대부분의 내용은 리액트 깃허브의 코드와 챗지피티와 씨름하며 공부한 내용이기에
추가로 공부하면서 정정되는 내용들이 있을 수 있어 부정확 할 수 있습니다
이번 파트를 공부하면서 해당 아티클에서 많은 도움을 받았습니다.
정말 좋은 아티클이니 제 글보다 더 도움이 될 수 있습니다 !!
ReactElement Recap
이전 docs 에서 리액트에서 JSX 는 Babel 을 통해
createElement 메소드로 변경해 ReactElement 를 생성한다는 것을 배웠다.
이렇게 생성된 ReactElement 들은 type ,key , props 등에 대한 정보를 담고 있다.
react/src/jsx/ReactJSXElement
function ReactElement(type, key, _ref, self, source, owner, props) {
let ref;
if (enableRefAsProp) {
const refProp = props.ref;
ref = refProp !== undefined ? refProp : null;
} else {
ref = _ref;
}
// ... 여러 부분 생략
element = {
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE, // Symbol 객체
type,
key,
ref,
props,
};
}
return element;
}ReactElement 에서 $$typeof 에 들어가는 REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE 심볼 객체는 다음과 같이 정의되어 있다.
shared/ReactSymbol
...
export const REACT_LEGACY_ELEMENT_TYPE: symbol = Symbol.for('react.element');
export const REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE: symbol = renameElementSymbol
? Symbol.for('react.transitional.element')
: REACT_LEGACY_ELEMENT_TYPE;
...shared/ReactFlags
...
// Renames the internal symbol for elements since they have changed signature/constructor
export const renameElementSymbol = true;
...실제로도 그런지 확인해보자
const FirstComponent = ({ content }: { content: string }) => {
return <h1>{content}</h1>;
};
const SecondComponent = ({ text }: { text: string }) => {
return <h2>{text}</h2>;
};
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<FirstComponent content='하이~!' />
<SecondComponent text='방가루' />
</div>
);
};
console.log(App());
export default App;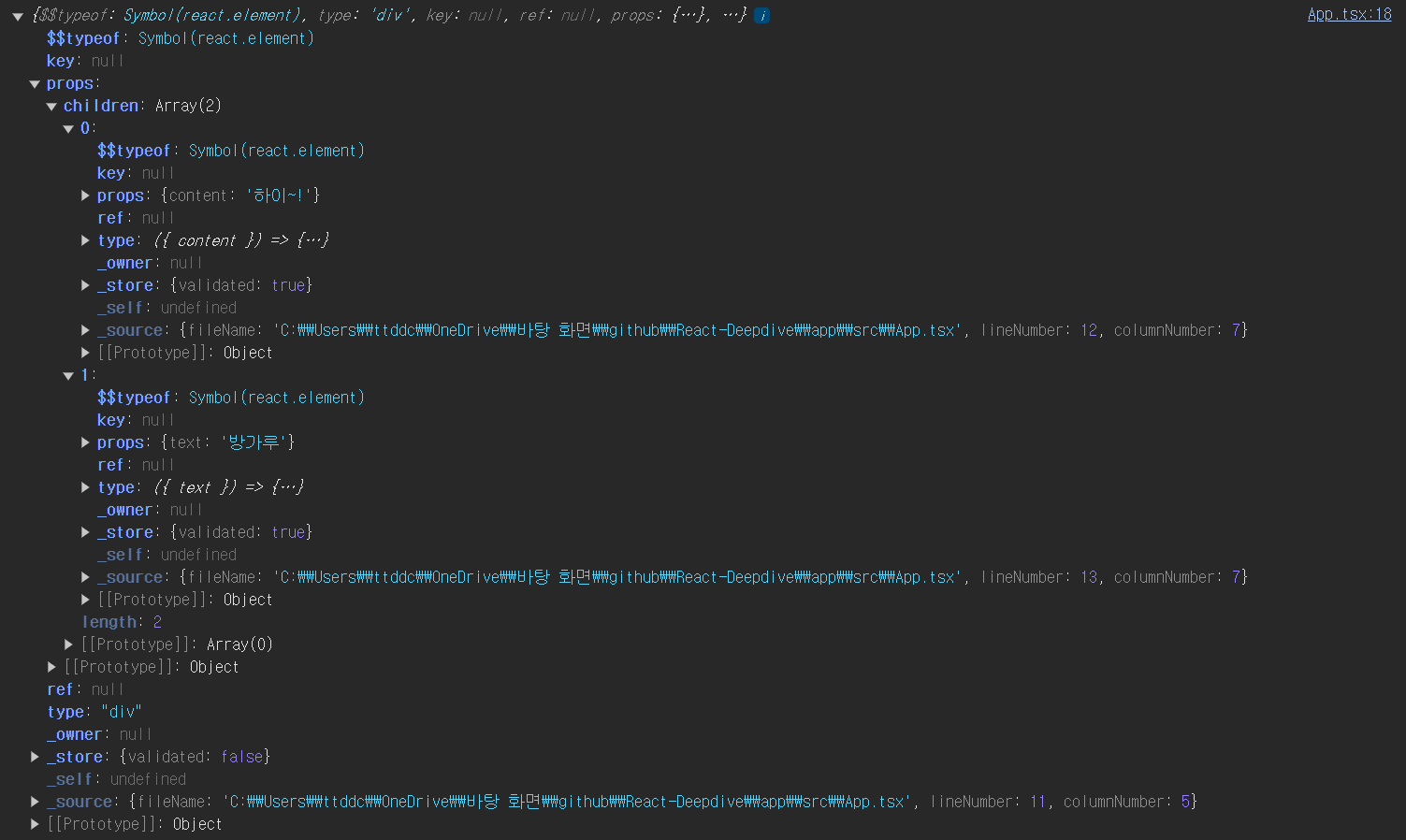
흠 .. typeof 는 Symbol(react.element) 이다. 기존 코드에선 Symbol.for('react.transitional.element') 이 값이 될줄 알았는데
빌드 될 떄의 설정값이 다른지 Symbol(react.element) 로 나온다. 뭐 어쨌든 ~!
간략하게 살펴보는 Virtaul DOM
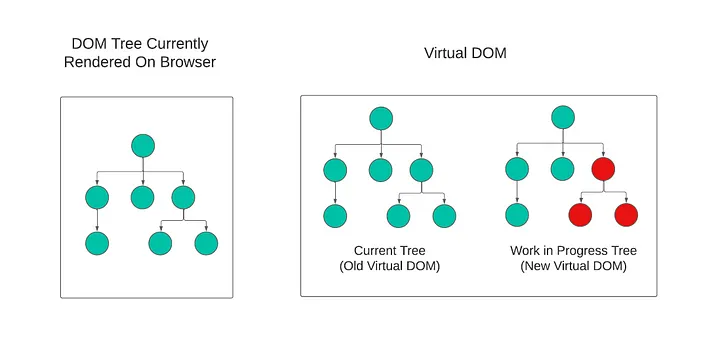
리액트를 배우기 시작하면 중요한듯 다뤄지는 이야기가 아마 Virtual DOM 일 것이다.
리액트는 Actual DOM 의 모습과 동기화되는 자바스크립트 객체인 Virtual DOM 을 생성하며
해당 Virtual DOm 을 current Tree 혹은 current 라고 한다.
Virtual DOM 의 모습은 JSX-> ReactElement 로 생성되는 트리의 구조와 유사하다.
유사하다고 한 이유는 트리의 구조는 같지만 내부
Node들은ReactElement로 이뤄져있지 않기 때문이다.
이 때 만약 컴포넌트의 상태가 변경되거나 렌더링 하기 위해 받는 값이 변경되어 컴포넌트의 변경이 일어나게 된다면
리액트는 current Tree 객체를 복사한 WorkinProgress Tree 를 생성하고
생성된 WorkinProgress Tree 를 순회하며 업데이트 될 내용을 확인하며 업데이트가 필요한 노드는 업데이트하여 새로운 노드로 생성한다.
순회가 종료되어 current 에서 업데이트가 된 WorkinProgress Tree 를 current Tree 로 지정하며
(여기까지가 render phase , 이후는 commit phase)
새롭게 변경된 current Tree 에서 변경된 사항을 Actual DOM 에 적용시킨다.
용어 정리
current , WorkinProgress와 같이 두 가지의Virtual DOM을 이용하는 이런 시스템을double buffer라고 한다.
Virtual DOM 의 Node 는 그럼 무엇일까 ?
위에서 리액트는 JSX 를 통해 ReactElement 를 만들고 트리구조인
Virtual DOM 인 current Tree 를 생성한다고 하였다.
그럼 문득 궁금해진다. current Tree 혹은 WorkinProgress Tree 들의 Node 는 어떻게 생겼을까 ?
ReactElement 일까 ?
그렇지 않다.
/* reactElement 의 예시 */
{
"type": Container,
"props": {
"children": {
"type": Title,
"props": {
"text": "Hello~!",
"children": null
},
"key": null,
"ref": null
}
},
"key": null,
"ref": null
}리액트에 존재하는 다양한 컴포넌트의 종류들을 담기에는 ReactElement.$$typeof 는 고작 심볼 객체 하나뿐이고
컴포넌트 내부에 정의된 state 와 같은 상태값을 저장하는 프로퍼티도 존재하지 않는다.
이에 리액트는 복잡한 정보들을 담기 위해 ReactElement 를 이용해 Fiber 라는 객체를 만들어 사용한다.
즉 , Virtual DOM 의 node 는 Fiber 이다.
Fiber Node 를 만들기 위한 여정
react-reconciler/src/ReactFiber.js
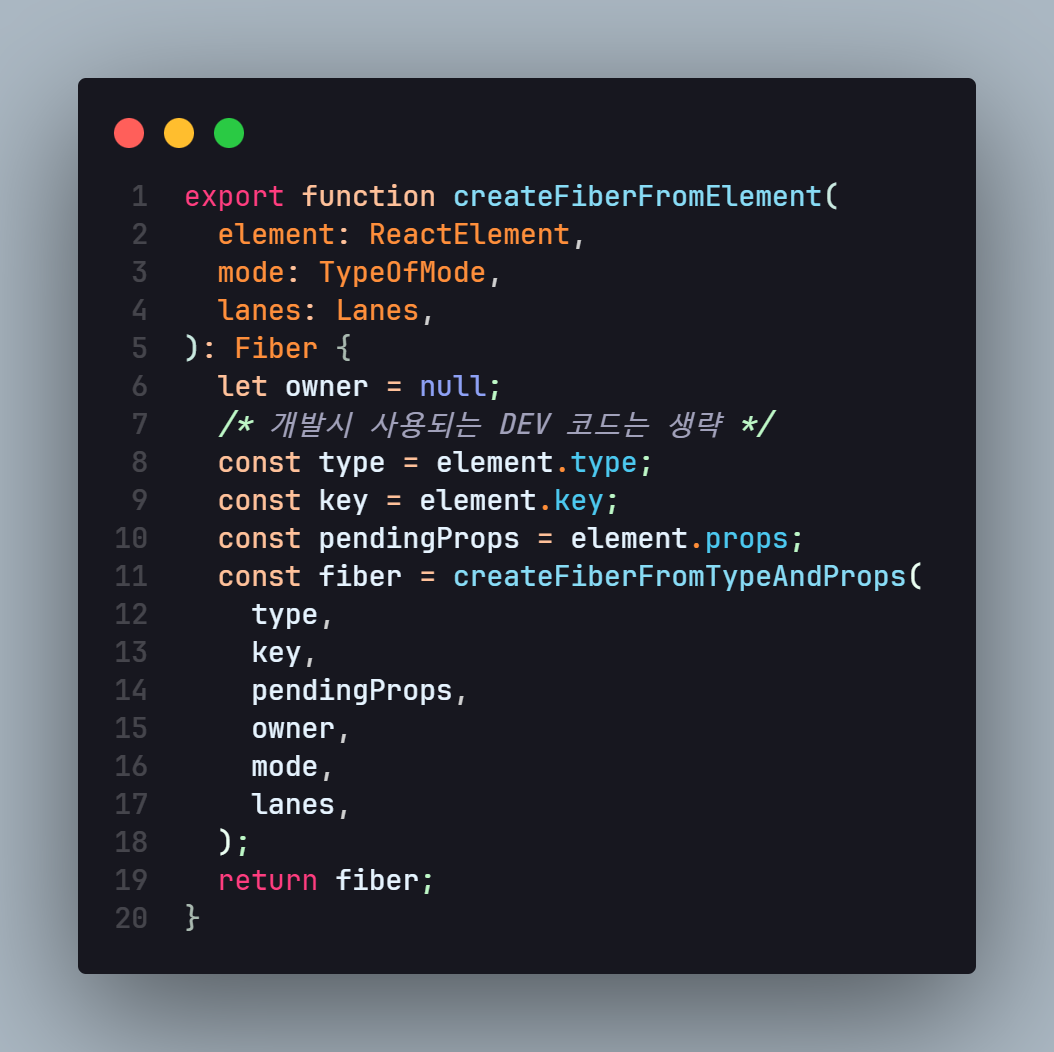
createFibberFromElement
export function createFiberFromElement(
element: ReactElement,
mode: TypeOfMode,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber {
let owner = null;
/* 개발시 사용되는 DEV 코드는 생략 */
const type = element.type;
const key = element.key;
const pendingProps = element.props;
const fiber = createFiberFromTypeAndProps(
type,
key,
pendingProps,
owner,
mode,
lanes,
);
return fiber;
}reconiler 패키지를 살펴보면 다음과 같이 ReactElement 를 받아 Fiber 를 생성하는 함수를 볼 수 있다.
ReactElement 내부에 존재하는 type , key , pendingProps 를 받은 후
createFiberFromTypeAndProps 함수를 이용해 Fiber 객체를 생성후 반환한다.
아직 Fiber 가 뭔지 createFiberFromTypeAndProps 뭔지는 모르지만
ReactElement 가 Fiber 객체로 변경되는 모습은 볼 수 있다.
createFiberFromTypeAndProps
export function createFiberFromTypeAndProps(
type: any, // React$ElementType
key: null | string,
pendingProps: any,
owner: null | ReactComponentInfo | Fiber,
mode: TypeOfMode,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber {
let fiberTag = FunctionComponent;
// The resolved type is set if we know what the final type will be. I.e. it's not lazy.
let resolvedType = type;
if (typeof type === 'function') {
if (shouldConstruct(type)) {
fiberTag = ClassComponent;
}
} else if (typeof type === 'string') {
if (supportsResources && supportsSingletons) {
const hostContext = getHostContext();
fiberTag = isHostHoistableType(type, pendingProps, hostContext)
? HostHoistable
: isHostSingletonType(type)
? HostSingleton
: HostComponent;
} else if (supportsResources) {
const hostContext = getHostContext();
fiberTag = isHostHoistableType(type, pendingProps, hostContext)
? HostHoistable
: HostComponent;
} else if (supportsSingletons) {
fiberTag = isHostSingletonType(type) ? HostSingleton : HostComponent;
} else {
fiberTag = HostComponent;
}
} else {
getTag: switch (type) {
case REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE:
return createFiberFromFragment(pendingProps.children, mode, lanes, key);
case REACT_STRICT_MODE_TYPE:
fiberTag = Mode;
mode |= StrictLegacyMode;
if (disableLegacyMode || (mode & ConcurrentMode) !== NoMode) {
// Strict effects should never run on legacy roots
mode |= StrictEffectsMode;
if (
enableDO_NOT_USE_disableStrictPassiveEffect &&
pendingProps.DO_NOT_USE_disableStrictPassiveEffect
) {
mode |= NoStrictPassiveEffectsMode;
}
}
break;
case REACT_PROFILER_TYPE:
return createFiberFromProfiler(pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
case REACT_SUSPENSE_TYPE:
return createFiberFromSuspense(pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
case REACT_SUSPENSE_LIST_TYPE:
return createFiberFromSuspenseList(pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
case REACT_OFFSCREEN_TYPE:
return createFiberFromOffscreen(pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
case REACT_LEGACY_HIDDEN_TYPE:
if (enableLegacyHidden) {
return createFiberFromLegacyHidden(pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
}
// Fall through
case REACT_SCOPE_TYPE:
if (enableScopeAPI) {
return createFiberFromScope(type, pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
}
// Fall through
case REACT_TRACING_MARKER_TYPE:
if (enableTransitionTracing) {
return createFiberFromTracingMarker(pendingProps, mode, lanes, key);
}
// Fall through
case REACT_DEBUG_TRACING_MODE_TYPE:
if (enableDebugTracing) {
fiberTag = Mode;
mode |= DebugTracingMode;
break;
}
// Fall through
default: {
if (typeof type === 'object' && type !== null) {
switch (type.$$typeof) {
case REACT_PROVIDER_TYPE:
if (!enableRenderableContext) {
fiberTag = ContextProvider;
break getTag;
}
// Fall through
case REACT_CONTEXT_TYPE:
if (enableRenderableContext) {
fiberTag = ContextProvider;
break getTag;
} else {
fiberTag = ContextConsumer;
break getTag;
}
case REACT_CONSUMER_TYPE:
if (enableRenderableContext) {
fiberTag = ContextConsumer;
break getTag;
}
// Fall through
case REACT_FORWARD_REF_TYPE:
fiberTag = ForwardRef;
if (__DEV__) {
resolvedType = resolveForwardRefForHotReloading(resolvedType);
}
break getTag;
case REACT_MEMO_TYPE:
fiberTag = MemoComponent;
break getTag;
case REACT_LAZY_TYPE:
fiberTag = LazyComponent;
resolvedType = null;
break getTag;
}
}
let info = '';
throw new Error(
'Element type is invalid: expected a string (for built-in ' +
'components) or a class/function (for composite components) ' +
`but got: ${type == null ? type : typeof type}.${info}`,
);
}
}
}
const fiber = createFiber(fiberTag, pendingProps, key, mode);
fiber.elementType = type;
fiber.type = resolvedType;
fiber.lanes = lanes;
return fiber;해당 함수를 보면 매우 길고 복잡해보이지만 중요한 점만 찝어서 살펴보자
코드 초반에 존재하는 로직들은 모두 fiberTag 를 구하기 위한 로직들이다.
리액트에서 사용하는
fiberTag들은 글 하단에 첨부하도록 한다.
만약 type 이 문자일 경우 (div , h1 , span .. etc) 엔 내부 다양한 함수 로직을 통해 HostComponent 태그를 갖게 되고
함수일 경우엔 FunctionComponent 등의 값이 태그로 부착된다.
이후 만약 tag 가 필요 없는 경우엔 tag 없이 Fiber 노드를 생성하여 반환하고
tag 가 필요한 경우 코드 마지막 부분에 존재하는
export function createFiberFromTypeAndProps(
type: any, // React$ElementType
key: null | string,
pendingProps: any,
owner: null | ReactComponentInfo | Fiber,
mode: TypeOfMode,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber {
...
const fiber = createFiber(fiberTag, pendingProps, key, mode);
fiber.elementType = type;
fiber.type = resolvedType;
fiber.lanes = lanes;
return fiber;
}와 같이 fiberTag 를 이용해 createFiber 함수를 실행하고 생성된 fiber 객체를 반환한다.
정리
내용이 너무 복잡하기 때문에 정리하자
Virtual DOM의node가 되는Fiber는createFiberFromElement를 통해 생성된다.
이 때Element.type에 따라 다양한fiberTag가 생성되고
fiberTag를 인수로 받는createFiber함수를 실행하여fiber객체를 반환한다.
createFiber
function createFiber(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
): Fiber {
// $FlowFixMe[invalid-constructor]: the shapes are exact here but Flow doesn't like constructors
return new FiberNode(tag, pendingProps, key, mode);
}createFiber 는 단순이 인수들을 받아 new FiberNode 를 이용해 fiber 객체를 생성하여 반환한다.
그럼 반환하는 fiber 가 어떻게 생겼는지만 안다면 우리는 Virtual DOM 의 node 가 어떻게 생겼는지를 알 수 있다.
⭐ FiberNode 드디어 발견
function FiberNode(
this: $FlowFixMe,
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
) {
// Instance
this.tag = tag; /* ReactFiberFlags 의 Tag 가 부착 */
this.key = key;
this.elementType = null;
this.type = null;
this.stateNode = null;
// Fiber
this.return = null;
this.child = null;
this.sibling = null;
this.index = 0;
this.ref = null;
this.refCleanup = null;
this.pendingProps = pendingProps;
this.memoizedProps = null;
this.updateQueue = null;
this.memoizedState = null;
this.dependencies = null;
this.mode = mode;
// Effects
this.flags = NoFlags;
this.subtreeFlags = NoFlags;
this.deletions = null;
this.lanes = NoLanes;
this.childLanes = NoLanes;
this.alternate = null;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
// Note: The following is done to avoid a v8 performance cliff.
//
// Initializing the fields below to smis and later updating them with
// double values will cause Fibers to end up having separate shapes.
// This behavior/bug has something to do with Object.preventExtension().
// Fortunately this only impacts DEV builds.
// Unfortunately it makes React unusably slow for some applications.
// To work around this, initialize the fields below with doubles.
//
// Learn more about this here:
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/14365
// https://bugs.chromium.org/p/v8/issues/detail?id=8538
this.actualDuration = Number.NaN;
this.actualStartTime = Number.NaN;
this.selfBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
this.treeBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
// It's okay to replace the initial doubles with smis after initialization.
// This won't trigger the performance cliff mentioned above,
// and it simplifies other profiler code (including DevTools).
this.actualDuration = 0;
this.actualStartTime = -1;
this.selfBaseDuration = 0;
this.treeBaseDuration = 0;
}
}Fiber 노드를 보면 ReactElement 때와 다르게 수많은 프로퍼티들을 갖고 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
몇 가지 값은 ReactElement 의 값을 그대로 받아 쓰거나 대부분 Null 값으로 선언되어 있는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
아무래도 초기 생성 이후 Fiber 들의 프로퍼티를 설정해주는 것은 다른 메소드들이 해주는듯 싶다.
다만 각 프로퍼티들이 갖는 의미들을 여러 블로그와 지피티를 통해 찾아와봤다.
Fiber 의 다양한 프로퍼티들이 갖는 의미
Fiber / instance
this.tag = tag; /* ReactFiberFlags 의 Tag 가 부착 */
this.key = key;
this.elementType = null;
this.type = null;
this.stateNode = null;해당 프로퍼티들은 Fiber 인스턴스가 가지고 있을 정보들을 의미한다.
대부분의 값들은 ReactElement 에서 전달 받은 값이 부착되며
stateNode 는 해당 Fiber 가 가리키는 실제 인스턴스인 DOM 또는 클래스형 컴포넌트의 인스턴스 , null 등의 값이 담긴다.
Fiber / Fiber
this.return = null; // 부모 노드
this.child = null; // 첫 번째 자식 노드
this.sibling = null; // 다음 형제 노드
this.index = 0; // 형제 노드들 사이에서의 위치
// 참조 관련 속성
this.ref = null; // ref 속성
this.refCleanup = null; // ref가 해제될 때 실행되는 정리 함수
// Props 및 State 관련 속성
this.pendingProps = pendingProps; // 최신의 아직 적용되지 않은 props
this.memoizedProps = null; // 이미 렌더링된 이전의 props
this.memoizedState = null; // 이미 렌더링된 이전의 state
this.updateQueue = null; // 업데이트가 대기 중인 작업들의 큐
this.dependencies = null; // 컨텍스트나 기타 의존성
// 기타 속성
this.mode = mode; // 현재 작동 모드return , child , sibling 값은 해당 노드의 부모노드 , 자식노드 , 형제노드를 가리키는 포인터 값이다.
각 Fiber 들은 단방향 연결리스트 형태로 연결되어 있다.
이러한 단방향 연결리스트 형태는 Virtual DOM 을 순회할 때 빠르게 순회하는 것을 가능하게 한다.
이후 현재 props 를 담는 pendingProps 와 memoized 된 props , state 값을 담고 있는 memoizedProps , memoizedState 프로퍼티 와
Fiber 에서 실행되어야 할 작업들을 담는 updateQueue , 의존성이 담긴 dependencies 등이 존재한다.
updateQueue
updateQueue 는 연결 리스트 형태로 존재하며 만약 해당 Fiber 가 가리키는 Component 의 상태가 업데이트 되거나 재렌더링 되어야 한다면
updateQueue 에 연결리스트 형태로 추가된다.
dependencies
디펜던시는 해당 Fiber 와 의존성을 가지고 있는 값이 Map 형태로 저장되며
주로 해당 Fiber 가 구독하고 있는 Context (리렌더링을 야기하는 상태 값) 나
해당 Fiber 의 리렌더링을 트리거 하는 경우들이 저장되어 있다.
Fiber 는 작업 단위이다 ?
// Effects
this.flags = NoFlags;
this.subtreeFlags = NoFlags;
this.deletions = null;Fiber 는 본인에게 일어날 업데이트 뿐 아니라 자식 노드들에서 일어날 작업들을 flags , subtreeFlags 에 저장한다.
Effects 라 표현되어 있는 것은 변경 이후 해당 Fiber 에 일어날 영향을 저장하는 것으로
결국 Fiber 들은 본인과 , 본인을 포함한 자식 노드들에게 일어날 작업들을 저장하고 있다.
비트 연산자를 이용하여 작업 단위를 저장한다.
react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberFlags.js
export type Flags = number;
// Don't change these values. They're used by React Dev Tools.
export const NoFlags = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000;
export const PerformedWork = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000001;
export const Placement = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000010;
export const DidCapture = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000010000000;
export const Hydrating = /* */ 0b0000000000000001000000000000;
// You can change the rest (and add more).
export const Update = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000100;
/* Skipped value: 0b0000000000000000000000001000; */
export const ChildDeletion = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000010000;
export const ContentReset = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000100000;
export const Callback = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000001000000;
/* Used by DidCapture: 0b0000000000000000000010000000; */
export const ForceClientRender = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000100000000;
export const Ref = /* */ 0b0000000000000000001000000000;
export const Snapshot = /* */ 0b0000000000000000010000000000;
export const Passive = /* */ 0b0000000000000000100000000000;
/* Used by Hydrating: 0b0000000000000001000000000000; */
export const Visibility = /* */ 0b0000000000000010000000000000;
export const StoreConsistency = /* */ 0b0000000000000100000000000000;
...flag 들은 다음과 같이 비트형태로 저장된 값을 이용한다.
그럼 의문이 든다. 왜 비트 형태로 저장할까 ?
flag 등을 추가하는 나중에 다룰 함수를 살펴보자
function completeWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes) {
// 하위 노드의 작업을 마치고 현재 노드의 작업을 완료
const newFlags = workInProgress.flags | workInProgress.subtreeFlags;
// 부모 노드의 subtreeFlags에 현재 노드의 flags를 추가
let parent = workInProgress.return;
if (parent !== null) {
parent.subtreeFlags |= newFlags;
}
}|= 연산자를 이용해 본인의 flag 뿐 아니라 부모 Fiber 의 flag 에도 플래그를 추가해주고 있는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
if (flags & Placement) {
console.log('Placement 플래그가 설정되어 있습니다.');
}
if (flags & Update) {
console.log('Update 플래그가 설정되어 있습니다.');
}플래그를 비트 연산자로 관리해주면 플래그에서 특정한 작업이 있는지를 아주 빠르게 확인 할 수 있으며
flags &= ~Placement;플래그들에서 어떤 플래그를 제거하는 것도 매우 빠르게 하는 것이 가능하다.
그럼 Flag 들을 저장하고 있는 것이 어떤 도움이 되는데 ?
추후 나올 내용이지만 컴포넌트에 re-render 가 일어나 Virtual DOM 을 새로 생성 할 때
Virtual DOM 을 순회하며 업데이트가 일어날 노드의 flag 에 일어날 업데이트들을 추가하고
부모 노드의 subtree flag 에도 같은 업데이트들을 추가한다.
이렇게 설정된 flag 들은 추후 commit phase 에서 actual dom 에 변화를 줄 때
브라우저상에 렌더링 될 항목들을 결정하는 지표가 된다.
또 부모 노드에서 자식 노드들의 작업 단위를 subtree flags 로 관리함으로서
Virtual DOM 을 순회 할 때 순회하지 않아도 될 항목을 불필요하게 순회 할 필요가 없게 만든다.
부록
ReactFiberFlags
ReactWorkTags
fiberTag 는 다음과 같은 값들을 가질 수 있다.
export type WorkTag =
| 0
| 1
| 2
| 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
| 12
| 13
| 14
| 15
| 16
| 17
| 18
| 19
| 20
| 21
| 22
| 23
| 24
| 25
| 26
| 27
| 28;
export const FunctionComponent = 0;
export const ClassComponent = 1;
export const HostRoot = 3; // Root of a host tree. Could be nested inside another node.
export const HostPortal = 4; // A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer.
export const HostComponent = 5;
export const HostText = 6;
export const Fragment = 7;
export const Mode = 8;
export const ContextConsumer = 9;
export const ContextProvider = 10;
export const ForwardRef = 11;
export const Profiler = 12;
export const SuspenseComponent = 13;
export const MemoComponent = 14;
export const SimpleMemoComponent = 15;
export const LazyComponent = 16;
export const IncompleteClassComponent = 17;
export const DehydratedFragment = 18;
export const SuspenseListComponent = 19;
export const ScopeComponent = 21;
export const OffscreenComponent = 22;
export const LegacyHiddenComponent = 23;
export const CacheComponent = 24;
export const TracingMarkerComponent = 25;
export const HostHoistable = 26;
export const HostSingleton = 27;
export const IncompleteFunctionComponent = 28;