책임 연쇄 패턴
핸들러들의 체인을 따라 요청을 전달하는 디자인 패턴
각 핸들러는 요청을 처리할지 다음 핸들러로 전달할지를 결정한다.
구조
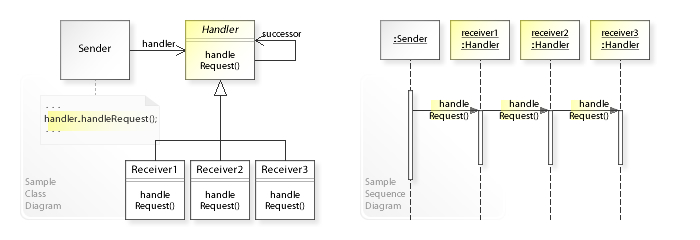
- 핸들러: 모든 구상 핸들러에 공통적인 인터페이스를 선언한다. 요청을 처리하기 위한 단일 메서드와 체인의 다음 핸들러를 세팅하기 위한 메서드가 있을 수 있다.
- 기초 핸들러: 기초 핸들러는 선택적 클래스이며 모든 핸들러에서 사용될 공통적인 코드를 넣을 수 있다. 일반적으로 다음 핸들러에 대한 참조를 저장하는 필드를 정의하여 클라이언트가 다음 핸들러를 지정해 체인을 구축할 수 있도록 한다.
- 구상 핸들러: 요청을 처리하기 위한 실제 코드가 포함된다
예시 코드
interface ComponentWithContextualHelp {
void showHelp();
}
abstract class Component implements ComponentWithContextualHelp {
protected String tooltipText;
protected Container container;
@Override
public void showHelp() {
if (tooltipText != null) {
System.out.println("Tooltip: " + tooltipText);
} else if (container != null) {
container.showHelp();
}
}
}
abstract class Container extends Component {
protected java.util.List<Component> children = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
public void add(Component child) {
children.add(child);
child.container = this;
}
}
class Button extends Component {
public Button(String tooltipText) {
this.tooltipText = tooltipText;
}
}
class Panel extends Container {
private String modalHelpText;
public Panel(String modalHelpText) {
this.modalHelpText = modalHelpText;
}
@Override
public void showHelp() {
if (modalHelpText != null) {
System.out.println("Modal Help: " + modalHelpText);
} else {
super.showHelp();
}
}
}
class Dialog extends Container {
private String wikiPageURL;
public Dialog(String wikiPageURL) {
this.wikiPageURL = wikiPageURL;
}
@Override
public void showHelp() {
if (wikiPageURL != null) {
System.out.println("Opening wiki page: " + wikiPageURL);
} else {
super.showHelp();
}
}
}
class Application {
private Dialog dialog;
public void createUI() {
dialog = new Dialog("http://...");
Panel panel = new Panel("This panel does XYZ.");
Button okButton = new Button("This is the OK button.");
Button cancelButton = new Button("This is the Cancel button.");
panel.add(okButton);
panel.add(cancelButton);
dialog.add(panel);
}
public void onF1KeyPress(Component component) {
component.showHelp();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application app = new Application();
app.createUI();
Component component = app.dialog.children.get(0).children.get(0); // OK Button
app.onF1KeyPress(component);
component = app.dialog.children.get(0); // Panel
app.onF1KeyPress(component);
component = app.dialog; // Dialog
app.onF1KeyPress(component);
}
}- 핸들러 인터페이스를 선언하고 요청을 처리하는 메서드의 시그니처를 작성한다.
- 구상 핸들러에서 중복 코드를 제거하려면 추상 기초 핸들러 클래스를 만드는 것을 고려한다.
- 구상 핸들러 자식 클래스를 만들고 처리 메서드를 구현한다. 이 때 각 핸들러는 요청을 받았을 때 요청을 처리할지, 아니면 체인을 따라 요청을 전달할지 결정을 내려야한다.
- 클라이언트는 자체적으로 체인을 조립하거나 다른 객체들에서부터 미리 구축된 체인을 받을 수 있다.
- 클라이언트는 가장 첫 번째 핸들러 뿐만 아니라 다른 핸들러를 활성화할 수 있다.
장단점
장점
- 요청의 처리 순서를 제어할 수 있다.
- 단일 책임 원칙: 작업을 호출하는 클래스와 작업을 수행하는 클래스를 분리
- 개방/폐쇄 원칙: 기존 클라이언트 코드를 손상하지 않고 새 핸들러를 도입 가능
단점
- 일부 요청들은 처리되지 않을 수 있다.