Description
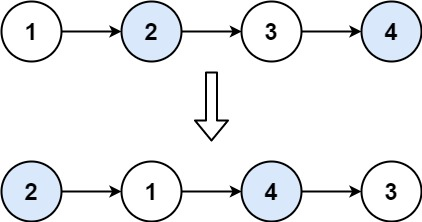
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
Examples
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,1,4,3]
Explanation:
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,2,3]
Output: [2,1,3]
Approach
Every recursion call is responsible for swapping a pair of nodes.
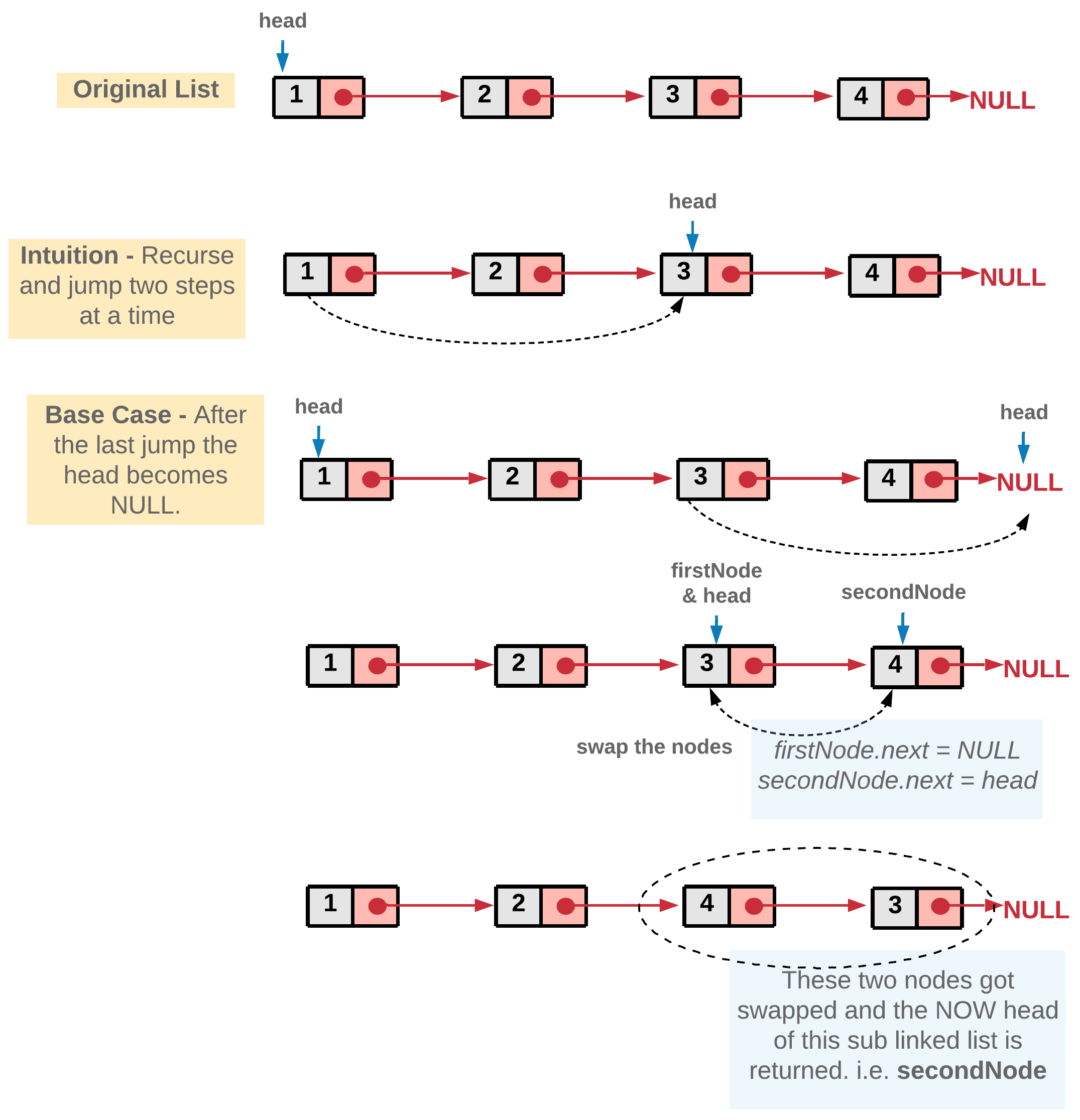
Next recursion is made by calling the function with head of the next pair of nodes. This call would swap the next two nodes and make further recursive calls if there are nodes left in the linked list.
Here, we would also use a dummy node to ensure that the head can be returned at all times.
Also, there are several edge cases that must be considered, each with where there's only one, two, and no nodes.
Solution
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head == None: return head
if head.next == None: return head
if head.next.next == None:
head.next.next = head
temp = head.next
head.next = None
return temp
def swap(curr, nxt):
temp = curr.next
temp.next = curr
curr.next = nxt
if nxt and nxt.next:
temp.next.next = swap(nxt, nxt.next.next)
return temp
dummy = head
return swap(head, head.next.next)