1. 문제 소개


2. 나의 풀이법
보자마자 bfs가 떠올랐다. 문제는 에 따라서 어떻게 효율적으로 알고리즘을 조정하는 것이다. 감이 잘 안잡혀 조금 검색하며 풀어보았다.
import heapq as hq
class Solution:
def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(grid)
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
dirs = [(1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), (0,-1)]
q = [(grid[0][0], 0, 0)]
visited[0][0] = True
while q:
h, x, y = hq.heappop(q)
if x == n-1 and y == n-1:
return h
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny]:
visited[nx][ny] = True
nh = max(h, grid[nx][ny])
hq.heappush(q, (nh, nx, ny))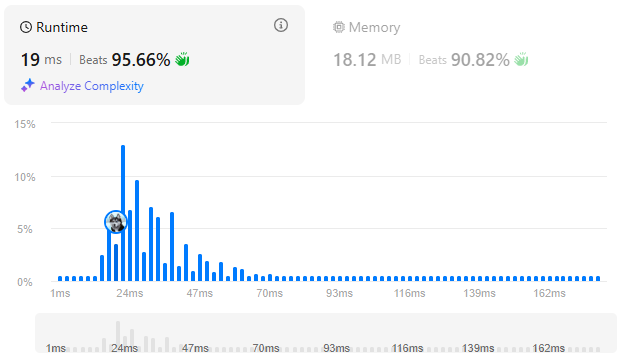
꽤나 좋은 성적을 냈다.
이전 문제와 비슷하게 풀었는데 말이다.
기분이 좋다.
이 경우 시간복잡도는 이고 공간복잡도는 이다.
3. 다른 풀이법
class Solution:
def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
def possible(mid):
seen = set()
def dfs(r, c):
if r == m-1 and c == n-1:
return True
seen.add((r, c))
for dr, dc in [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n and (nr, nc) not in seen:
if grid[nr][nc] <= mid:
if dfs(nr, nc):
return True
return False
return grid[0][0] <= mid and dfs(0, 0)
def binary_search():
lo, hi = grid[0][0], max(max(row) for row in grid)
while lo < hi:
mid = (lo + hi) // 2
if possible(mid):
hi = mid
else:
lo = mid + 1
return lo
return binary_search()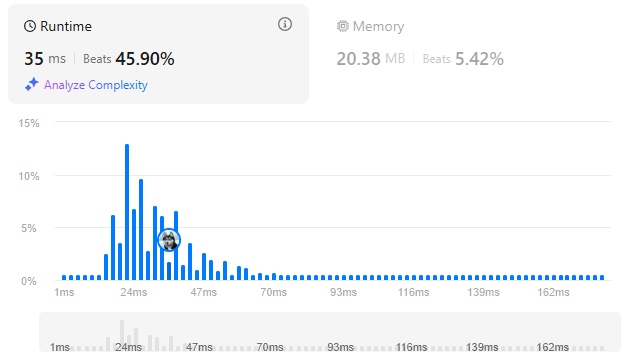
이 풀이법의 경우 binary search와 dfs를 사용했다.
이 경우도 시간복잡도는 이고 공간복잡도는 이다.
4. 결론
지금까지는 bfs를 이용한 풀이가 마음에 들어서 이를 반복했다. 구현도 재귀를 사용하는 dfs보다 쉽기 때문일 것이다.
둘 모두 잘 사용해서 풀어야겠다.
