Spring: Spring Data JPA
개념 비교: JPA vs Hibernate vs Spring Data JPA
- JPA
- Java Persistence API
- javax.persistence 패키지를 보면 interface, enum, Exception 등으로만 이루어져 있고 implementation은 없다.
- 예를 들어
javax.persistence.EntityManager는persist,merge,find등의 메소드가 정의만 되어 있다.
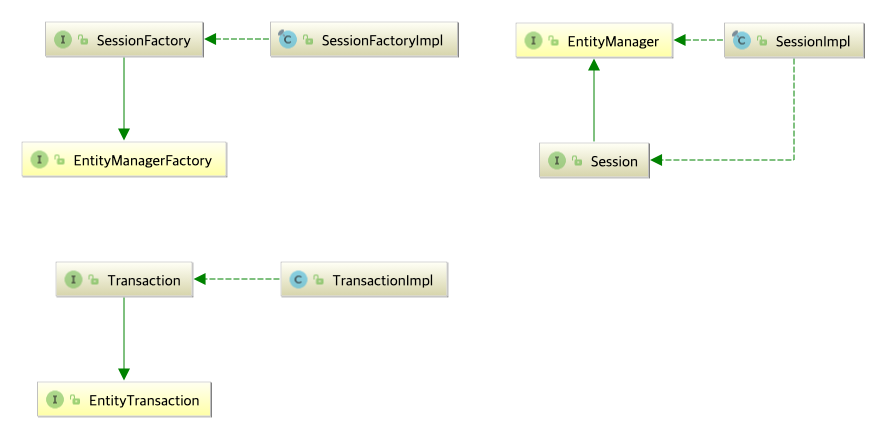
- Hibernate
- 라이브러리로서 JPA의 구현체이다.
- 예를 들어 Hibernate의
Session은EntityManager를 상속받고SessionImpl에서 메소드를 구현했다.
- Spring Data JPA
- Spring에서 제공하는 모듈로서 JPA를 한 단계 추상시킨
Repository라는 인터페이스를 제공한다. SimpleJpaRepository를 보면 여기도 내부적으로EntityManager를 사용하고 있다.
- Spring에서 제공하는 모듈로서 JPA를 한 단계 추상시킨
Spring Data JPA와 Hibernate 개념이 겹치는 듯하여 헷갈릴 수 있다.
- Spring Data JPA는 high level abstraction이고 Hibernate는 low level implementation이다.
- Spring Data JPA는 편리하게 데이터를 접근하는 데 목적이 있고 Hibernate는 다양한 기능을 활용한 ORM 프레임워크를 제공한다.
- 웬만하면 Spring Data JPA 쓰는 게 편리한 것 같다.
Spring Data JPA
Repository보다 더 확장된 인터베이스는 CrudRepository, ListCrudRepository가 있다.
ListCrudRepository는 Iterable 대신 List를 반환한다는 차이가 있다.
JpaRepository나 MongoRepository는 CrudRepository를 extend한다.
이 외에도 페이지 기능을 사용할 수 있는 PagingAndSortingRepository, List PagingAndSortingRepository도 있다.
Defining Repository Interfaces
인터페이스는 Repository 를 상속해야하고 domain class와 ID type 으로 타입이 정의된다.
interface MyBaseRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {
...
}Configuration
- Java configuration: Annotation-based Configuration
- XML configuration: Spring Namespace
Persisting Entities
CrudRepository.save() 를 통해 entity를 저장할 수 있다. 이는 JPA EntityManager를 통해 이루어진다.
저장하고자 하는 entity가 새로운 entity라면 entityManager.persist() 함수가 호출되고 이미 있다면 entityManager.merge()가 호출된다.
Spring Data JPA는 entity가 새로운 건지 아닌지를 다음 strategy 들로 판단할 수 있다.
- Version-Property and Id-Property inspection(default)
- non-primitive 타입의 Version-property를 확인한다. 이게 있으면 해당 값이 null일 때 새로운 entity라고 판단한다.
- Version-property가 없으면 해당 entity의 Id-property를 확인한다. 해당 값이 null이면 새로운 entity로 판단한다.
- 이게 아니라면 새로운 entity가 아닌 것으로 판단한다.
- Implementing
Persistable- entity에서
Persistable을 구현하면isNew()함수를 통해서 판단한다.
- entity에서
- Implementing
EntityInformationSimpleJpaRepository에서 사용되는EntityInformation을 customize할 수 있다.JpaRepositoryFactory의 subclass를 생성하고getEntityInformation()을 오버라이딩한다.- 그 다음에는
JpaRepositoryFactory를 Spring bean으로 등록해야한다. - 이건 거의 안 쓰인다고 한다.
Defining Query Methods
메소드 이름에서 직접 쿼리를 만들어내는 방법과 직접 구현한 쿼리를 사용하는 방법이 있다.
사용 가능한 Query lookup strategy는 다음과 같다.
- CREATE
- 메소드 이름을 파싱해서 store-specific 한 쿼리를 생성한다.
- USE_DECLARED_QUERY
- 각 메소드에 대한 쿼리를 annotation 등을 이용하여 정의한다. 정해진 쿼리를 찾아보고 없으면 exception을 던진다.
- bootstrap 때 매핑하는 쿼리를 찾지 못하면 앱이 실패한다.
- CREATE_IF_NOT_FOUND (default)
- CREATE 와 USE_DECLARED_QUERY 를 합친 것이다. declared query를 먼저 찾아보고 없으면 name-based 쿼리를 생성한다.
- 메소드 이름을 통해 쿼리를 빠르게 만들 수 있으면서도 필요한 경우 직접 정의하여 사용할 수도 있다.
Defining Query Methods: CREATE
메소드 이름에서 쿼리를 추출하여 사용하는 예시
interface PersonRepository extends Repository<Person, Long> {
List<Person> findByEmailAddressAndLastname(EmailAddress emailAddress, String lastname);
// Enables the distinct flag for the query
List<Person> findDistinctPeopleByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname);
List<Person> findPeopleDistinctByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname);
// Enabling ignoring case for an individual property
List<Person> findByLastnameIgnoreCase(String lastname);
// Enabling ignoring case for all suitable properties
List<Person> findByLastnameAndFirstnameAllIgnoreCase(String lastname, String firstname);
// Enabling static ORDER BY for a query
List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameAsc(String lastname);
List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameDesc(String lastname);
}
접근하고자 하는 property가 객체의 field일 때
List<Person> findByAddressZipCode(ZipCode zipCode);Person 객체에 Address 객체가 있고 그 안에 ZipCode가 있다고 가정해보자. 그러면 메소드는 x.address.zipCode를 통해 쿼리를 해야 한다.
findByAddressZipCode 라는 메소드이름으로 정의할 때 처음에는 AddressZipCode 전체를 보고 이게 domain class에 있는 property인지 확인한다. (소문자로 변환 후 비교)
만약 없다면 이걸 camel-case로 쪼개서 오른쪽부터 쪼갠다. 이 예시의 경우는 AddressZip과 Code로 먼저 쪼개진다. 이렇게 쪼개면서 property 체크를 한다.
하지만 Person 클래스에 addressZip 라는 property가 있다면 알고리즘은 addressZip 과 code 로 잘못 나누게 되고 이후에 code 라는 property가 없다면 실패하게 된다.
이런 문제를 해결하기 위해 underscore를 사용할 수 있다.
List<Person> findByAddress_ZipCode(ZipCode zipCode);이렇게 하면 address 객체에서 zipCode 라는 property를 찾게 된다. 이렇게 method name을 볼 때 underscore를 reserved character로 사용하기 때문에 property 이름에 underscore를 사용하는 것은 좋지 않다.
자세한 문법은 https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/reference/repositories/query-keywords-reference.html 를 참고한다.
Defining Query Methods: USER_DECLARED_QUERY
XML 설정을 통해서 쿼리를 정의할 수 있다.
<named-query name="User.findByLastname">
<query>select u from User u where u.lastname = ?1</query>
</named-query>annotation을 통해 정의할 수도 있다.
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
@Query("select u from User u where u.emailAddress = ?1")
User findByEmailAddress(String emailAddress);
}쿼리에 주어진 변수를 넣을 때 기본적으로는 position-based 로 동작하지만 실수를 방지하기 위해 param annotation을 사용할 수도 있다.
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
@Query("select u from User u where u.firstname = :firstname or u.lastname = :lastname")
User findByLastnameOrFirstname(@Param("lastname") String lastname,
@Param("firstname") String firstname);
}Custom Repository Implementations
Spring Data가 여러 유용한 옵션을 제공하지만 이게 맞지 않는다면 직접 repository 메소드를 구현할 수 있다.
직접 fragment interface를 정의한 후에 구현을 한다.
interface CustomizedUserRepository {
void someCustomMethod(User user);
}class CustomizedUserRepositoryImpl implements CustomizedUserRepository {
public void someCustomMethod(User user) {
// Your custom implementation
}
}Fragment interface에 대응하는 클래스 이름은 repositoryImplementationPostfix 값으로 설정된 postfix(default는 Impl인 듯)를 붙여야 scan이 가능하다.
만약 implement하는 클래스 이름이 동일한 게 있다면 bean name으로 판단한다. 예를 들어 @Component("specialCustom") 로 annotate 된 repository interface가 있다면 @Component("specialCustomImpl") 으로 annotate 된 클래스가 implement하게 된다.
이 구현은 Spring Data 를 사용하지 않기 때문에 일반적인 Spring bean이다. 따라서 JdbcTemplate와 같은 다른 bean에 대한 reference를 inject하기 위해 standard dependency injection을 사용할 수 있다.
그 다음에는 다음과 같이 repository interface가 fragment interface를 상속하도록 한다.
interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long>, CustomizedUserRepository {
// Declare query methods here
}이렇게 하면 CRUD 기능도 쓸 수 있고 custom functionality도 쓸 수 있다.
Spring Data repository는 fragment 들로 이루어져있다.(base respository, functional aspects, custom interfaces)
base repository를 다음과 같이 override 해서 save 동작을 바꿀 수 있다.
interface CustomizedSave<T> {
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
}
class CustomizedSaveImpl<T> implements CustomizedSave<T> {
public <S extends T> S save(S entity) {
// Your custom implementation
}
}interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long>, CustomizedSave<User> {
}
interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<Person, Long>, CustomizedSave<Person> {
}Null Handling of Repository Methods
package com.acme;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
interface UserRepository extends Repository<User, Long> {
// query가 아무 결과를 반환하지 않으면 EmptyResultDataAccessException 를 throw한다.
// emailAddress가 null로 들어오면 IllegalArgumentException 를 throw한다.
User getByEmailAddress(EmailAddress emailAddress)
// query가 아무 결과를 반환하지 않으면 null을 반환한다.
// emailAddress로 null이 들어올 수 있다.
@Nullable
User findByEmailAddress(@Nullable EmailAddress emailAdress);
// query가 아무 결과를 반환하지 않으면 Optional.emtpy() 를 반환한다.
// emailAddress 가 null로 들어오면 IllegalArgumentException 을 throw한다.
Optional<User> findOptionalByEmailAddress(EmailAddress emailAddress);
}Kotlin에서는 @Nullable 대신 ?를 사용하여 표시한다.
fun findByEmailAddress(emailAdress: EmailAddress?): User?References
