http://bysql.net/index.php?mid=w201201s&page=2&document_srl=24314
http://www.gurubee.net/lecture/2393
⭐️ 성능튜닝의 3대 요소 ⭐️
- sql파싱부하해소
- 데이터베이스 call최소화
- I/O효율화
[1] 데이터베이스 Call 종류
(1) SQL 커서에 대한 작업 요청에 따른 구분
- Parse Call : SQL 파싱을 요청하는 Call
- 소프트 파싱 : SQL과 실행계획을 캐시에서 찾아 곧바로 실행단계로 넘어가는 경우를 말함.
- 하드 파싱 : SQL과 실행계획을 캐시에서 찾지 못해 최적화 과정을 거치고 나서 실행단계로 넘어가는 경우를 말함. - Execute Call : SQL 실행을 요청하는 Call
- Fetch Call
- SELECT 문의 결과 데이터 전송을 요청하는 Call
- SELECT문의 결과 데이터 전송을 요청하는 Call
- ⭐️ INSERT , UPDATE , DELETE 문장에서는 fetch call이 전혀 일어나지 않음
- ⭐️ SELECT ~ GROUP BY 절인 경우 GROUP BY 절은 fetch call 단계에서 일어난다.(메모리에서 작업하니깐 그런듯)
1. 실행계획 보기
-- DB Call 실행계획 분석 :: 정렬 연산에 대한 정보는 알 수 없다.
select cust_nm, birthday from customer where cust_id = :cust_id
call count cpu elapsed disk query current rows
----- ------ ----- ------- ---- ----- ------ -----
Parse 1 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0
Execute 5000 0.18 0.14 0 0 0 0
Fetch 5000 0.21 0.25 0 20000 0 50000
----- ------ ----- ------- ---- ----- ------ -----
total 10001 0.39 0.40 0 20000 0 50000 - count : Parse, Execute, Fetch 각 단계가 수행된 횟수
- cpu : 현재 커서가 각 단계에서 사용한 cpu time
- elapsed : 현재 커서가 각 단계를 수행하는데 소요된 시간.
- disk : 디스크를 읽은 블록수
- query : consistent 모드에서 읽은 버퍼 블록 수 . (consistent gets)
- Current : Current 모드에서 읽은 버퍼 블록수. (physical reds)
(2) Call 발생 위치에 따른 구분
1. User Call
- DBMS로부터 요청되는 Call
- User Call이 많으면 성능이 좋을수 없으므로, DBMS 확장성을 높이려면 User Call을 최소화 하려는 노력이 중요함
- 동시 접속자 수가 많은 Peak 시간대에 시스템 확장성을 떨어뜨리는 가장 큰 요인 중 한 가지이다.
- User Call이 많이 발생하도록 개발된 프로그램은 결코 성능이 좋을 수 없다.
- 많은 경우 애플리케이션 설계와 프레임워크 기술구조에 기인한다.
- Array Processing을 제대로 지원하지 않는 프레임워크- 화면 페이지 처리에 대한 잘못 설계된 표준가이드
- 사용자 정의 함수/프로시저에 대한 무조건적인 제약
- 프로시저 단위 모듈을 지나치게 잘게 쪼개서 SQL을 건건이 호출하도록 설계하는 것
- User Call을 줄이기 위한 기술요소
- Loop 쿼리를 해소하고 집합적 사고를 통해 One SQL로 구현
- Array Processing : Array 단위 Fetch, Bulk Insert/Update/Delete
- 부분범위처리 원리 활용
- 효과적인 화면 페이지 처리
- 사용자 정의 함수/프로시저/트리거의 적절한 활용
2. Recursive Call
- DBMS 내부에서 발생하는 Call
- SQL 파싱과 최적화 과정에서 발생한다.
- 데이터 딕셔너리 조회시
사용자 정의함수/프로시저 내에서의 SQL 수행시 - Recursive Call 최소화 방안
- 바인드 변수 사용하여 하드파싱 발생 횟수 감소
- 사용자 정의 함수/프로시저의 적절한 사용
- 무조건 사용하지 못하도록 제약하거나 무분별하게 사용하지 말아야 한다.
[2] 데이터베이스 Call과 성능
(1) One SQL 구현의 중요성
반복 수행하는 프로그램을 One SQL로 구현한다면 데이터베이스 Call 횟수가 줄어든다.
[예시]
- 만약 처리해야 할 월요금납부실적이 10만 건이면 이 테이블에 대한 Fetch Call이 10만 번 일어난다.
- 아래와 같이 JAVA나 C, VB, Delphi 등으로 개발된 애플리케이션에선 수행 성능에 심각한 문제가 나타난다.
- 대부분 시간을 네트워크 구간에서 소비(일부는 애플리케이션 단에서 소비한 시간)한다.
- 또는 데이터베이스 Call이 발생할 때마다 OS로부터 CPU와 메모리 리소스를 할당받으려고 기다리면서 소비한다.
for list in (select 고객번호, 납입월... from 월요금납부실적 where 납입월 = ?) loop
i:= i + 1;
insert into 테이블 values(고객번호(i), 납입월(i)...)
end loop;이를 아래와 같이 One SQL로 통합하면 1~2초 내에 수행된다.
- 사용자 정의 프로시저로 개발하면 네트워크 트래픽 없는 Recursive Call만 발생하므로 상대적으로 빠르게 수행된다.
- 최대 백만 번 발생할 수 있는 데이터베이스 Call을 단 2회(Parse Call 1회, Execute Call 1회)로 줄인 덕분이다.
insert into 테이블 select * from 테이블;
(2) 데이터베이스 Call과 시스템 확장성
- 데이터베이스 Call은 개별 프로그램 수행속도 뿐 아니라 궁극적으로 시스템 전체의 확장성에도 영향을 미친다.
[예시] 인터넷 쇼핑몰에서 조회한 상품 5개를 선택후 위시리스트에 등록하는 프로그램
- 5번의 메소드를 호출한다면 Parse Call과 Execute Call이 각각 5번씩 발생한다.
void insertWishList ( String p_custid , String p_goods_no ) {
SQLStmt = "insert into wishlist "
+ "select custid, goods_no "
+ "from cart "
+ "where custid = ? "
+ "and goods_no = ? " ;
stmt = con.preparedStatement(SQLStmt);
stmt.setString(1, p_custid);
stmt.setString(2, p_goods_no); stmt.execute();
}
- 메소드를 1번만 호출하여 Parse Call과 Execute Call도 각각 한 번씩만 발생한다.
- 24시간 내내 이 프로그램만 수행된다면 시스템이 앞 프로그램보다 5배의 확장성을 갖게 된다.
- AP 설계가 DBMS 성능을 좌우하는 중요한 요인임을 보여주는 사례이다.
void insertWishList ( String p_custid , String[] p_goods_no ) {
SQLStmt = "insert into wishlist "
+ "select custid, goods_no "
+ "from cart "
+ "where custid = ? "
+ "and goods_no in ( ?, ?, ?, ?, ? )" ;
stmt = con.preparedStatement(SQLStmt);
stmt.setString(1, p_custid);
for(int i=0; i < 5; i++){
stmt.setString(i+2, p_goods_no[i]);
}
stmt.execute();
} [3] Array Processing 활용
- 한번의 SQL(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) 수행으로 다량의 레코드를 동시 처리할 수 있으며 아래 효과를 볼 수 있다.
- 네트워크 Call 감소
- SQL 수행시간 감소
- CPU 사용량 감소 - Call 횟수를 줄이는것이 성능개선에 도움이 되는것을 알수 있다.
- 대용량 데이터의 처리에는 Array Processing이 필수이다.
- ⭐️ 효과를 극대화 하기위해 연속된 일련의 처리과정 모두 Array 단위로 진행해야한다.
- select, insert 모두 해당한다.
[예시 1] 납입방법별_월별요금집계
1 public class JavaArrayProcessing{
2 public static void insertData( Connection con
3 , PreparedStatement st
4 , String param1
5 , String param2
6 , String param3
7 , long param4) throws Exception{
8 st.setString(1, param1);
9 st.setString(2, param2);
10 st.setString(3, param3);
11 st.setLong(4, param4);
12 st.addBatch();
13 }
14
15 public static void execute(Connection con, String input_month)
16 throws Exception {
17 long rows = 0;
18 String SQLStmt1 = "SELECT 고객번호, 납입월"
19 + ", 지로, 자동이체, 신용카드, 핸드폰, 인터넷 "
20 + "FROM 월요금납부실적 "
21 + "WHERE 납입월 = ?";
22
23 String SQLStmt2 = "INSERT INTO 납입방법별_월요금집계 "
24 + "(고객번호, 납입월, 납입방법코드, 납입금액) "
25 + "VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?)";
26
27 con.setAutoCommit(false);
28
29 PreparedStatement stmt1 = con.prepareStatement(SQLStmt1);
30 PreparedStatement stmt2 = con.prepareStatement(SQLStmt2);
31 stmt1.setFetchSize(1000);
32 stmt1.setString(1, input_month);
33 ResultSet rs = stmt1.executeQuery();
34 while(rs.next()){
35 String 고객번호 = rs.getString(1);
36 String 납입월 = rs.getString(2);
37 long 지로 = rs.getLong(3);
38 long 자동이체 = rs.getLong(4);
39 long 신용카드 = rs.getLong(5);
40 long 핸드폰 = rs.getLong(6);
41 long 인터넷 = rs.getLong(7);
42
43 if(지로 > 0)
44 insertData (con, stmt2, 고객번호, 납입월, "A", 지로);
45
46 if(자동이체 > 0)
47 insertData (con, stmt2, 고객번호, 납입월, "B", 자동이체);
48
49 if(신용카드 > 0)
50 insertData (con, stmt2, 고객번호, 납입월, "C", 신용카드);
51
52 if(핸드폰 > 0)
53 insertData (con, stmt2, 고객번호, 납입월, "D", 핸드폰);
54
55 if(인터넷 > 0)
56 insertData (con, stmt2, 고객번호, 납입월, "E", 인터넷);
57
58 if(++rows%1000 == 0) stmt2.executeBatch();
59
60 }
61
62 rs.close();
63 stmt1.close();
64
65 stmt2.executeBatch();
66 stmt2.close();
67
68 con.commit();
69 con.setAutoCommit(true);
70 }
71
72 static Connection getConnection() throws Exception { }
73 static void releaseConnection(Connection con) throws Exception { ...... }
74
75 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
76 Connection con = getConnection();
77 execute(con, "200903");
78 releaseConnection(con);
79 }
80 } 1.INSERT할 데이터를 계속 Array에 담는다. (12번 라인)
2.Select 결과집합을 Fetch할때도 1000건씩 하도록 조정한다. (31번째라인)
3.1,000건 쌓일 때마다 한 번씩 executeBatch를 수행한다. (58번 라인)
[예시 2] PL/SQL을 이용하여 1000건씩 Fetch 후 Bulk Insert하기
DECLARE
l_fetch_size NUMBER DEFAULT 1000; -- 1,000건씩 Array 처리
CURSOR c IS
SELECT empno, ename, job, sal, deptno, hiredate
FROM emp;
...
BEGIN
OPEN C;
LOOP
FETCH c BULK COLLECT
INTO p_empno, p_ename, p_job, p_sal, p_deptno, p_hiredate
LIMIT l_fetch_size;
FORALL i IN p_empno.first..p_empno.last
INSERT INTO emp2
VALUES ( p_empno (i)
, p_ename (i)
, p_job (i)
, p_sal (i)
, p_deptno (i)
, p_hiredate (i) );
EXIT WHEN c%NOTFOUND;
END LOOP;
CLOSE C; [4] Fetch Call 최소화
(1) 부분범위처리 원리
- 쿼리 결과집합을 전송할 때, 전체 데이터를 연속적으로 전송하지 않고 사용자로부터 Fetch Call이 있을 때마다 일정량씩 나누어서 전송하는 것이다.
- INSERT INTO SELECT ~ 문은 인덱스를 사용하지 못한다.
- 모든 데이터 처리가 서버 내에서 이루어지는 경우
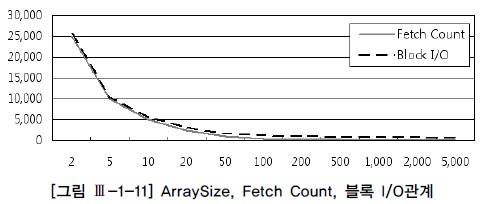
(2) ArraySize 조정에 의한 Fetch Call 감소 및 블록 I/O 감소 효과
- 대량의 데이터파일을 전송한다면 arraysize 크게하여 fetch call 횟수를 줄여주는것이 유리하다.
- 적은량의 데이터만 fetch 하다가 멈추는 프로그램이라면 arraysize를 작게 설정하는것이 유리하다.
- arraysie를 증가시키면 네트워크 부하감소 및 서브프로세스가 읽어야할 블록의 갯수가 감소한다.
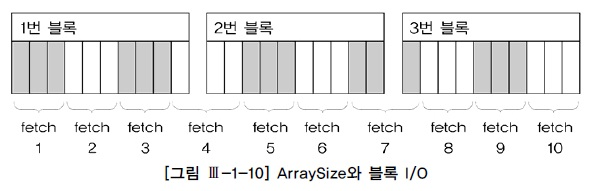
[예시] 10개의 행으로 구성된 3개의 블록인 경우
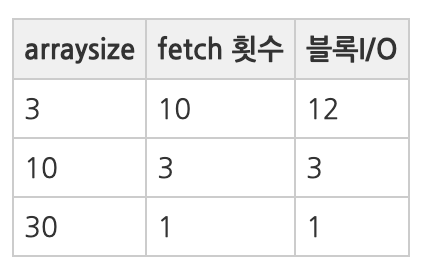
- ArraySize와 Fetch Count 및 블록 I/O는 반비례 관계를 가진다.
- ArraySize 를 키운다고 해서 Fetch count 와 블록 I/O가 같은 비율로 줄어드는 것이 아니다!
- ArraySize를 무작정 크게 설정한다고 좋은것이 아니며, 일정크기 이상이면 리소스만 낭비하는 결과를 초래할 수 있다.
[5] 페이지 처리 활용
- 부분범위처리 원리를 이용한 대용량 온라인 조회 성능 개선은 커서를 닫지 않은 상태에서 사용자가 명시적으로 요청할 때만 데이터를 Fetch 할 수 있는 개발환경에서나 가능하다.
- 이를테면 스크롤 바를 내리거나 ‘다음’ 버튼을 클릭하는 등 - 조회할 데이터가 일정량 이상이고 수행빈도가 높다면 필수적으로 페이지 처리를 구현해야 한다.
(1) 연결을 지속하지 않는 웹 애플리케이션 환경
⭐️ 데이터베이스와의 연결을 지속하지 않는 웹 애플리케이션 환경에선 커서를 계속 연 채로 결과집합을 핸들링할 수 없다.
(2) 페이지 처리를 하지 않았을 때 발생하는 부하요인
- 다량 발생하는 Fetch Call 부하
- 대량의 결과 집합을 클라이언트로 전송하면서 발생하는 네트워크 부하
- 대량의 데이터 블록을 읽으면서 발생하는 I/O 부하
- AP 서버 및 웹 서버 리소스 사용량 증가
(3) 부하를 해소하는 열쇠
- 페이지 단위로, 화면에서 필요한 만큼만 Fetch Call하기
- 페이지 단위로, 화면에서 필요한 만큼만 네트워크를 통해 결과 전송하기
- 인덱스와 부분범위처리 원리를 이용해 각 페이지에 필요한 최소량만 I/O 처리
- 데이터를 소량씩 나누어 전송하므로 AP웹 서버 리소스 사용량 최소화하기
[5] 페이지 처리 활용
- 부분범위처리 원리를 이용한 대용량 온라인 조회 성능 개선은 커서를 닫지 않은 상태에서 사용자가 명시적으로 요청할 때만 데이터를 Fetch 할 수 있는 개발환경에서나 가능하다.
- 이를테면 스크롤 바를 내리거나 ‘다음’ 버튼을 클릭하는 등 - 조회할 데이터가 일정량 이상이고 수행빈도가 높다면 필수적으로 페이지 처리를 구현해야 한다.
(1) 연결을 지속하지 않는 웹 애플리케이션 환경
⭐️ 데이터베이스와의 연결을 지속하지 않는 웹 애플리케이션 환경에선 커서를 계속 연 채로 결과집합을 핸들링할 수 없다.
(2) 페이지 처리를 하지 않았을 때 발생하는 부하요인
- 다량 발생하는 Fetch Call 부하
- 대량의 결과 집합을 클라이언트로 전송하면서 발생하는 네트워크 부하
- 대량의 데이터 블록을 읽으면서 발생하는 I/O 부하
- AP 서버 및 웹 서버 리소스 사용량 증가
(3) 부하를 해소하는 열쇠
- 페이지 단위로, 화면에서 필요한 만큼만 Fetch Call하기
- 페이지 단위로, 화면에서 필요한 만큼만 네트워크를 통해 결과 전송하기
- 인덱스와 부분범위처리 원리를 이용해 각 페이지에 필요한 최소량만 I/O 처리
- 데이터를 소량씩 나누어 전송하므로 AP웹 서버 리소스 사용량 최소화하기
[6] 분산 쿼리 : 네트워크를 통한 데이터 전송량을 줄임
분산 쿼리의 성능을 높이는 핵심 원리는, 네트워크를 통한 데이터 전송량을 줄이는 데 있다.
(1) 원격 조인이 자주 문제시되는데, 분산 DB 간 테이블을 조인할 때 성능을 높일 방안은 무엇일까?
- 테이블의 특정 조건에 해당하는 데이터만 원격으로 보내서 조인과 group by를 거친 결과집합을 전송받는다.
- group by한 결과집합 훨씬 더 적으므로 큰 성능 개선을 기대할 수 있다.
[예시]
- 원격(Remote)에 있는 sales 테이블을 전송받아 order 테이블과 NL 방식으로 조인한다.
- 다음 쿼리는 50만 건이나 되는 sales 데이터를 네트워크를 통해 전송받는 쿼리로 쿼리 성능이 나쁘다.
select channel_id, sum(quantity_sold) auantity_cold
from order a, sales@lk_sales b
where a.order_date between :1 and :2
and b.order_no = a.order no
group by channel_id
Rows Row Source Operation
----- ---------------------------------------------
5 SORT GROUP BY
10981 NESTED LOOPS
500000 REMOTE
10981 TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID ORDER
500000 INDEX UNIQUE SCAN (ORDER_PK)- 아래 쿼리는 원격 서버가 쿼리를 처리하도록 driving_site 힌트를 지정한 쿼리이다.
- 인덱스를 이용해 939건의 order 데이터를 읽어 원격으로 보냈고, 원격지에서 처리가 완료된 5건만 전송받았다.
select /*+ driving_site(b) */ channel_id, sum(quantity_sold) auantity_cold
from order a, sales@lk_sales b
where a.order_date between :1 and :2
and b.order_no = a.order no
group by channel_id
Rows Row Source Operation
---- ---------------------------------------------
5 SORT GROUP BY
10981 NESTED LOOPS
939 TABLE ACCESS (BY INDEX ROWID) OF ‘ORDER’
939 INDEX (RANGE SCAN) OF ‘ORDER_IDX2’ (NON-UNIQUE)
10981 REMOTE⭐️ 따라서 분산 쿼리의 성능을 높이는 핵심 원리는, 네트워크를 통한 데이터 전송량을 줄이는 데에 있다.
=================
[7] 사용자 정의 함수(= DB 저장형 함수)/프로시저의 특징과 성능
(1) 사용자 정의 함수(= DB 저장형 함수)/프로시저의 특징
1.내장함수 Native 코드로 완전 컴파일된 형태이다.
2. 사용자 정의 함수(= DB 저장형 함수)/프로시저
- Native 코드로 완전 컴파일된 형태가 아니어서 가상머신(Virtual Machine) 같은 별도의 실행엔진을 통해 실행된다.
- ⭐️ 실행할 때마다 컴파일이 되는 건 아니지만 VM에서 매번 바이트 코드를 해석한다.
- 실행될 때마다 컨텍스트 스위칭(Context Switching)이 일어난다.
- ⭐️ 메인 쿼리가 참조하는 사용자 정의 함수에 또 다른 쿼리문이 내장돼 있으면 수행 성능이 훨씬 나빠진다.
- 함수에 내장된 쿼리를 수행될 때마다 Execute Call, Fetch Call이 재귀적으로 일어나기 때문이다.
- Recursive Call이 반복적으로 일어난다.
- 다행히 Parse Call은 처음 수행할 때 한 번만 일어난다.
- ⭐️ 네트워크를 경유해 DBMS에 전달되는 User Call에 비해 Recursive Call의 성능 부하는 미미하다.
(2) 사용자 정의 함수(= DB 저장형 함수)/프로시저에 의한 성능 저하 해소 방안
1. 소량의 데이터를 조회할 때 또는 부분범위 처리가 가능한 상황에서 제한적으로 사용
[예시]
- 1,000만 개 주문 레코드를 사용자 정의 함수/프로시저로 검사한다.
결과
- 1,000만 번의 컨텍스트 스위칭이 발생함은 물론 Execute Call과 Fetch Call이 각각 1,000만 번씩 발생한다.
- ⭐️ 따라서 사용자 정의 함수는 소량의 데이터를 조회할 때, 또는 부분범위처리가 가능한 상황에서 제한적으로 사용하도록 한다.
