사용해서 실제 대상 객체의 메서드를 호출한다. 이 메서드를 호출하면 대상 객체의 메서드가 실행되므로 이 코드 이전과 이후에 공통 기능을 위한 코드를 위치시키면 된다.
ProceedingJoinPoint의 getSignature(), getTarget(), getArgs()의 메서드는 각각 호출한 메서드의 시그니처, 대상 객체, 인자 목록을 구하는데 사용된다. 이 메서드를 사용해서 대상 객체의 클래스 이름과 메서드 이름을 출력한다.
참고
자바에서 메서드 이름과 파라미터를 합쳐서 메서드 시그니처라고 한다. 메서드 이름이 다르거나 파라미터 타입, 개수가 다르면 시그니처가 다르다고 한다. 메서드의 리턴 타입이나 익셉션 타입은 시그니처에 포함되지 않는다.
스프링 설정 클래스
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppCtx{
@Bean
public ExeTimeAspect exeTimeAspect{
return new ExeTimeAspect();
}
@Bean
public Calculator calculator(){
return new RecCalculator();
}
}@Aspect 어노테이션을 붙이 클래스를 공통 기능으로 적용하려면 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 어노테이션을 설정 클래스에 붙여야 한다. 이 어노테이션을 추가하면 스프링은 @Aspect 어노테이션이 붙은 빈 객체를 찾아서 빈 객체의 @Pointcut 설정과 @Around 설정을 이용한다.
@Around 어노테이션은 Pointcut으로 publicTarget() 메서드를 설정했다. public Target() 메서드의 @Pointcut은 chap07 패키지나 그 하위 패키지에 속한 빈 객체 타입이 public 메서드를 설정한다. 설정한 Calculator 타입이 chap07에 속하므로 calculator 빈에 ExeTimeAspect 클래스에 정의한 공통 기능인 measure()를 적용한다.
public calss MainAspect{
public static void main(String[] args){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppCtx.class);
Calculator cal=ctx.getBean("calculator",Calculator.class);
long fiveFact=cal.factorial(5);
System.out.println("cal.factorial(5)="+finveFact);
System.out.println(cal.getClass().getName());
ctx.close();
}
}RecCalculator.factorial([5]) 실행시간ㅣ 50201 ns
cal.factorial(5)=120
com.sun.proxy.$Proxy17첫번째 줄은 ExeTimeAspect 클래스의 measure() 메서드가 출력한 결과이다. 세번째 줄은 cal.getClass().getName()을 출력한 결과이다. 타입이 스프링이 생성한 프록시 타입인 것을 볼 수 있다.
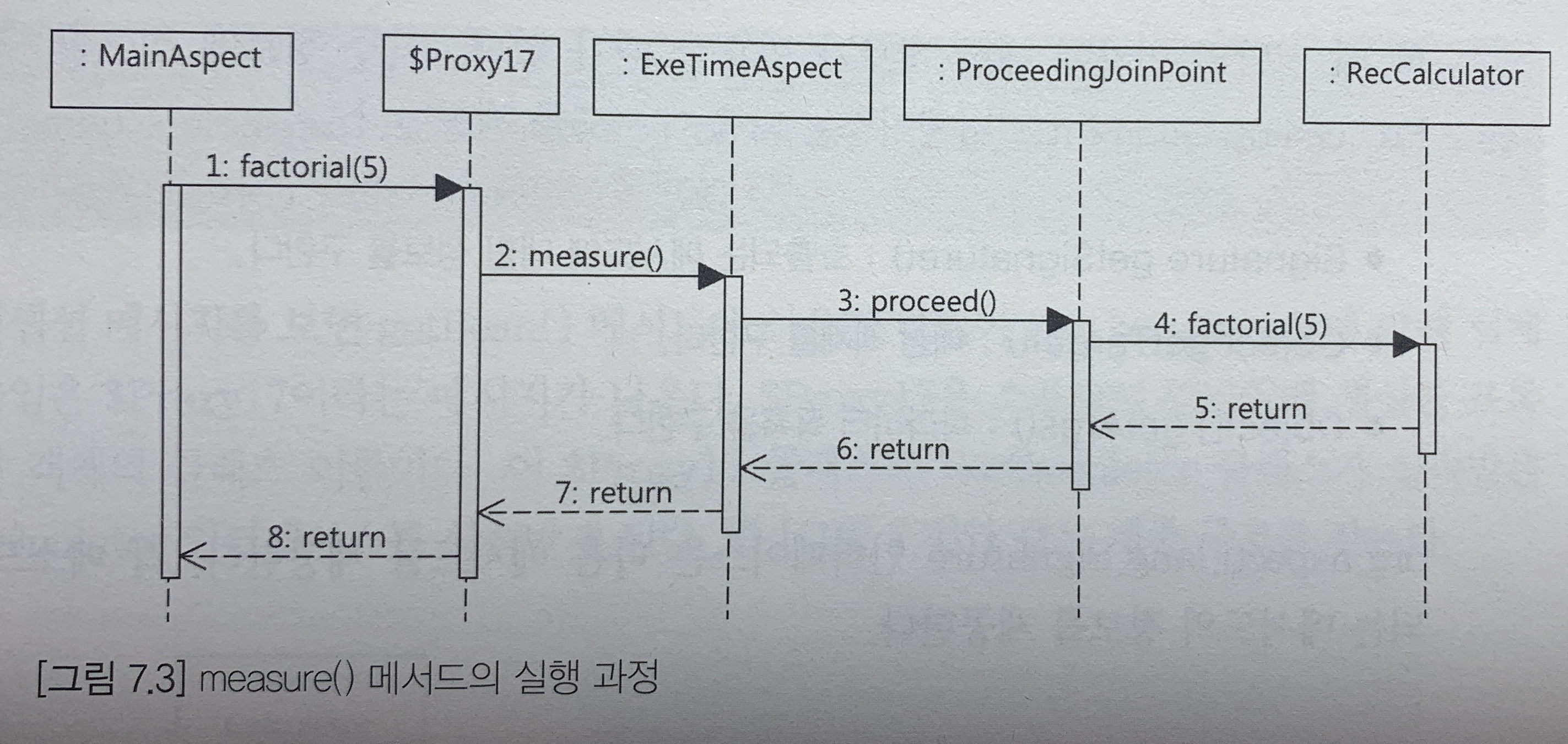
AOP를 적용하지 않았으면 세번째 줄의 리턴 값이 프록시 객체가 아닌 RecCalculator 타입이였을 것이다. AppCtx 클래스에서 exeTimeAspect() 메서드를 주석처리하고 다시 MainAspect 클래스를 출력하면 다음과 같다.
cal.factorial(5)=120
chap07.RecCalculator