구간은 높이 1 단위로 나누어진다.
위에서 자라는 거랑, 아래에서 자라는게 있어서..
석순 list (아래에서 자라)
종유석 list (위에서 자라 )
첫 번째 풀이 : 이진탐색 : lower_bound사용하기
lower_boud(k) : k보다 크거나 같은 수가 처음 등장하는 index를 구하는 방법
- 보통 그러한 수가 없는 경우, list의 길이를 반환하게 된다 ( index로는 list길이만큼의 수가 나올 수 없으니)
석순과 종유석 각각에 대한 이분탐색을 해야할 것 같다.
따라서
6 7
1
5
3
3
5
1석순 : 1,3,5
종유석: 5 3 1
실제로 높이 2인 구간이라 할 때, 석순에서는 2로 하는데 , 종유석이라면 h-2로 생각하도록 한다.
- 수정 → 이렇게 생각하면 틀린다. h-2+1로 생각하도록 해야 한다.
- 왜냐하면 높이가 2일 때 구간은 결국 두 번째 선과 세 번째 선 사이인데,
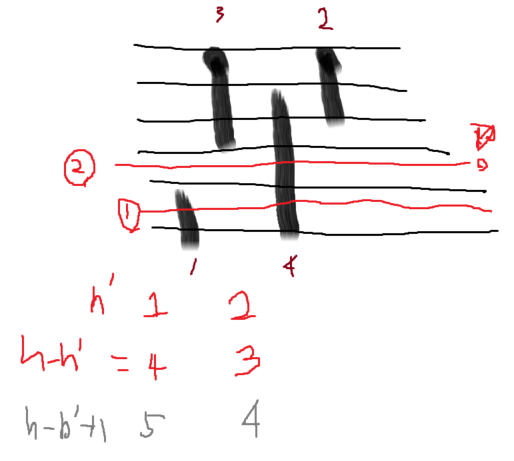
0~h를 나는 높이라고 했을 때,
석순 list에서 lower bound(x)를 구하고 , 종유석 list에서 lowerbound(h-x+1)를 구한다.
- lower bound (x) : x보다 크거나 같은 것 중 가장 작은 것의 index를 나타낸다. → 이진탐색으로 이것을 구하는 것이기 때문에 O(logn)시간이 걸린다.
- 50만 x O(logn)이기 때문에 시간복잡도에서는 문제 없을 것 같다
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main{
public static int n,h;
public static int[] low,high;
public static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static StringTokenizer st;
public static int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static int cnt=0;
public static void setting() throws IOException{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// n은 항상 짝수
int len = n/2;
low = new int[len];
high = new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
low[i] = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
high[i] = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
}
}
public static void solve(){
Arrays.sort(low);// 오름차순
Arrays.sort(high);// 오름차순
int sum=0;
int idx=0;
for(int height=1;height<=h;height++){
sum=0;
idx = lower_bound(low,height);
sum+=(low.length-idx);
idx = lower_bound(high,h-height+1);
sum+=(high.length-idx);
if(sum<min){
min=sum;
cnt=1;
}
else if(sum==min) cnt++;
}
}
// target보다 크거나 같은 것 중 가장 작은 것의 index를 리턴한다.
// 없을 경우 list.length를 리턴한다.
public static int lower_bound(int[] list,int target){
int left =0,right=list.length;
int mid = 0;
while(left<right){
mid = (left+right)/2;
if(list[mid]>=target)right = mid;
else left = mid+1;
}
return right;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
setting();
solve();
System.out.println(min+" "+cnt);
}
}다른 사람 풀이 : 누적합
높이에 따른 석순, 종유석의 개수를 저장 해 둔다.
low[h] = 개수
high[어떤h ] = 개수
그 후, 석순 리스트만일 일단 먼저 보자
6 7
1
5
3
3
5
1
인 경우 현재 석순 리스트는
h 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 0 1 0 1 0
이를 이제 누적합을 이용하면 된다.
- 석순[h]에는 이제, 높이가 h이상인 석순의 개수를 저장하면 되는 것 이다. ==⇒ 따라서 누적합을 하게 된다
- 이 때 주의할 것은, 뒤에서부터 누적을 해야한다 . 왜냐하면, h가 4인 석순은, 석순[0],석순[1],석순[2],석순[3]에 누적해야하기 때문
package coding;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main{
public static int n,h;
public static int[] low,high;
public static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static StringTokenizer st;
public static int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static int cnt=0;
public static void setting() throws IOException{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// n은 항상 짝수
int len = n/2;
low = new int[h+1];
high = new int[h+1];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
low[Integer.parseInt(br.readLine())]++;
high[Integer.parseInt(br.readLine())]++;
}
}
public static void solve() {
// 높이가 4인 종유석은 높이 1을 포함하고 있는 것이니, 뒤에서부터 누적
for(int height =h-1;height>=0;height--){
low[height]+=low[height+1];
high[height]+=high[height+1];
}
int sum=0;
for(int height=1;height<=h;height++){
sum=0;
sum+=low[height];
sum+=high[h-height+1];
if(sum<min){
min = sum;
cnt=1;
}else if(sum==min){
cnt++;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
setting();
solve();
System.out.println(min+" "+cnt);
}
}