연산(operator) = 명령어
= : 대입하라는 명령어
public class first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
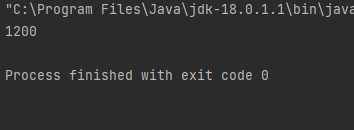
int number1 = 10;
// 가독성 차이로 number1 = number1 + 10;라고 할 것을 num += 10;이라고 표현 가능
System.out.println("number1 = 10 -> " + number1); // 10 출력
number1 += 10; // +10하고 대입
System.out.println("number1 += 10 -> " + number1); // 20 출력
number1 -= 10; // -10하고 대입
System.out.println("number1 -= 10 -> " + number1); // 10 출력
number1 *= 2; // *2하고 대입
System.out.println("number1 *= 2 -> " + number1); // 20 출력
number1 /= 2; // /2하고 대입
System.out.println("number1 /= 2 -> " + number1); // 10 출력
number1 %= 3; // /3하고 나머지 대입
System.out.println("number1 %= 3 -> " + number1); // 1 출력
}
}
public class first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 산술연산
// 나눗셈연산자 / 와 나머지연산자 % 차이
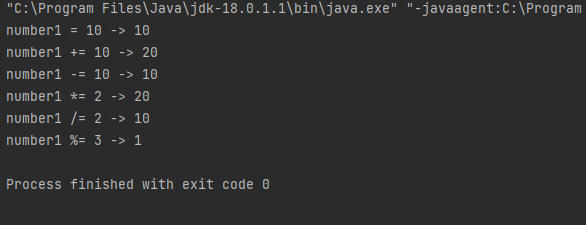
int a = 5;
int b = 2;
System.out.println(a/b); // 몫 : int이기 때문에 몫만 출력된 것, double일 경우 나눈 값이 출력
System.out.println(a%b); // 나머지
System.out.println((double)a/b); // ()안에 있는 것을 우선, double 값으로 강제형변환
// 증감연산
int c = 10;
++c; // 전위 연산
c++; // 후위 연산
// 우선수위의 차이
int d = 10;
int e = ++d;
System.out.println("result : " + e);
int x = 10;
int y = x++;
System.out.println("result : " + y);
System.out.println("x : " + x); // y를 먼저 10이라고 출력 후 증감연산 후 11이 되었음
}
}
public class first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 비교연산
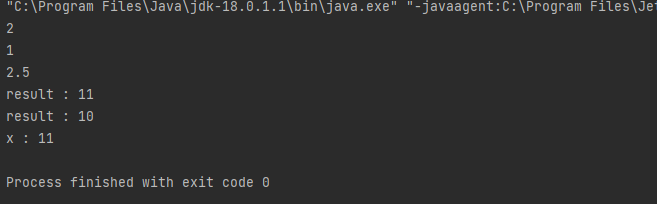
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
boolean c = a == b;
boolean d = a != b;
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(d);
// 논리연산
int x = 10;
int y = 5;
// and &&
System.out.println(x > y && x == 10); // true && true -> true
// 드모르간의 법칙 적용 가능
// or ||
System.out.println(x > y || x == y); // true || false -> true
// xor ^
System.out.println(x > y ^ x == 10); // true ^ true -> false
System.out.println(x < y ^ x == 10); // false ^ true -> true
// not 연산
System.out.println(x < y); // false
System.out.println(!(x < y)); // false -> true
System.out.println(x >= y); // !을 사용하는 것보다는 clean code
}
}
public class first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 삼항연산 ternary operator
// 조건식(결과값) ? 값1(true) : 값2(false)
int a = 70 > 60 ? 10 : 20;
int b = true ? 10 : 20;
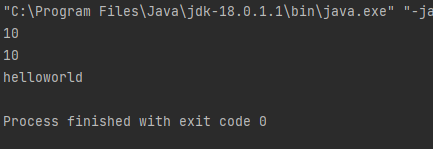
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
// 문자열 연산 +
String x = "hello";
String y = "world";
System.out.println("" + x + "" + y); // String에서는 - 연산 불가능
}
}
[연습문제]
package test;
public class practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int DOZEN = 12;
int colorPen = 5 * DOZEN;
int studentCount = 27;
int divColorPen = colorPen / studentCount;
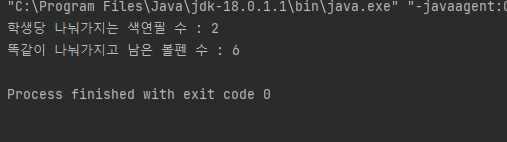
System.out.println("학생당 나눠가지는 색연필 수 : " + divColorPen);
int remainColorPen = colorPen % studentCount;
System.out.println("똑같이 나눠가지고 남은 볼펜 수 : " + remainColorPen);
}
}
package test;
public class practice4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 5;
double height = 130;
boolean withParent = false;
boolean heartDisease = true;
// 6살 이상인 경우, 6살 미만일 경우
boolean canRide = (age >= 6) && (height >= 120) && (!heartDisease) || (height >= 120 && withParent);
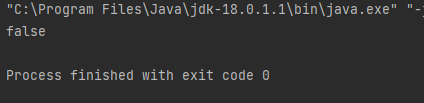
System.out.println(canRide);
}
}
package test;
public class practice5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year = 2022;
boolean isFourDivided = year % 4 == 0;
boolean isHundredDivided = year % 100 == 0;
boolean isFourHundredDivide = year % 400 == 0;
boolean leapYear = isFourDivided || (!isHundredDivided && isFourHundredDivide);
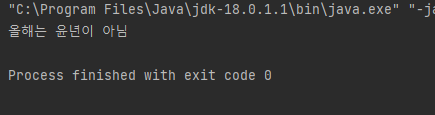
System.out.println("올해는 " + (leapYear ? "윤년임" : "윤년이 아님"));
}
}
package test;
public class practice6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int price = 187000;
int oman = price / 50000;
int ilman = (price - (oman * 50000)) / 10000;
int ochun = (price - (oman * 50000) - (ilman * 10000)) / 5000;
int ilchun = (price - (oman * 50000) - (ilman * 10000) - (ochun * 5000)) / 1000;
System.out.println("5만원권 : " + oman + "장");
System.out.println("1만원권 : " + ilman + "장");
System.out.println("5천원권 : " + ochun + "장");
System.out.println("1천원권 : " + ilchun + "장");
}
}
package test;
public class practice6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int price = 187000;
int oman = price / 50000;
price -= oman * 50000;
int ilman = price / 10000;
price -= ilman * 10000;
int ochun = price / 5000;
price -= ochun * 5000;
int ilchun = price / 1000;
System.out.println("5만원권 : " + oman + "장");
System.out.println("1만원권 : " + ilman + "장");
System.out.println("5천원권 : " + ochun + "장");
System.out.println("1천원권 : " + ilchun + "장");
}
}
// 이와 같이 더 단순하게 표현 가능package test.practice;
public class practice7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 1234;
int result = (number / 100) * 100;
System.out.println(result);
}
}