반복자 패턴
컬렉션의 요소들의 기본 표현을 노출하지 않고 하나씩 순회할 수 있도록 하는 행동 디자인 패턴
구조
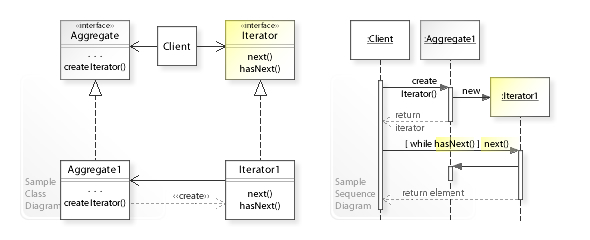
- 반복자: 컬렉션 순회에 필요한 작업들(다음 요소 가져오기, 현재 위치 가져오기, 반복자 다시 시작 등)을 선언
- 구상 반복자: 순회를 위한 특정 알고리즘을 구현. 순회의 진행 상황을 자체적으로 추적함으로써 여러 반복자들이 같은 컬렉션을 서로 독립적으로 순회 가능
- 컬렉션(Aggregate): 컬렉션과 호환되는 반복자들을 가져오기 위한 메서드를 선언
- 구상 컬렉션: 클라이언트가 요청할 때마다 특정 구상 반복자 클래스의 새 인스턴스를 반환
- 클라이언트: 클라이언트는 일반적으로 자체적으로 반복자들을 생성하지 않고 컬렉션을 통해 가져옴
예시 코드
// Profile.java
public class Profile {
private String id;
private String email;
private String name;
public Profile(String id, String email, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
this.name = name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
// SocialNetwork.java
public interface SocialNetwork {
ProfileIterator createFriendsIterator(String profileId);
ProfileIterator createCoworkersIterator(String profileId);
}
// ProfileIterator.java
public interface ProfileIterator {
boolean hasMore();
Profile getNext();
}
// Facebook.java
public class Facebook implements SocialNetwork {
// 실제 페이스북의 사회적 그래프 API 호출을 모사하기 위한 메서드
// 실제 구현에서는 네트워크 호출 등이 이루어지겠지만 여기서는 더미 데이터를 리턴합니다.
public Profile[] socialGraphRequest(String profileId, String type) {
System.out.println("Facebook: " + profileId + "의 " + type + " 데이터를 로드 중...");
if ("friends".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
Profile[] profiles = new Profile[3];
profiles[0] = new Profile("friend1", "friend1@example.com", "Friend One");
profiles[1] = new Profile("friend2", "friend2@example.com", "Friend Two");
profiles[2] = new Profile("friend3", "friend3@example.com", "Friend Three");
return profiles;
} else if ("coworkers".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
Profile[] profiles = new Profile[2];
profiles[0] = new Profile("coworker1", "coworker1@example.com", "Coworker One");
profiles[1] = new Profile("coworker2", "coworker2@example.com", "Coworker Two");
return profiles;
}
return new Profile[0];
}
@Override
public ProfileIterator createFriendsIterator(String profileId) {
return new FacebookIterator(this, profileId, "friends");
}
@Override
public ProfileIterator createCoworkersIterator(String profileId) {
return new FacebookIterator(this, profileId, "coworkers");
}
}
// FacebookIterator.java
public class FacebookIterator implements ProfileIterator {
private Facebook facebook;
private String profileId;
private String type;
// 반복자의 현재 위치
private int currentPosition = 0;
// 데이터를 캐싱하기 위한 배열 (lazy 초기화)
private Profile[] cache = null;
public FacebookIterator(Facebook facebook, String profileId, String type) {
this.facebook = facebook;
this.profileId = profileId;
this.type = type;
}
// 필요할 때 한 번만 데이터를 불러옵니다.
private void lazyInit() {
if (cache == null) {
cache = facebook.socialGraphRequest(profileId, type);
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasMore() {
lazyInit();
return currentPosition < cache.length;
}
@Override
public Profile getNext() {
if (hasMore()) {
Profile result = cache[currentPosition];
currentPosition++;
return result;
}
return null;
}
}
// SocialSpammer.java
public class SocialSpammer {
// ProfileIterator를 이용해 반복하며 이메일을 발송합니다.
public void send(ProfileIterator iterator, String message) {
while (iterator.hasMore()) {
Profile profile = iterator.getNext();
sendEmail(profile.getEmail(), message);
}
}
// 실제 이메일 발송 대신 콘솔에 출력하는 메서드입니다.
private void sendEmail(String email, String message) {
System.out.println("Sending email to " + email + " with message: " + message);
}
}
// Application.java
public class Application {
private SocialNetwork network;
private SocialSpammer spammer;
// 환경설정. 현재는 Facebook을 사용하지만, LinkedIn 등 다른 소셜 네트워크 클래스를 사용할 수도 있습니다.
public void config() {
// 예시로 Facebook을 사용
this.network = new Facebook();
// 다른 소셜 네트워크가 있다면, 조건에 따라 network를 할당하면 됩니다.
this.spammer = new SocialSpammer();
}
public void sendSpamToFriends(Profile profile) {
ProfileIterator iterator = network.createFriendsIterator(profile.getId());
spammer.send(iterator, "Very important message");
}
public void sendSpamToCoworkers(Profile profile) {
ProfileIterator iterator = network.createCoworkersIterator(profile.getId());
spammer.send(iterator, "Very important message");
}
// 애플리케이션 실행 예시
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application app = new Application();
app.config();
// 테스트용 프로필 생성
Profile user = new Profile("user123", "user123@example.com", "John Doe");
System.out.println("Sending spam to friends:");
app.sendSpamToFriends(user);
System.out.println("\nSending spam to coworkers:");
app.sendSpamToCoworkers(user);
}
}- 반복자 인터페이스를 선언한다. 최소한 컬렉션에서 다음 요소를 가져오는 메서드가 있어야 한다.
- 컬렉션 인터페이스를 선언하고 반복자를 가져오는 메서드를 설명한다.
- 구상 반복자 클래스를 구현한다. 반복자 객체는 단일 컬렉션 인스턴스와 반드시 연결되어야 하는데 보통 반복자의 생성자를 통해 연결된다.
- 컬렉션 클래스를 구현한다. 이 클래스는 클라이언트에 특정 컬렉션 클래스에 맞는 반복자를 생성하기 위한 바로가기를 제공한다.
장단점
장점
- 단일 책임 원칙: 순회 알고리즘들을 별도의 클래스로 추출
- 개방/폐쇄 원칙: 새로운 컬렉션과 반복자들을 훼손없이 기존 코드에 전달 가능
- 같은 컬렉션을 병렬로 순회 가능
- 순회를 지연하고 필요할 때 재개가능
단점
- 단순한 컬렉션만 사용하는 경우 과도할 수 있음
- 일부 특수 컬렉션들의 요소를 직접 탐색하는 것보다 덜 효율적일 수 있음