중재자 패턴
객체 간의 직접 통신을 제한하고 중재자 객체를 통해서만 협력하도록 하는 패턴
구조
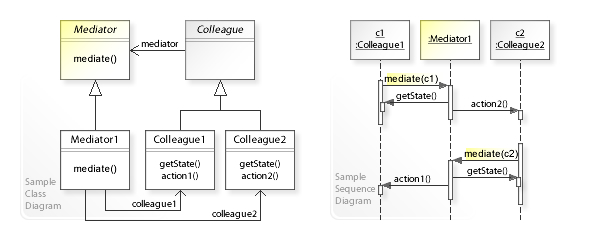
- 컴포넌트: 비즈니스 로직을 포함한 다양한 클래스들. 각 컴포넌트는 중재자에 대한 참조가 있고 컴포넌트는 중재자의 실제 클래스를 알지 못한다.
- 중재자: 일반적으로 단일 알림 메서드만을 포함하는 컴포넌트들과의 통신 메서드들을 선언한다.
- 구상 중재자: 자신이 관리하는 모든 컴포넌트에 대한 참조를 유지하고 때로는 수명 주기를 관리한다.
- 컴포넌트들은 다른 컴포넌트를 서로 인식하지 않아야 한다.
예시 코드
// MediatorPatternDemo.java
// 미디에이터 인터페이스
interface Mediator {
void notify(Component sender, String event);
}
// 모든 컴포넌트의 기본 클래스
abstract class Component {
protected Mediator mediator;
public Component(Mediator mediator) {
this.mediator = mediator;
}
public void click() {
mediator.notify(this, "click");
}
public void keypress() {
mediator.notify(this, "keypress");
}
}
// Button 컴포넌트
class Button extends Component {
private String name;
public Button(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
// Textbox 컴포넌트
class Textbox extends Component {
private String name;
private String text;
public Textbox(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator);
this.name = name;
this.text = "";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
}
// Checkbox 컴포넌트
class Checkbox extends Component {
private String name;
private boolean checked;
public Checkbox(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator);
this.name = name;
this.checked = false;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public boolean isChecked() {
return checked;
}
// 상태 변경 시 미디에이터에게 알립니다.
public void setChecked(boolean checked) {
this.checked = checked;
mediator.notify(this, "check");
}
// 토글 방식도 구현할 수 있습니다.
public void toggle() {
this.checked = !this.checked;
mediator.notify(this, "check");
}
}
// 구상 미디에이터 클래스: AuthenticationDialog
class AuthenticationDialog implements Mediator {
private String title;
// 컴포넌트들
private Checkbox loginOrRegisterChkBx;
private Textbox loginUsername, loginPassword;
private Textbox registrationUsername, registrationPassword, registrationEmail;
private Button okBtn, cancelBtn;
public AuthenticationDialog() {
// 모든 컴포넌트들을 생성할 때, 현재 미디에이터(this)를 전달합니다.
loginOrRegisterChkBx = new Checkbox(this, "Login/Register Checkbox");
loginUsername = new Textbox(this, "Login Username");
loginPassword = new Textbox(this, "Login Password");
registrationUsername = new Textbox(this, "Registration Username");
registrationPassword = new Textbox(this, "Registration Password");
registrationEmail = new Textbox(this, "Registration Email");
okBtn = new Button(this, "OK Button");
cancelBtn = new Button(this, "Cancel Button");
// 초기 모드를 로그인 모드로 설정 (체크박스 true: 로그인, false: 등록)
loginOrRegisterChkBx.setChecked(true);
}
// 컴포넌트에서 이벤트가 발생하면 notify 메서드를 호출합니다.
@Override
public void notify(Component sender, String event) {
if (sender == loginOrRegisterChkBx && event.equals("check")) {
if (loginOrRegisterChkBx.isChecked()) {
title = "Log in";
System.out.println("Mediator: Switching to Login mode.");
showLoginComponents();
hideRegistrationComponents();
} else {
title = "Register";
System.out.println("Mediator: Switching to Registration mode.");
showRegistrationComponents();
hideLoginComponents();
}
}
if (sender == okBtn && event.equals("click")) {
if (loginOrRegisterChkBx.isChecked()) {
System.out.println("Mediator: OK button clicked in Login mode.");
System.out.println("Attempting to log in with credentials:");
System.out.println("Username: " + loginUsername.getText());
System.out.println("Password: " + loginPassword.getText());
// 예시로, username이 "user"이고 password가 "pass"일 경우 로그인 성공 처리
if (loginUsername.getText().equals("user") && loginPassword.getText().equals("pass")) {
System.out.println("Login successful!");
} else {
System.out.println("Login failed: Incorrect username or password.");
}
} else {
System.out.println("Mediator: OK button clicked in Registration mode.");
System.out.println("Attempting to register with details:");
System.out.println("Username: " + registrationUsername.getText());
System.out.println("Password: " + registrationPassword.getText());
System.out.println("Email: " + registrationEmail.getText());
// 등록 성공 후, 자동 로그인 등의 처리
System.out.println("Registration successful! Logging in...");
}
}
}
// UI에서 로그인 관련 컴포넌트를 표시하는 메서드 (시뮬레이션)
private void showLoginComponents() {
System.out.println("Displaying login components.");
// 실제 UI에서는 로그인 폼을 보이게 하는 로직을 추가합니다.
}
// UI에서 로그인 관련 컴포넌트를 숨기는 메서드 (시뮬레이션)
private void hideLoginComponents() {
System.out.println("Hiding login components.");
// 실제 UI에서는 로그인 폼을 숨기는 로직을 추가합니다.
}
// UI에서 등록 관련 컴포넌트를 표시하는 메서드 (시뮬레이션)
private void showRegistrationComponents() {
System.out.println("Displaying registration components.");
// 실제 UI에서는 등록 폼을 보이게 하는 로직을 추가합니다.
}
// UI에서 등록 관련 컴포넌트를 숨기는 메서드 (시뮬레이션)
private void hideRegistrationComponents() {
System.out.println("Hiding registration components.");
// 실제 UI에서는 등록 폼을 숨기는 로직을 추가합니다.
}
// 테스트 및 시뮬레이션을 위한 각 컴포넌트에 대한 Getter들
public Checkbox getLoginOrRegisterChkBx() {
return loginOrRegisterChkBx;
}
public Textbox getLoginUsername() {
return loginUsername;
}
public Textbox getLoginPassword() {
return loginPassword;
}
public Textbox getRegistrationUsername() {
return registrationUsername;
}
public Textbox getRegistrationPassword() {
return registrationPassword;
}
public Textbox getRegistrationEmail() {
return registrationEmail;
}
public Button getOkBtn() {
return okBtn;
}
public Button getCancelBtn() {
return cancelBtn;
}
}
// 애플리케이션 실행 클래스
public class MediatorPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// AuthenticationDialog 미디에이터 생성
AuthenticationDialog dialog = new AuthenticationDialog();
// ----- 로그인 시나리오 -----
System.out.println("=== Simulating Login Scenario ===");
// 로그인 모드 선택: 체크박스가 true이면 로그인 모드입니다.
dialog.getLoginOrRegisterChkBx().setChecked(true); // notify() 호출됨
// 로그인 정보를 입력 (예: 올바른 정보: user / pass)
dialog.getLoginUsername().setText("user");
dialog.getLoginPassword().setText("pass");
// OK 버튼 클릭 (로그인 시도)
dialog.getOkBtn().click();
System.out.println();
// ----- 등록 시나리오 -----
System.out.println("=== Simulating Registration Scenario ===");
// 등록 모드 선택: 체크박스 false이면 등록 모드입니다.
dialog.getLoginOrRegisterChkBx().setChecked(false); // notify() 호출됨
// 등록 정보를 입력
dialog.getRegistrationUsername().setText("newUser");
dialog.getRegistrationPassword().setText("newPass");
dialog.getRegistrationEmail().setText("newUser@example.com");
// OK 버튼 클릭 (등록 시도)
dialog.getOkBtn().click();
}
}- 독립적으로 만들었을 때 유지관리나 재사용이 쉬워지는 클래스들을 식별한다.
- 중재자 인터페이스를 선언하고 중재자와 컴포넌트 간의 원하는 통신 프로토콜을 설명한다.
- 구상 중재자 클래스를 구현한다. 모든 컴포넌트에 대한 참조를 중재자 내부에 저장하면 중재자의 메서드에서 어떤 컴포넌트라도 호출할 수 있다.
- 중재자가 컴포넌트 객체의 생성 및 파괴를 담당할 수도 있으며 이 경우 중재자는 팩토리 또는 퍼사드와 유사할 수 있다.
- 컴포넌트들은 중재자 객체에 대한 참조를 저장한다.
- 중재자의 알림 메서드를 호출하도록 클라이언트 코드를 변경한다.
장단점
장점
- 단일 책임 원칙: 다양한 컴포넌트 간의 통신을 한 곳으로 추출
- 개방/폐쇄 원칙: 실제 컴포넌트를 변경하지 않고 새로운 중재자를 도입 가능
- 프로그램의 다양한 컴포넌트 간의 결합도를 줄일 수 있음
- 개별 컴포넌트들을 더 쉽게 재사용 가능
단점
- 중재자는 전지전능한 객체로 발전할 수도 있음