Description
You are given an array of integers nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position.
Return the max sliding window.
Example
Input: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 Output: [3,3,5,5,6,7] Explanation: Window position Max --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
Approach
We are concerned about the largest elements. We want to store the elements in a way that when the maximum element is removed, we know the second maximum, and when that element is removed, we know the third maximum, and so forth.
Here, the key point is to avoid checking redudant elements. If the current element we are attempting to insert is the maximum element, then there is no point in looking at the other elements inside the queue, which can be removed.
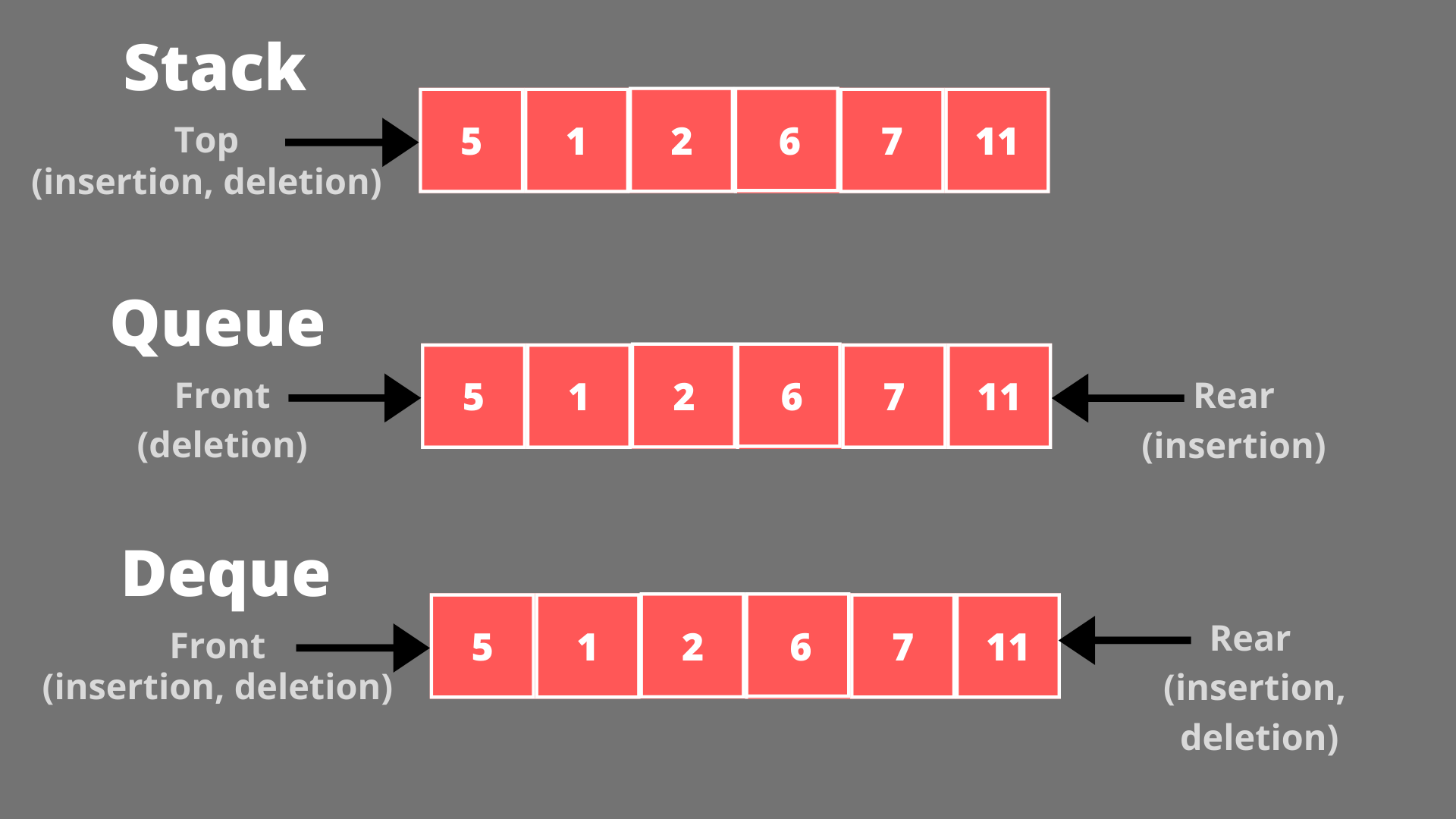
The problem describes a sliding window, which we know adds elements on the right and removes them from the left - this suggests a queue since operations are happening at opposite ends. Therefore, we use a double-ended queue (deque) for efficient operations.
Solution
import collections
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums, k):
queue = collections.deque()
answer = []
for i in range(k):
while len(queue) > 0 and nums[queue[-1]] < nums[i]:
queue.pop()
queue.append(i)
answer.append(nums[queue[0]])
for i in range(k, len(nums)):
while len(queue) > 0 and nums[queue[-1]] < nums[i]:
queue.pop()
queue.append(i)
if queue[0] + k == i:
queue.popleft()
answer.append(nums[queue[0]])
return answer