브리지
큰 클래스 또는 밀접하게 관련된 클래스들의 집합을 두 개의 계층구조로 나눈 뒤 독립적으로 개발할 수 있도록 하는 패턴
구조
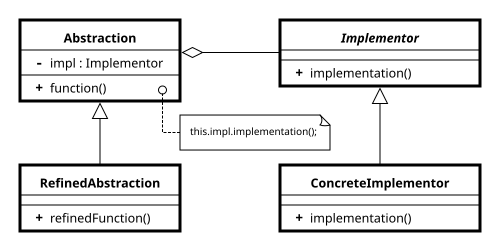
- 추상화: 구현 객체에 의존해 실제 하위 작업들을 수행
- 구현: 모든 구상 구현들에 공통적인 인터페이스를 선언하며 추상화는 여기에 선언된 메서드들을 통해서만 구현 객체와 소통 가능
- 구상 구현: 플랫폼별 맞춤형 코드를 포함
- 정제된 추상화: 제어 논리의 변형들을 제공
예시 코드
public interface Device {
boolean isEnabled();
void enable();
void disable();
int getVolume();
void setVolume(int percent);
int getChannel();
void setChannel(int channel);
void printStatus();
}
public class Radio implements Device {
private boolean on = false;
private int volume = 30;
private int channel = 1;
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return on;
}
@Override
public void enable() {
on = true;
}
@Override
public void disable() {
on = false;
}
@Override
public int getVolume() {
return volume;
}
@Override
public void setVolume(int volume) {
if (volume > 100) {
this.volume = 100;
} else if (volume < 0) {
this.volume = 0;
} else {
this.volume = volume;
}
}
@Override
public int getChannel() {
return channel;
}
@Override
public void setChannel(int channel) {
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void printStatus() {
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
System.out.println("| I'm radio.");
System.out.println("| I'm " + (on ? "enabled" : "disabled"));
System.out.println("| Current volume is " + volume + "%");
System.out.println("| Current channel is " + channel);
System.out.println("------------------------------------\n");
}
}
public class Tv implements Device {
private boolean on = false;
private int volume = 30;
private int channel = 1;
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return on;
}
@Override
public void enable() {
on = true;
}
@Override
public void disable() {
on = false;
}
@Override
public int getVolume() {
return volume;
}
@Override
public void setVolume(int volume) {
if (volume > 100) {
this.volume = 100;
} else if (volume < 0) {
this.volume = 0;
} else {
this.volume = volume;
}
}
@Override
public int getChannel() {
return channel;
}
@Override
public void setChannel(int channel) {
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void printStatus() {
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
System.out.println("| I'm TV set.");
System.out.println("| I'm " + (on ? "enabled" : "disabled"));
System.out.println("| Current volume is " + volume + "%");
System.out.println("| Current channel is " + channel);
System.out.println("------------------------------------\n");
}
}
public interface Remote {
void power();
void volumeDown();
void volumeUp();
void channelDown();
void channelUp();
}
public class BasicRemote implements Remote {
protected Device device;
public BasicRemote() {}
public BasicRemote(Device device) {
this.device = device;
}
@Override
public void power() {
System.out.println("Remote: power toggle");
if (device.isEnabled()) {
device.disable();
} else {
device.enable();
}
}
@Override
public void volumeDown() {
System.out.println("Remote: volume down");
device.setVolume(device.getVolume() - 10);
}
@Override
public void volumeUp() {
System.out.println("Remote: volume up");
device.setVolume(device.getVolume() + 10);
}
@Override
public void channelDown() {
System.out.println("Remote: channel down");
device.setChannel(device.getChannel() - 1);
}
@Override
public void channelUp() {
System.out.println("Remote: channel up");
device.setChannel(device.getChannel() + 1);
}
}
public class AdvancedRemote extends BasicRemote {
public AdvancedRemote(Device device) {
super.device = device;
}
public void mute() {
System.out.println("Remote: mute");
device.setVolume(0);
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testDevice(new Tv());
testDevice(new Radio());
}
public static void testDevice(Device device) {
System.out.println("Tests with basic remote.");
BasicRemote basicRemote = new BasicRemote(device);
basicRemote.power();
device.printStatus();
System.out.println("Tests with advanced remote.");
AdvancedRemote advancedRemote = new AdvancedRemote(device);
advancedRemote.power();
advancedRemote.mute();
device.printStatus();
}
}- 클래스에서 직교 차원들을 식별하고 클라이언트가 필요로 하는 작업들을 기초 추상 클래스에 정의
- 모든 플랫폼에 제공되어야 하는 작업을 결정 후 추상화에 필요한 작업은 일반 구현 인터페이스에 선언
- 모든 플랫폼에 대해 구상 구현 클래스를 생성
- 추상화 클래스에서 구현 유형에 대한 참조 필드를 추가
- 클라이언트는 구현 객체를 추상화의 생성자에 전달하여 연결하고 추상화 객체와 작업
장단점
장점
- 플랫폼 독립적인 클래스와 앱을 만들 수 있다.
- 클라이언트는 추상화를 통해 작동할 수 있다.
- 개방/폐쇄 원칙: 새로운 추상화와 구현들을 독립적으로 도입할 수 있다.
- 단일 책임 원칙: 추상화의 상위 수준 논리와 구현의 세부 정보에 집중할 수 있다.
단점
- 결합도가 높은 클래스는 코드를 더 복잡하게 만들 수 있다.