1. 문제 소개


2048. Next Greater Numerically Balanced Number
2. 나의 풀이법
처음 생각은 dfs였다.
문제의 범위는 까지였고, 그에 맞춰서 상한을 정해두었다.
이후에는 list에 숫자의 사용횟수를 적어가며 계산했다.
class Solution:
def nextBeautifulNumber(self, n: int) -> int:
if n == 0:
return 1
elif n > 1224444:
return
l = len(str(n)) + 1
used = [0] * 7
cand = set()
def is_balanced():
for d in range(1, 7):
if used[d] not in (0, d):
return False
return True
def dfs(path):
if path and is_balanced():
cand.add(int("".join(path)))
if len(path) == l:
return
for d in range(1, 7):
if used[d] < d:
used[d] += 1
path.append(str(d))
dfs(path)
path.pop()
used[d] -= 1
dfs([])
arr = sorted(cand)
i = bisect_right(arr, n)
return arr[i]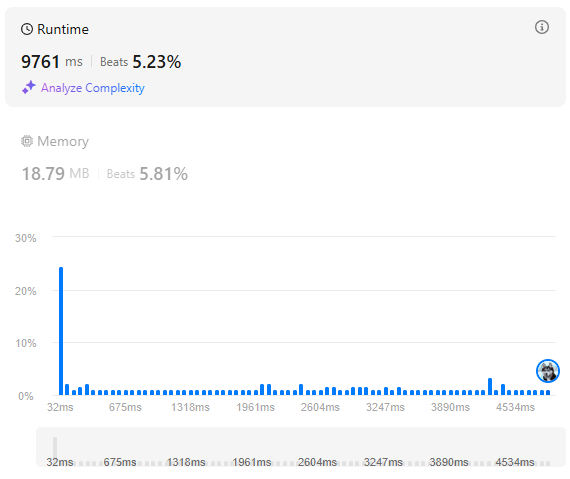
3. 다른 풀이법
class Solution:
def nextBeautifulNumber(self, n: int) -> int:
for i in range(n+1, 1224445):
count = Counter(str(i))
if all(count[d] == int(d) for d in count):
return i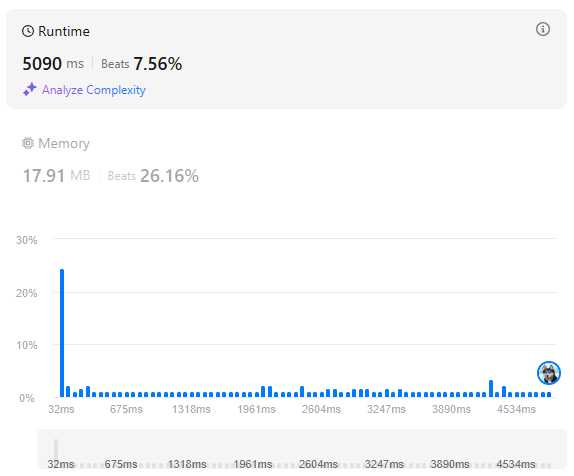
Editorial의 풀이는 굉장히 단순한 BruteForce였다.
시간복잡도는 이지만 확실한 풀이였다.
4. 결론
이렇게 적은 숫자의 경우에는 가능한 조합의 경우를 전부 박아넣어서 코드를 돌리기도 했다.
가능하다면 하드코딩이 제일인 것도 같다.
balance = [
1,
22,
122,
212,
221,
333,
1333,
3133,
3313,
3331,
4444,
14444,
22333,
23233,
23323,
23332,
32233,
32323,
32332,
33223,
33232,
33322,
41444,
44144,
44414,
44441,
55555,
122333,
123233,
123323,
123332,
132233,
132323,
132332,
133223,
133232,
133322,
155555,
212333,
213233,
213323,
213332,
221333,
223133,
223313,
223331,
224444,
231233,
231323,
231332,
232133,
232313,
232331,
233123,
233132,
233213,
233231,
233312,
233321,
242444,
244244,
244424,
244442,
312233,
312323,
312332,
313223,
313232,
313322,
321233,
321323,
321332,
322133,
322313,
322331,
323123,
323132,
323213,
323231,
323312,
323321,
331223,
331232,
331322,
332123,
332132,
332213,
332231,
332312,
332321,
333122,
333212,
333221,
422444,
424244,
424424,
424442,
442244,
442424,
442442,
444224,
444242,
444422,
515555,
551555,
555155,
555515,
555551,
666666,
1224444,
]
class Solution:
def nextBeautifulNumber(self, n: int) -> int:
return balance[bisect_right(balance, n)]