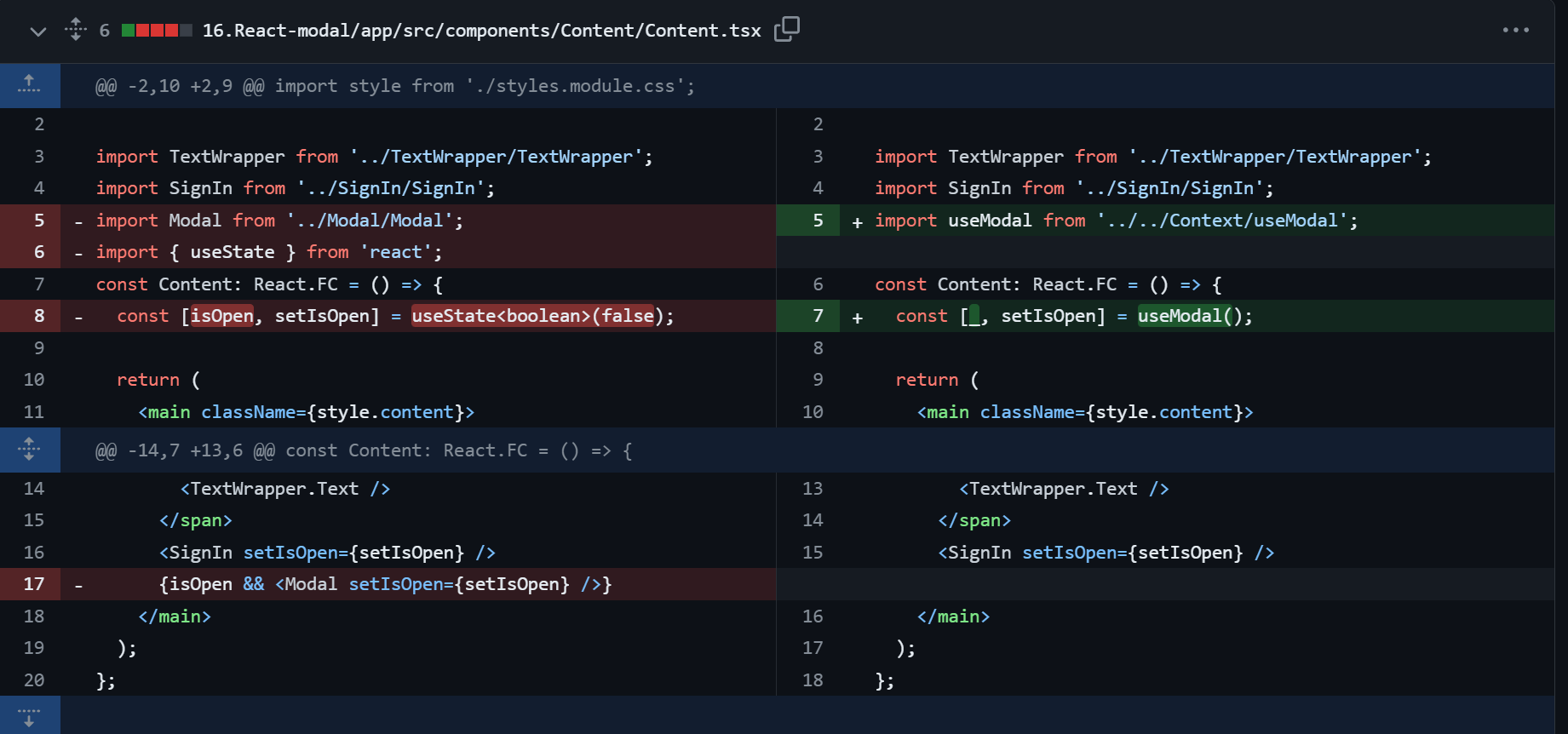
기존 Modal 기능 수정하기
이전 게시글에서 Modal 을 다음과 같이 구현해줬었다.
App
function App() {
return (
<Wrapper>
<Header />
<Content /> // Modal 을 여닫는 트리거 , 모달 렌더링 위치
</Wrapper>
);
}Content
const Content: React.FC = () => {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState < boolean > false; // 모달 제어하기 위한 state
return (
<main className={style.content}>
<span>
<TextWrapper.Title />
<TextWrapper.Text />
</span>
<SignIn setIsOpen={setIsOpen} /> // 해당 버튼이 눌리면 isOpen = true
{isOpen && <Modal setIsOpen={setIsOpen} />}
// isOpen true 일 때 Modal 컴포넌트 렌더링
</main>
);
};Modal
const Modal: React.FC<Props> = ({ setIsOpen }) => {
const formRef = useRef<HTMLFormElement>(null);
const handleSubmit = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
// Submit 을 하는 어떤 로직들 ..
setIsOpen(false);
};
const handleCancle = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
setIsOpen(false);
};
const handleClickWrapper = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLOptionElement>) => {
// 1. formRef.current 가 null 이 아니고 (mount 이후)
// 2. 눌린 e.target 이 formRef.current 내부 엘리먼트가 면
if (formRef.current && !formRef.current.contains(e.target as Node)) {
setIsOpen(false);
}
};
return (
// 전체 화면을 흐리게 만들기 위한 wrapper
<section className={style.modalWrapper} onClick={handleClickWrapper}>
// 이후 부분이 모달
<form action='/' ref={formRef}>
<div className={style.group}>
<input
type='text'
id='username'
name='username'
placeholder='아이디를 입력하세요'
/>
</div>
<div className={style.group}>
<input
type='text'
id='password'
name='password'
placeholder='비밀번호를 입력하세요'
/>
</div>
<div className={style.buttonWrapper}>
<button className={style.submit} onClick={handleSubmit}>
제출하기
</button>
<button className={style.submit} onClick={handleCancle}>
취소
</button>
</div>
</form>
</section>
);
};
다음과 같은 컴포넌트들의 조합을 통해 모달 컴포넌트를 구현해줬었다.
이렇게 하여도 기능 구현에는 전혀 문제가 없으나 몇 가지 불편한 점이 존재한다.
기존 Modal 의 문제점 찾기
Modal 컴포넌트의 올바르지 않은 의미론적 구조
const Modal: React.FC<Props> = ({ setIsOpen }) => {
/**
* 생략 ..
**/
return (
// ModalWrapper
<section className={style.modalWrapper} onClick={handleClickWrapper}>
// 실제 Modal ..
<form action='/' ref={formRef}></form>
</section>
);
};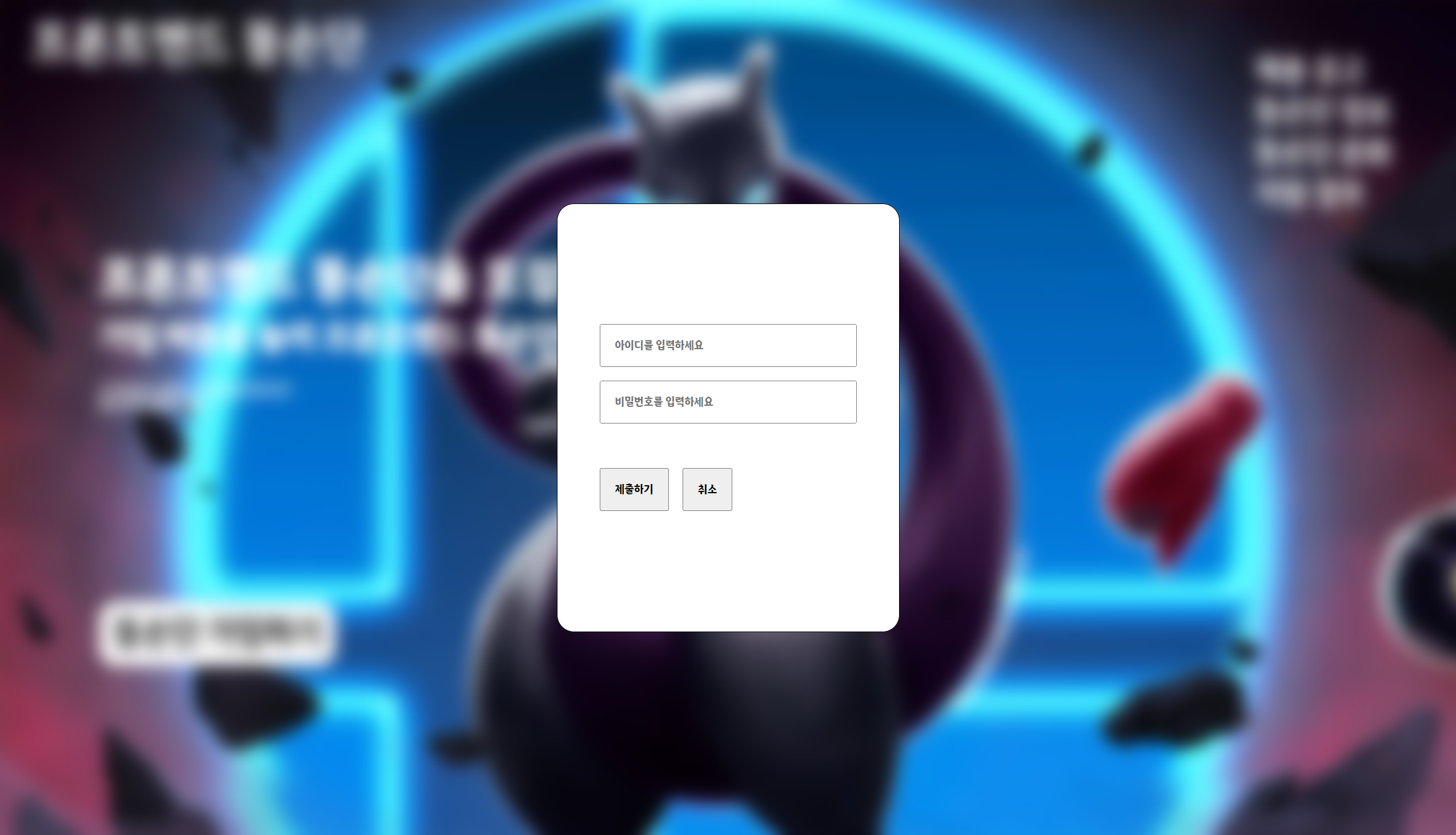
모달 컴포넌트가 반환하는 컴포넌트를 살펴보면 실제 모달에 해당하는 form 태그 외에
form 태그를 감싸고 있는 section 태그가 가장 상단에 존재한다.
이는 모달 역할을 하는 form 컴포넌트가 렌더링 될 때 주변 UI 를 흐리게 만들기 위해
뷰포트 전체를 덮는 컴포넌트가 필요했기 때문이다.
의미론적으로 이름을 좀 붙여보자면
form 태그 부분이 실제 Modal 에 해당 할 것이고
Modal 을 덮는 부모 태그인 section 태그는 모달을 감싸는 ModalWrapper 의 의미를 가지고 있다.
그렇다면 , Modal 컴포넌트에서 ModalWrapper 까지 함께 렌더링 하는 것은 의미론적으로 맞지 않는다.
또한, 현재는 모달이 1개만 존재하지만
모달이 여러개 존재 할 때 동일한 ModalWrapper 를 항상 생성해주기 위해
동일한 스타일을 갖는 section 태그를 서로 다른 모달을 생성 할 때 마다 매번 작성해야하는 비효율적인 과정이 추가된다.
Modal 이 존재하는 Content 의 올바르지 않은 의미론적 구조
const Content: React.FC = () => {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState<boolean>(false);
return (
<main className={style.content}>
<span>
<TextWrapper.Title />
<TextWrapper.Text />
</span>
<SignIn setIsOpen={setIsOpen} />
// Modal 컴포넌트는 Content 컴포넌트 내부에서 렌더링 되는게 맞을까?
{isOpen && <Modal setIsOpen={setIsOpen} />}
</main>
);
};모달의 렌더링 유무를 트리거 하는 SignIn 컴포넌트가 존재하는 Content 컴포넌트 내부에서
Modal 컴포넌트는 SignIn 에 의해 변경되는 상태값들인 isOpen , setIsOpen 에 영향을 받는다.
이로 인해 Modal 컴포넌트는 Content 컴포넌트 내부에서만 호출되어야 하는 강한 종속성을 갖게 되었다.
현재 우리는 Modal 컴포넌트를 전역적인 위치에서 띄우고 싶고 , Modal 컴포넌트가 렌더링 될 때엔
body 태그 이하에 존재하는 모든 컴포넌트의 기능을 block 하고 싶다.

빨간 영역은
Content컴포넌트의 범위
하지만 현재의 구조에서는 Content 컴포넌트와의 종속성으로 인해
우리 Modal 의 의미론적 구조에 맞지 않게 Content 컴포넌트 내부에서 호출되고 있다.
이러한 문제로 인해 전체 뷰포트를 덮는 ModalWrapper 라는 인위적인 태그를 Modal 컴포넌트 내부에서 생성해주었다.
const Modal: React.FC<Props> = ({ setIsOpen }) => {
...
return (
<section className={style.modalWrapper} onClick={handleClickWrapper}>
<form action='/' ref={formRef}></form>
</section>
);
};
ModalWrapper는width : 100vw , height : 100vh , position : fixed , top : 0px , left : 0px의 스타일 속성을 가지고 있다.
즉ModalWrapper는 뷰포트를 모두 덮는HTMLElementTag이다.
ModalWrapper덕에Modal역할을 하는form태그가 어느 컴포넌트 내부에서 호출되더라도 뷰포트 기준으로 렌더링 되게 해주었다.
이렇게 Content 컴포넌트 내부에서 뷰포트를 모두 덮는 (Content 컴포넌트 범위를 넘어가는) 인위적이고 어색한 구조는
Content 컴포넌트의 의미론적 구조 뿐 아니라 Modal 컴포넌트의 의미론적 구조 마저 이상하게 만든다.
const Content: React.FC = () => {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState<boolean>(false);
return (
<main className={style.content}>
<span>
<TextWrapper.Title />
<TextWrapper.Text />
</span>
// 모달의 렌더링을 trigger 하는 컴포넌트
<SignIn setIsOpen={setIsOpen} />
// trigger 는 Content 에서 되지만 실제 Modal 은 뷰포트를 기준으로 렌더링 됨
{isOpen && <Modal setIsOpen={setIsOpen} />}
</main>
);
};이런 어색한 구조로 인해 Content 컴포넌트 내부에 존재하는 Modal 이
Content 컴포넌트 내부에서만 렌더링 되는 모달인지, 뷰포트를 덮는 모달인지 파악 할 수 없게 되었다.
기존 Modal 의 문제점 해결하기
그럼 현재의 문제점을 제대로 정의하고 문제점을 해결해나가보자
현재의 가장 큰 문제점은 Modal 이 global 적으로 렌더링 되어야 하는데
Content 내부에 선언된 isOpen state 값에 종속되어 있어 Content 컴포넌트 내부에서만 호출되어야 한다는 점이다.
Modal 렌더링에 관여하는 state 전역적으로 선언하기
이를 해결하기 위해 Modal 컴포넌트 렌더링에 관여하는 state 를 전역적으로 관리해주도록 하자
Modal 과 관련된 state 를 전역적으로 관리해줌으로서
굳이 Modal 컴포넌트가 본인의 렌더링을 트리거하는 컴포넌트 내부에서 호출되지 않도록 하여
트리거 하는 컴포넌트와의 종속성을 끊어줄 수 있다.
여러 전역 상태 관리 라이브러리가 있지만 단순하게 Context 를 이용한다고 가정해보자
ModalContext
import { createContext, Dispatch, SetStateAction } from 'react';
type ModalContextType = [boolean, Dispatch<SetStateAction<boolean>>];
const ModalContext = createContext<ModalContextType>([false, () => {}]);
export default ModalContext;다음과 같이 Modal 의 상태를 저장할 Context 인 ModalContext 를 생성해준다.
이후 ModalContext 를 이용한 컴포넌트인 ModalProvider 와 useModal 커스텀 훅을 생성해주도록 하자
ModalProvider
import ModalContext from './Context';
type Props = {
children: ReactNode;
};
const ModalProvider: React.FC<Props> = ({ children }) => {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState<boolean>(false); // 전역적으로 관리될 state 생성
return (
<ModalContext.Provider value={[isOpen, setIsOpen]}>
{children}
</ModalContext.Provider>
);
};useModal
import { useContext, Dispatch, SetStateAction } from 'react';
import ModalContext from './Context';
type ModalContextType = [boolean, Dispatch<SetStateAction<boolean>>];
const useModal = (): ModalContextType => {
const [open, setIsOpen] = useContext(ModalContext);
return [open, setIsOpen];
};
export default useModal;이제 Context 가 전달하는 value 값들을 받기 위한 커스텀 훅을 생성해주자
useModal 은 ModalContext 가 전달하는 value 값들을 반환하는 useContext 를 캡슐화 한 훅이다.
function App() {
return (
<ModalProvider>
// 이제 [isOpen , setIsOpen] 은 전역적으로 사용 가능하게 되었다. //
useModal 훅을 이용해 모달을 렌더링 하기 위한 상태 값을 변경 할 수 있다.
<Wrapper>
<Header />
<Content />
</Wrapper>
</ModalProvider>
);
}전역적으로 관리되는 Modal 을 렌더링 할 영역 생성하기
GlobalModalWrapper
import useModal from '../../Context/useModal';
import Modal from '../Modal/Modal';
import style from './style.module.css';
const visibleStyle = {
display: 'flex',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
};
const inVisibleStyle = {
display: 'none',
};
const GlobalModalWrapper: React.FC = () => {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useModal();
const handleClickWrapper = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLOptionElement>) => {
setIsOpen(false);
};
return (
<section
className={style.global}
style={isOpen ? { ...visibleStyle } : { ...inVisibleStyle }}
onClick={handleClickWrapper}
>
{isOpen && <Modal />}
</section>
);
};
export default GlobalModalWrapper;.global {
position: absolute;
z-index: 999;
top: 0px;
left: 0px;
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
background-color: inherit;
backdrop-filter: blur(20px);
}다음과 같이 전역에서 모달을 띄울 GlobalModalWrapper 컴포넌트를 생성해준다.
GlobalModalWrapper 내부에는 전역적으로 생성될 Modal 들을 감싸고 있는 랩퍼 컴포넌트이다.
해당 랩퍼 컴포넌트는 isOpen 이 true 일 때만 렌더링 노드에 추가 되는 컴포넌트이며
모달의 상태에 관여하는 isOpen 값이 true 일 때에만 렌더링 된다.
App.tsx
import './App.css';
import ModalProvider from './Context/Provider';
import Wrapper from './components/Wrapper/Wrapper';
import Header from './components/Header/Header';
import Content from './components/Content/Content';
import GlobalModalWrapper from './components/GlobalModalWrapper/GlobalModalWrapper';
function App() {
return (
<ModalProvider>
<Wrapper>
<Header />
<Content /> // 모달을 트리거 하는 영역
<GlobalModalWrapper /> // 모달을 렌더링 하는 영역
</Wrapper>
</ModalProvider>
);
}
역역;
export default App;이후 다음과 같이 엔트리 파일에 GlobalModalWrapper 컴포넌트를 추가해줌으로서
모달 렌더링을 트리거 하는 영역과 모달을 렌더링 하는 영역을 분리해준다.
기존 Modal 컴포넌트 수정하기
import style from './styles.module.css';
import useModal from '../../Context/useModal';
const Modal: React.FC = () => {
// const formRef = useRef<HTMLFormElement>(null); 불필요하기에 제거
const [_, setIsOpen] = useModal();
/**
* 생략
**/
const stopPropoation = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLFormElement>) => {
e.stopPropagation();
};
return (
<form action='/' ref={formRef} onClick={stopPropoation}>
// ... 생략
</form>
);
};
export default Modal;이후 기존 Modal 컴포넌트에서 인위적으로 생성해두었던 section 태그를 제거해주고
모달 자체에 e.stopPropagation 을 추가해줌으로서
GlobalModalWrapper 내에서의 클릭 이벤트 (isOpen 을 false 로 변경하는 ) 가 모달에 전파되지 않도록 수정해준다.
수정된 부분 평가
이렇게 수정함으로서 이전과 무엇이 달라졌을까 ?
Content 컴포넌트 수정사항
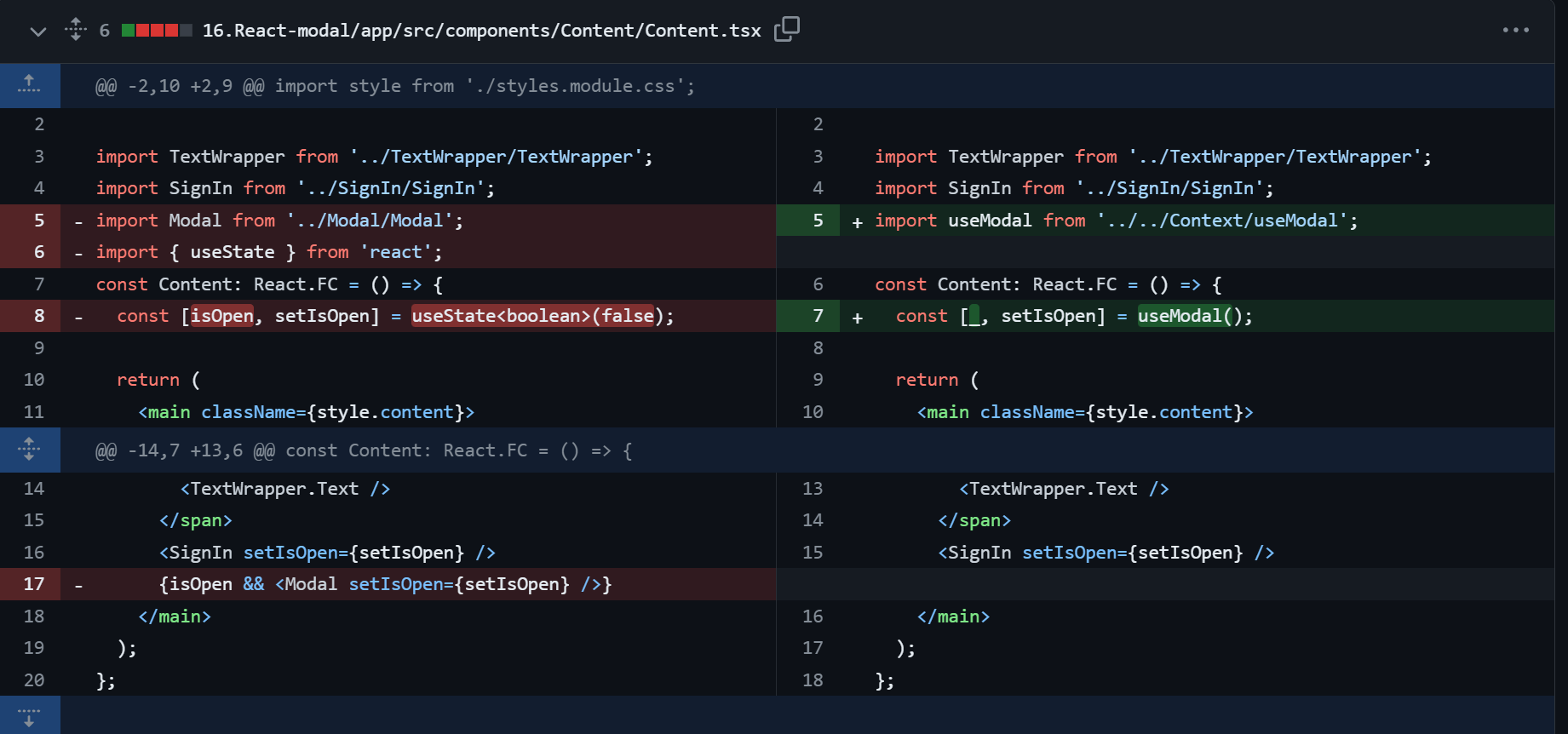
이전과 다르게 Content 컴포넌트에서 Modal 컴포넌트가 제거되어
Content 컴포넌트의 역할이 명확히 된 모습을 볼 수 있다.
이전 Content 의 영역은 Modal 이 렌더링 되게 trigger 시킬 뿐 아니라
Modal 컴포넌트를 렌더링 하는 역할을 하고 있었다.
심지어
Content컴포넌트 이외의 영역에Modal을 렌더링 시키기 위해 뷰포트만한ModalWrapper로 감싸져있는Modal을 렌더링 하는 어색한 구조의Modal컴포넌트를 말이다.
하지만 수정된 이후의 Conten의 컴포넌트는 Modal 컴포넌트를 trigger 하는 컴포넌트를 담은
본인만의 역할에 집중 할 수 있도록 수정되었다.
Modal 컴포넌트 수정사항
Modal 컴포넌트에선 어떤 부모 컴포넌트 내부에서 렌더링 되지 않고 뷰포트 내에서 생성되게 하기 위해 만들었던
section className= {style.modalWrapper} 태그가 사라졌다.
더이상 Modal 컴포넌트는 더이상 본인을 trigger 시키는 컴포넌트 내에서 렌더링 되는 것이 아니라
뷰포트 크기의 랩퍼 컴포넌트 내부에서만 렌더링 되기 때문이다.
확장성은 어떤데 ?
만약 전역적으로 렌더링 되어야 하는 모달이 더 추가되었다고 가정해보자
const GlobalModalWrapper: React.FC = () => {
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useModal();
const [isOpen2, setIsOpen2] = useModal2(); // 두 번째 모달이 생성되었다고 가정
const handleClickWrapper = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLOptionElement>) => {
setIsOpen(false);
setIsOpen2(false);
};
// 모달이 하나라도 열린게 있는지 확인하는 boolean
const isModalsOpen = [isOpen, isOpen2].reduce((pre, cur) => pre + cur);
return (
<section
className={style.global}
style={isModalsOpen ? { ...visibleStyle } : { ...inVisibleStyle }}
onClick={handleClickWrapper}
>
{isOpen && <Modal />}
{isOpen2 && <Modal2 />} // 추가된 Modal 렌더링
</section>
);
};그럴 경우엔 다음과 같이 단순하게 GlobalModalWrapper 내부에서 모달을 추가해주기만 하면 된다.
이렇게 전역적으로 생성되는 Modal 들을 GlobalModalWrapper 내부에서 중앙 집권화 하여 관리해줌으로서
전역적으로 생성되는 Modal 을 관리해주는 것도 더 간편해졌다.
