[250620금1165H] 자연어 처리 이론 (5) Word2Vec, FastText, GloVe, Vanilla RNN, LSTM, GRU
비전공자 부트캠프 생존기
목록 보기
84/169
오늘까지만 이론 바짝 공부하고 내일부터 실전으로 들어가야지!
학습시간 09:00~03:00(당일18H/누적1165H)
◆ 학습내용
키워드 요약
| 모델명 | 핵심 아이디어 | 주요 특징 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word2Vec | 주변 단어를 통해 단어를 예측 (예측 기반) | CBOW, Skip-gram, Negative Sampling | 단어 간 의미적/문법적 관계 표현 우수, 비교적 빠른 학습 | OOV 문제, 단어를 원자 단위로 취급 |
| FastText | 단어를 문자 n-gram의 합으로 표현 | Subword information | OOV 및 희귀 단어 처리 가능, 형태소 정보 반영 | 모델 크기가 큼, 계산 비용 증가 |
| GloVe | 전체 말뭉치의 단어 동시 등장 통계 활용 (카운트 기반) | Co-occurrence Matrix, 목적 함수 | 전체 통계 정보를 활용하여 학습이 빠름, 단어 유추 성능 우수 | OOV 문제, 동시 등장 행렬의 메모리 부담 |
| Vanilla RNN | 이전 시점의 출력을 현재 시점의 입력으로 사용 (순환 구조) | Hidden State () | 구조가 간단함, 기본적인 시퀀스 패턴 학습 가능 | 장기 의존성 문제 (그래디언트 소실/폭주) |
| LSTM | 셀 상태와 3개의 게이트(Forget, Input, Output)로 정보 흐름 제어 | Cell State, Forget/Input/Output Gates | 장기 의존성 문제 해결, 복잡한 시퀀스 패턴 학습 | 구조 복잡, 파라미터 수 많음, 계산 비용 높음 |
| GRU | LSTM을 간소화한 모델. 2개의 게이트(Reset, Update) 사용 | Reset Gate, Update Gate | LSTM보다 파라미터가 적고 계산 효율이 높음, 대등한 성능 | LSTM보다 정교한 제어는 어려움 |
1. Embedding Models
- 단어를 컴퓨터가 이해하고 처리할 수 있는 형태인 벡터(vector)로 변환하는 기술.
- 단어의 의미적, 문법적 정보를 벡터 공간에 표현하는 것을 목표로 함.
(1) Word2Vec
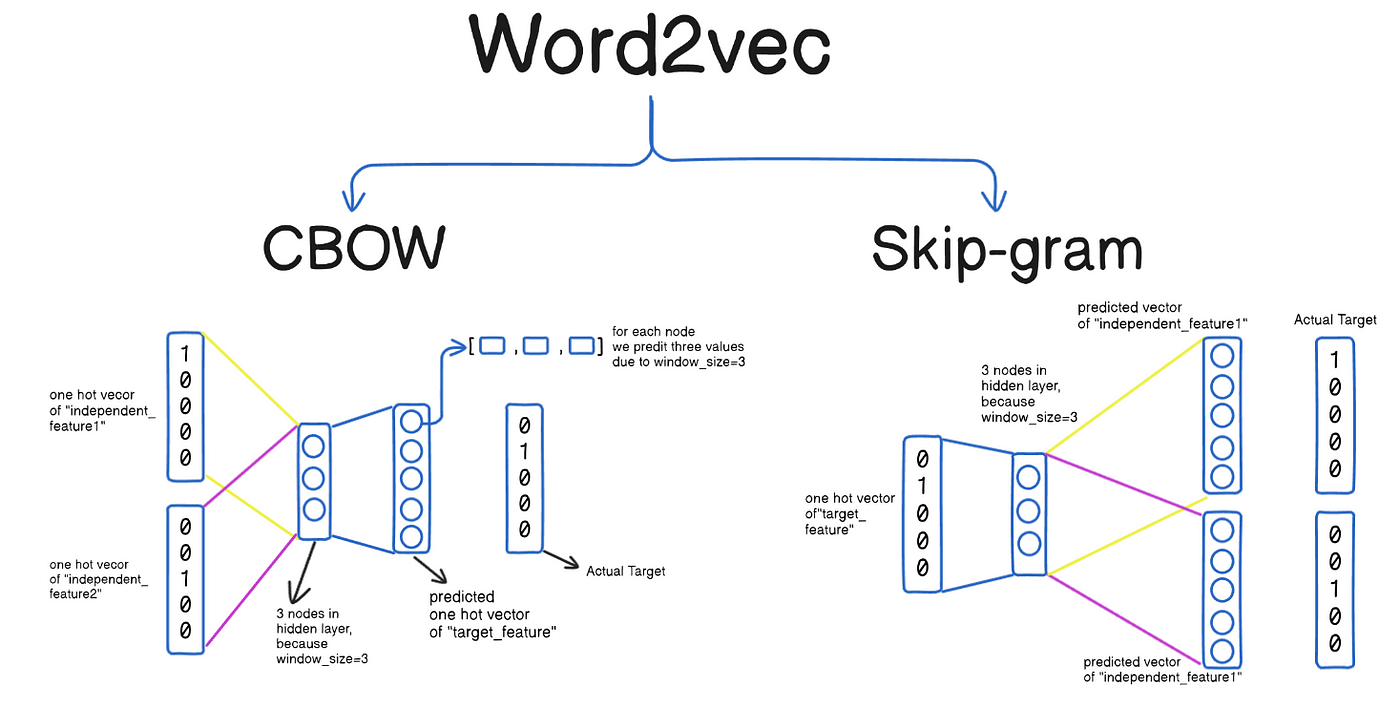
- 예측 기반의 임베딩 모델로, 특정 단어 주변에 나타나는 단어들을 기반으로 해당 단어의 의미를 학습함. "비슷한 위치에 나타나는 단어는 비슷한 의미를 가질 것이다"라는 분포 가설에 기반함.
A. 핵심 구조
- CBOW (Continuous Bag-of-Words): 주변 단어들(context words)을 통해 중심 단어(center word)를 예측하는 모델.
- 예:
[the, cat, __, on, the, mat]에서sat을 예측. - 여러 문맥 단어 벡터의 평균 또는 합을 사용하여 중간 단어를 예측하므로, 작은 데이터셋에서도 준수한 성능을 보임.
- 예:
- Skip-gram: 중심 단어를 통해 주변 단어들을 예측하는 모델.
- 예:
sat을 통해[the, cat, on, the, mat]을 예측. - 하나의 중심 단어로 여러 주변 단어를 예측해야 하므로, CBOW보다 학습이 오래 걸리지만 일반적으로 더 큰 데이터셋에서 높은 품질의 임베딩을 생성함. 특히 희귀 단어에 대해 성능이 좋음.
- 예:
B. 학습 최적화 기법
- Negative Sampling: 전체 단어 집합이 아닌, 몇 개의 무작위 '오답' 단어(negative samples)를 뽑아 정답 단어와 비교하여 학습 속도를 높이는 기법. Skip-gram 모델의 출력층이 모든 단어에 대한 확률을 계산해야 하는 부담을 줄여줌.
- Hierarchical Softmax: 출력층을 이진 트리 구조로 만들어 특정 단어를 찾아가는 방식으로 계산 복잡도를 에서 로 줄이는 기법. (V: 단어 집합의 크기)
C. 특징
- 장점: 단어 간의 의미적, 문법적 관계(유추)를 벡터 공간에서 잘 표현함 (예: ).
- 단점: 학습 데이터에 없었던 단어(Out-of-Vocabulary, OOV)에 대한 벡터를 생성할 수 없음. 단어를 형태소나 내부 구조를 고려하지 않는 원자 단위(atomic unit)로 취급함.
D. 코드 예시
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
sentences = [['this', 'is', 'the', 'first', 'sentence', 'for', 'word2vec'],
['this', 'is', 'the', 'second', 'sentence'],
['yet', 'another', 'sentence'],
['one', 'more', 'sentence'],
['and', 'the', 'final', 'sentence']]
model = Word2Vec(sentences, vector_size=100, window=5, min_count=1, workers=4, sg=1)
vector = model.wv['sentence']
print(vector)
similar_words = model.wv.most_similar('sentence', topn=3)
print(similar_words)
(2) FastText

- Word2Vec의 단점을 보완하기 위해 Facebook에서 개발한 모델. 단어를 더 작은 단위인 문자 n-gram(character n-gram)의 집합으로 표현하여 OOV(Out-of-Vocabulary) 문제에 강건한 구조를 가짐.
A. 핵심 구조
- Subword Information: 각 단어를 내부 단어(subword)들의 집합으로 간주함.
- 예:
apple이라는 단어를 3-gram으로 분해하면<ap,app,ppl,ple,le>와 같은 부분 문자열로 구성됨. (<와>는 단어의 시작과 끝을 표시) - 최종 단어 벡터는 이 n-gram 벡터들의 합으로 표현됨.
- 예:
B. 특징
- OOV 처리: 학습 시 보지 못한 단어가 등장해도, 해당 단어를 구성하는 n-gram 벡터들의 합으로 새로운 단어 벡터를 추정할 수 있음.
- 희귀 단어 처리: 등장 빈도가 적은 단어라도, 다른 단어와 공유하는 n-gram이 있다면 상대적으로 준수한 품질의 임베딩 벡터를 얻을 수 있음.
- 형태소 정보 반영: 형태학적으로 유사한 단어들은 유사한 n-gram을 공유하므로, 벡터 공간에서도 가깝게 표현될 가능성이 높음 (예:
running,runner는run이라는 n-gram을 공유). - 단점: n-gram 정보를 모두 저장해야 하므로 모델의 크기가 커지고, 계산 비용이 Word2Vec보다 높음.
C. 코드 예시
from gensim.models import FastText
sentences = [['this', 'is', 'the', 'first', 'sentence', 'for', 'fasttext'],
['this', 'is', 'the', 'second', 'sentence'],
['yet', 'another', 'sentence'],
['one', 'more', 'sentence'],
['and', 'the', 'final', 'sentence']]
model = FastText(sentences, vector_size=100, window=5, min_count=1, workers=4, sg=1)
vector = model.wv['sentence']
print(vector)
oov_vector = model.wv['fasttextual']
print(oov_vector)
(3) GloVe
- Global Vectors for Word Representation
- 예측 기반인 Word2Vec, FastText와 달리, 말뭉치 전체의 통계 정보(global co-occurrence statistics)를 직접 활용하는 카운트 기반 모델.
A. 핵심 구조
- 동시 등장 행렬 (Co-occurrence Matrix): 말뭉치 전체에서 특정 단어 의 문맥 내에 단어 가 함께 등장하는 빈도를 행렬 로 표현함. 는 단어 가 단어 의 문맥에 나타난 횟수.
- 목적 함수: 임베딩된 벡터 간의 관계가 전체 동시 등장 확률 정보를 잘 반영하도록 설계됨. 목적 함수는 다음과 같음.
- : 중심 단어 의 벡터
- : 문맥 단어 의 벡터
- : 각 벡터에 대한 편향(bias)
- : 가중치 함수로, 빈도가 매우 높은 단어(the, is 등)의 영향을 줄이는 역할을 함.
B. 특징
- 글로벌 통계 정보 활용: 말뭉치 전체의 통계 정보를 초기에 한 번만 계산하여 학습에 반영하므로, 학습이 빠르고 효율적임.
- 준수한 성능: 단어 유추 평가(word analogy task) 등에서 Word2Vec과 유사하거나 더 나은 성능을 보이는 경우가 많음.
- 단점: Word2Vec과 마찬가지로 OOV 문제에 취약하며, 동시 등장 행렬을 저장하기 위해 상당한 메모리가 필요할 수 있음.
C. 코드 예시
# Pre-trained GloVe 로딩
import torch
import torchtext.vocab as vocab
glove = vocab.GloVe(name='6B', dim=100)
vector = glove.get_vecs_by_tokens(['king', 'man', 'woman'], lower_case_except_case_sensitive=True)
king_vec, man_vec, woman_vec = vector[0], vector[1], vector[2]
queen_vec = king_vec - man_vec + woman_vec
cos = torch.nn.CosineSimilarity(dim=0)
similarities = []
for i, token in enumerate(glove.itos):
if i % 10000 == 0:
print(f"Processing... {i}/{len(glove.itos)}")
token_vec = glove.vectors[i]
similarity = cos(queen_vec, token_vec)
similarities.append((token, similarity.item()))
similarities.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(similarities[:5])
2. RNN Models
- 시퀀스(sequence) 데이터 처리에 특화된 인공 신경망. 이전 시간 단계(time step)의 정보를 현재 시간 단계의 입력으로 재사용하는 '순환' 구조를 통해 시계열 데이터의 시간적 종속성을 학습함.
(1) Vanilla RNN
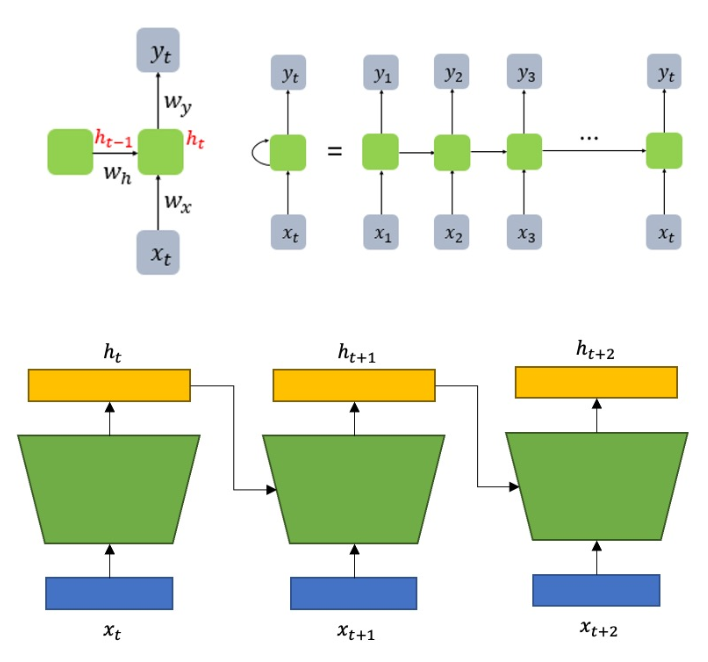
- 가장 기본적인 형태의 순환 신경망.
A. 핵심 구조
- 은닉 상태 (Hidden State): RNN 셀은 현재 입력()과 이전 시간 단계의 은닉 상태()를 받아 현재의 은닉 상태()를 계산함. 이 은닉 상태가 '기억'의 역할을 수행.
- 수식:
- : 시간 에서의 은닉 상태
- : 시간 에서의 입력
- : 시간 에서의 출력
- : 가중치 행렬
- : 편향 벡터
- : 활성화 함수 (쌍곡탄젠트)
B. 특징
- 장점: 구조가 간단하고, 시퀀스 데이터의 기본적인 패턴을 학습할 수 있음.
- 단점: 장기 의존성 문제 (Long-Term Dependency Problem)가 치명적임. 시퀀스가 길어질수록 과거의 정보가 현재까지 전달되기 어려움. 이는 역전파 과정에서 그래디언트가 너무 작아지거나(Vanishing Gradient) 너무 커지는(Exploding Gradient) 문제 때문에 발생함.
C. 코드 예시
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class VanillaRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(VanillaRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(1, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(x.device)
out, _ = self.rnn(x, h0)
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out
input_size = 10
hidden_size = 20
output_size = 5
seq_length = 15
batch_size = 3
model = VanillaRNN(input_size, hidden_size, output_size).to(device)
input_tensor = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_length, input_size).to(device)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.shape)
(2) LSTM
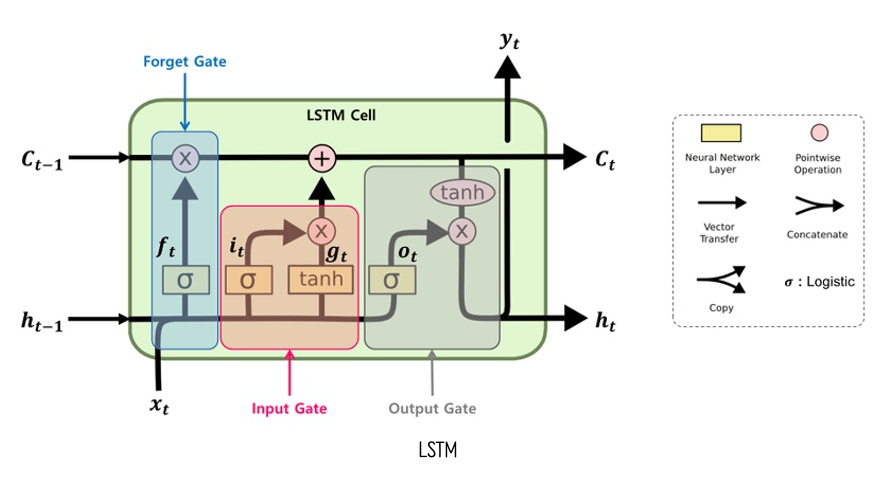
- Long Short-Term Memory
- Vanilla RNN의 장기 의존성 문제를 해결하기 위해 고안된 구조. '셀 상태(Cell State)'와 여러 '게이트(Gate)'를 도입하여 정보의 흐름을 정교하게 제어함.
A. 핵심 구조
- 셀 상태 (): 네트워크 전체를 관통하며 흐르는 정보의 고속도로. 게이트들에 의해 정보가 추가되거나 제거됨. 장기 기억을 담당.
- 게이트 (Gate): 시그모이드(sigmoid) 함수를 통해 0과 1 사이의 값을 출력하여 정보의 통과량을 조절하는 장치.
- Forget Gate (): 과거 정보를 얼마나 잊을지 결정.
- Input Gate (): 새로운 정보를 얼마나 셀 상태에 저장할지 결정.
- Output Gate (): 셀 상태의 정보를 바탕으로 무엇을 출력할지 결정.
B. 정보 흐름
- Forget Gate가 이전 셀 상태()에서 버릴 정보를 결정.
- Input Gate가 현재 입력()과 이전 은닉 상태()를 통해 셀 상태에 추가할 새로운 후보 정보()를 만들고, 얼마나 반영할지 결정.
- 이전 셀 상태()의 일부를 버리고, 새로운 정보()를 더해 현재 셀 상태()를 업데이트.
- Output Gate가 셀 상태()에서 어떤 부분을 출력할지 결정하고, 이를 처리한 값과 곱하여 현재 은닉 상태()를 생성.
C. 특징
- 장점: 게이트 메커니즘을 통해 그래디언트 소실/폭주 문제를 효과적으로 완화하고, 시퀀스의 장기 의존성을 잘 학습함.
- 단점: Vanilla RNN보다 구조가 복잡하고 파라미터 수가 많아 계산 비용이 높음.
D. 코드 예시
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class LSTMModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers):
super(LSTMModel, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(x.device)
c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(x.device)
out, _ = self.lstm(x, (h0, c0))
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out
input_size = 10
hidden_size = 20
output_size = 5
num_layers = 2
seq_length = 15
batch_size = 3
model = LSTMModel(input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers).to(device)
input_tensor = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_length, input_size).to(device)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.shape)
(3) GRU
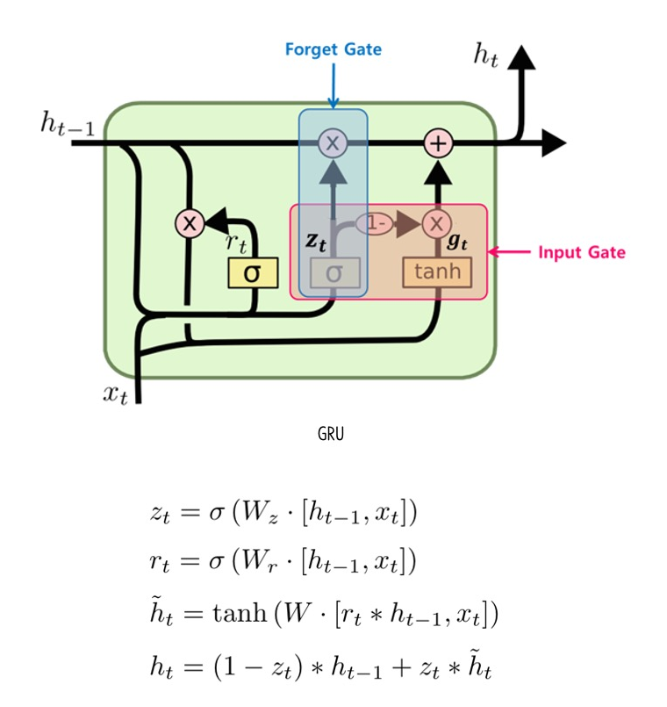
- Gated Recurrent Unit
- LSTM의 복잡한 구조를 간소화하면서 비슷한 성능을 내도록 제안된 모델. 셀 상태와 은닉 상태를 하나로 통합하고, 게이트 수를 2개로 줄임.
A. 핵심 구조
- Reset Gate (): 과거 정보를 얼마나 무시할지 결정.
- Update Gate (): 과거 정보와 현재 정보의 조합 비율을 결정. LSTM의 Forget Gate와 Input Gate 역할을 동시에 수행.
B. 정보 흐름
- Reset Gate가 이전 은닉 상태()의 어느 부분을 새로운 후보 은닉 상태()를 만드는 데 사용할지 결정.
- 후보 은닉 상태()를 계산.
- Update Gate가 이전 은닉 상태()를 얼마나 유지하고, 새로운 후보 은닉 상태()를 얼마나 반영할지 결정하여 최종 은닉 상태()를 계산.
C. 특징
- 장점: LSTM보다 파라미터 수가 적어 계산 효율이 높고, 학습 속도가 빠름. 많은 경우 LSTM과 대등한 성능을 보임.
- 단점: 데이터셋의 특성에 따라 LSTM보다 성능이 약간 낮게 나올 수 있음. LSTM만큼 정교한 정보 흐름 제어는 어려움.
D. 코드 예시
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class GRUModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers):
super(GRUModel, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(x.device)
out, _ = self.gru(x, h0)
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out
input_size = 10
hidden_size = 20
output_size = 5
num_layers = 2
seq_length = 15
batch_size = 3
model = GRUModel(input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers).to(device)
input_tensor = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_length, input_size).to(device)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.shape)
