객체들의 관계를 트리구조로 구성하여 부분-전체 계층을 표현하는 패턴.
사용자가 단일 객체와 복합 객체 모두 동일하게 다루도록 함.
클라이언트는 전체-부분 구분없이 동일한 인터페이스 사용 가능 -> 일괄적인 관리가 가능해짐
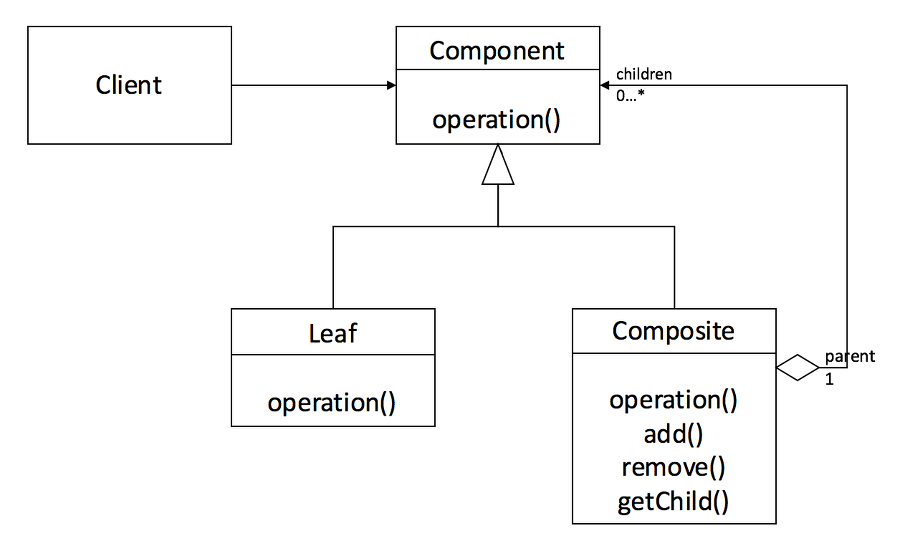
Component
- 구체적인 부분
- 즉 Leaf 클래스와 전체에 해당하는 Composite 클래스에 공통 인터페이스를 정의Leaf
- 구체적인 부분 클래스
- Composite 객체의 부품으로 설정Composite
- 전체 클래스
- 복수 개의 Component를 갖도록 정의
- 그러므로 복수 개의 Leaf, 심지어 복수 개의 Composite 객체를 부분으로 가질 수 있음컴포지트 패턴의 예시
1. Base Component
Shape 인터페이스 내에 각각 도형마다 색을 입히는 draw() 메소드를 정의하는 예제
- Base Component는 Leaf와 Composite의 공통되는 메소드들을 정의해야 함
// Shape.java
public interface Shape {
public void draw(String fillColor);
}2. Leaf Objects
Leaf 객체들은 복합체에 포함되는 요소
- Base Component 구현해야 함
- 여기서는 Triangle, Circle 클래스 정의
// Triangle.java
public class Triangle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw(String fillColor) {
System.out.println("Drawing Triangle with color "+fillColor);
}
}// Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw(String fillColor) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle with color "+fillColor);
}
}3. Composite Objects
- Composite 객체는 Leaf 객체를 포함하고
- 또한, Base Component를 구현과 Leaf 그룹에 대해 add와 remove 할 수 있는 메소드들을 클라이언트에게 제공
- Composite Object 또한 Base Component를 구현해야만 클라이언트가 Composite 객체에 대해서 다른 Leaf들과 동일하게 취급될 수 있음
// Drawing.java
public class Drawing implements Shape {
//collection of Shapes
private List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<Shape>();
@Override
public void draw(String fillColor) {
for(Shape sh : shapes) {
sh.draw(fillColor);
}
}
//adding shape to drawing
public void add(Shape s) {
this.shapes.add(s);
}
//removing shape from drawing
public void remove(Shape s) {
shapes.remove(s);
}
//removing all the shapes
public void clear() {
System.out.println("Clearing all the shapes from drawing");
this.shapes.clear();
}
}실행
// TestCompositePattern.java
public class TestCompositePattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape tri = new Triangle();
Shape tri1 = new Triangle();
Shape cir = new Circle();
Drawing drawing = new Drawing();
drawing.add(tri1);
drawing.add(tri1);
drawing.add(cir);
drawing.draw("Red");
List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<>();
shapes.add(drawing);
shapes.add(new Triangle());
shapes.add(new Circle());
for(Shape shape : shapes) {
shape.draw("Green");
}
}
}결과
Drawing Triangle with color Red
Drawing Triangle with color Red
Drawing Circle with color Red
Drawing Triangle with color Green
Drawing Triangle with color Green
Drawing Circle with color Green
Drawing Triangle with color Green
Drawing Circle with color Green- drawing 객체를 통해 Triangle, Circle 등의 Leaf 객체들을 Group으로 묶어서 한 번에 동작을 수행할 수 있음
- drawing 객체 또한 다른 도형들과 마찬가지로 Shape 인터페이스를 구현하고 있음
- 때문에 변수 shapes에서 살펴보는 것과 같이 drawing이 다른 도형들과 함께 취급될 수 있음
컴포지트 패턴의 장단점
장점
- 객체들이 모두 같은 타입으로 취급 됨 -> 새로운 클래스 추가가 용이
- 단일 객체 및 집합 객체 구분하지 않고 코드 작성 가능 -> 사용자 코드가 단순해짐
- 단일 객체와 집합 객체로 구성된 하나의 일관된 클래스 계통을 정의
- 런타임 단일 객체와 집합 객체를 구분 않고 일관된 프로그래밍 가능
단점
- 설계가 지나친 범용성을 가짐 -> 복합체 구성요소에 제약을 걸기 어려움
- 복합체가 오직 한개의 구성요소만 가지게 하고싶어도 컴포지트 클래스만 가지고는 이를 제어하기 어려움 -> 런타임 점검 들어가게 됨