1. Graphs 개념
What is it?
- Bunch of nodes or points connected together without hierarchy. they are all treated equally.
Terminology
- vertex: node.(이하 vtx)
- edge: connection.
- undirected graph: two-way connections, or no direction or polarity.
- directed graph: there is certain direction assigned to an edge. ex) facebook.
- unweigthed graph: no value or maginitude with each edge.
- weighted graph: it does have value associated with edge. ex) road map.
쉽게 말해서, node간의 위계질서가 없다. 그러니 시작점도 끝점도 없다. 내가 어디서 시작하느냐에 따라 끝도 달라진다. 또한 edge에 value를 설정할 수 있다. edge에 설정한 value로 인해서 최단거리를 구할 수 도 있다.(Dijsktra에서 배울라나?)
그럼 이 graph를 어떻게 나타낼 것인지 알아보자.
Compare storing method
- Adjacency list
- Can take up less space(in sparse graphs)
- Faster to iterate over all edges
- Can be slower to look up specific edge
- Adjacency matrix
-
Takes up more space (in sparse graphs)
-
Slower to iterate over all edges
-
Faster to look up specific edge
-
We choose Adjacency list because most data in the real-world tends to lend itself(to be good for a particular use. it is good enough to lend) to sparser and/or larger graphs.
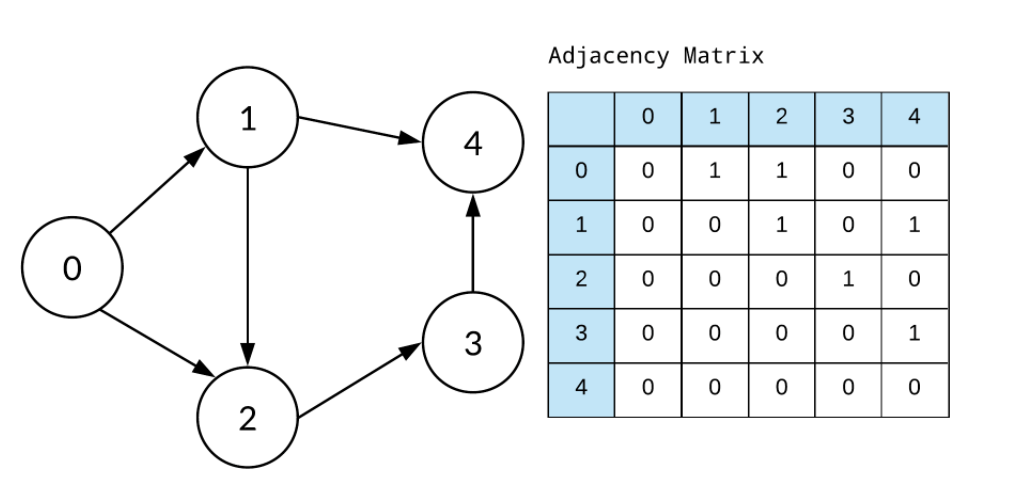
사실상 list방식을 많이 따른다. maxtrix는 iterate 해야할게 너무 많아서그렇다. 무슨말인지 모르니깐 그림으로 쉽게 알아보자.
Matrix
List
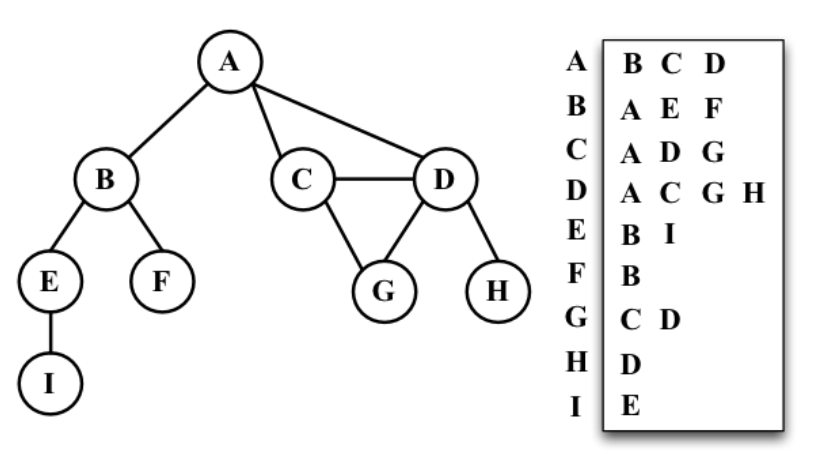
요런식으로 그려지지만 실제로 data에 저장되는 형태는 list의 형태이다.
그럼 vtx와 edge를 추가하는 코드를 작성해보자.
2. addVertex / addEdge
굉장히 간단하다. vtx는 그냥 list obj에 추가해주면 되고. edge는 연결되는 vtx두개에 서로 추가해주면 된다.
class Graph {
constructor() {
this.adjacencyList = {};
}
addVertex(val) {
if (this.adjacencyList[val] in this.adjacencyList) {
return;
} else {
this.adjacencyList[val] = [];
}
return this.adjacencyList;
}
addEdge(v1, v2) {
this.adjacencyList[v1].push(v2);
this.adjacencyList[v2].push(v1);
return this.adjacencyList;
}
}3. deleteEdge/Vtx
지우는것도 간단하다. v1에서 v2를 지우고 v2에서 v1을 지우면 끝난다. list는 arr를 이용하기 때문에 indexOf를 사용했다.
그리고 vtx를 지울때도 vtx안에 연관되어있는 vtx와의 연결을 다 끊고 없어지도록 했다. 나는 while안에 for를 사용했는데 이중 loop는 O(n제곱) 이므로 our lovely Colt의 방법을 사용했다
removeEdge(v1, v2) {
var indexV1 = this.adjacencyList[v2].indexOf(v1);
if (indexV1 >= 0) this.adjacencyList[v2].splice(indexV1, 1);
var indexV2 = this.adjacencyList[v1].indexOf(v2);
if (indexV2 >= 0) this.adjacencyList[v1].splice(indexV2, 1);
}
removeVertex(vertex) {
// while(this.adjacencyList[vertex].length) 라고 해도 됨. 0=false 이므로 0이 되면 빠져나가니깐
// 반복문 안에 반복문은 바람직하지 않음 time-wise
// while (this.adjacencyList[vertex].length > 0) {
// for (const city of this.adjacencyList[vertex]) {
// console.log(city, vertex);
// this.removeEdge(city, vertex);
// }
// }
while (this.adjacencyList[vertex].length) {
var city = this.adjacencyList[vertex].pop();
this.removeEdge(city, vertex);
}
delete this.adjacencyList[vertex];
}
그럼 이제 graph를 traverse해보도록 하자!
