공부 내용
- Generative Model
- Generative Model 파라미터 수 감소 방법
- Auto-regressive Model
Generative Model
- 그럴듯한 이미지나 문장을 생성하는 모델 -> 하지만 그것이 전부는 아님
- Generator 외에 Discriminator까지 포함
-> 학습 시켰을 때 이미지 생성 외에 이미지 구별도 가능(explicit model)
explicit model : 확률 값을 얻어낼 수 있는 모델
implicit model : 단순히 생성만 할 수 있는 모델(ex. VAE, GAN)
Learning a Generative Model
- dog 이미지가 있다고 가정
- Generative Model 활용 다음과 같은 probability distribution P(x) 학습
- Generation : dog와 비슷한 새로운 sample 를 만듦(sampling)
- Density estimation: p(x) 활용 dog와 비슷한지 구별(분류)
-> anomaly detection에 활용 가능 - Unsupervised representation learning : 강아지의 일반적인 특징 학습(feature learning)
Basic Discrete Distributions
유한한 data set에 대한 확률분포
-
Bernoulli distribution : (biased) coin flip
- 0 또는 1
- p 값 한개로 확률분포 표현
-
Categorical distribution : (biased) m-sided dice
- 카테고리 m개 존재 -> 확률값 총합 1
- m-1 개의 파라미터 필요
Categorical Distribution Example
- RGB joint distribution (One Pixel)
- 경우의 수 :
- 파라미터 수 :

- n개의 binary pixels
- 경우의 수 :
- 파라미터 수 : - 1

파라미터 수가 너무 많다 -> 학습 어려워지므로 파라미터 수 감소시킬 필요 있음
Generative Model 파라미터 수 감소 방법
Structure Through Independence
-
n개의 pixel들이 모두 independent 하다고 가정 -> 파라미터 전부 더하면 됨
- 경우의 수 :
- 파라미터 수 :
-> 각 픽셀에 대해 파라미터 1개만 있으면 됨
-
개의 경우의 수를 단순히 n개로 표현
-> 모든 픽셀이 independent하다는 가정은 말이 안된다.(표현할 수 있는 이미지가 적음)
Conditional Independence
Fully Dependent와 Independent의 중간
-> Conditional independence와 Chain rule을 잘 섞음
-
Three important rules
- Chain rule: n개의 joint distribution -> n개의 conditional distribution
- independent 여부와 상관없이 항상 만족
- Bayes'rule:
- Conditional independence: z가 주어졌을 때 x와 y가 independent
-> x를 표현할 때 z가 주어지면 y는 없어도 됨(Conditional한 부분을 없애는 효과)
- Chain rule: n개의 joint distribution -> n개의 conditional distribution
-
단순 chain rule 활용 유도 방식
- 파라미터 수 -> chain rule을 활용했을 뿐 달라진 게 없음
- : 1개
- : 2개 -> x1이 주어졌을 때 0 또는 1일 확률
- : 4개
n에 대한 파라미터 수 : -> 이전과 같음
- 파라미터 수 -> chain rule을 활용했을 뿐 달라진 게 없음
-
Markov assumption 활용 유도 방식
- i+1 pixel은 i번째 pixel에만 dependent -> 나머지 pixel에는 independent
- 다음과 같은 식으로 유도 -> independent 한 pixel 없애 줌
- 파라미터 수 :
chain rule 적용 후 Markov assumption을 가하면, conditional independence를 활용해서
개의 파라미터를 개로 감소 가능
Auto-regressive Model
- Auto-regressive model은 conditional independency와 chain rule를 잘 활용한 모델
Example

- binary pixel을 가지고 있다고 가정
- 목표 : binary pixel에 대한 확률 분포 만드는 것
- 표현 방법
- joint distribution에 chain rule 적용 -> autoregressive model
- 이전 pixel에 대해서만 dependent하다는 보장 없음
-> i번째 pixel이 1부터 i-1번째 모든 픽셀에 대해 dependent 해도 Auto-regressive model - 어떤 식으로 conditional independence를 적용하느냐에 따라 모델 구조 달라짐
- 이전 pixel에 대해서만 dependent하다는 보장 없음
- ordering이 중요
- 이미지 각 pixel에 대한 순서를 매겨야 함
- 순서를 어떻게 정하느냐에 따라 성능 달라짐
- 이전 N개를 고려 할 때 Ar-N 모델이라고 부름
- joint distribution에 chain rule 적용 -> autoregressive model
NADE : Neural Autoregressive Density Estimator
- NADE는 주어진 input에 대한 density를 계산할 수 있는 explicit model
- density 계산 방법
- n개의 binary pixel이 주어졌다고 가정
- joint distribution을 chain rule을 통해 conditional distribution으로 표현
-> 각각을 independent하게 계산하여 확률 구함 - continuous random variable일 경우 gaussian mixture 활용
-> continuous한 distribution을 만듦
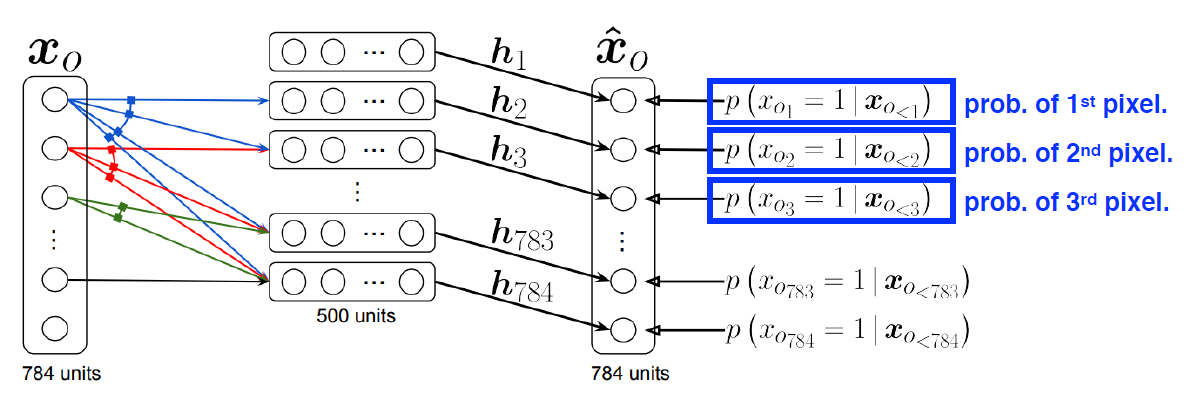
- i번째 픽셀을 1번째부터 i-1번째 픽셀에 대해 dependent하게 함
- neural network 입장에서는 입력 차원이 계속 달라짐 -> weight가 계속 커짐
Pixel RNN
- 이미지의 픽셀을 만들어 내기 위해 RNN 활용한 Auto-regressive model
- RGB image가 있을 때 i번째 pixel R, G, B 순차적으로 만듦
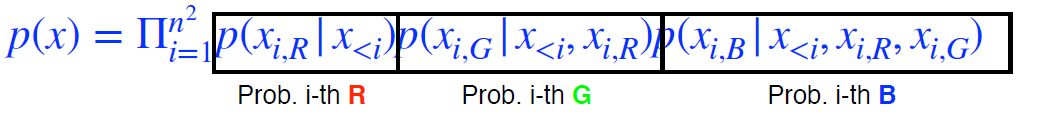
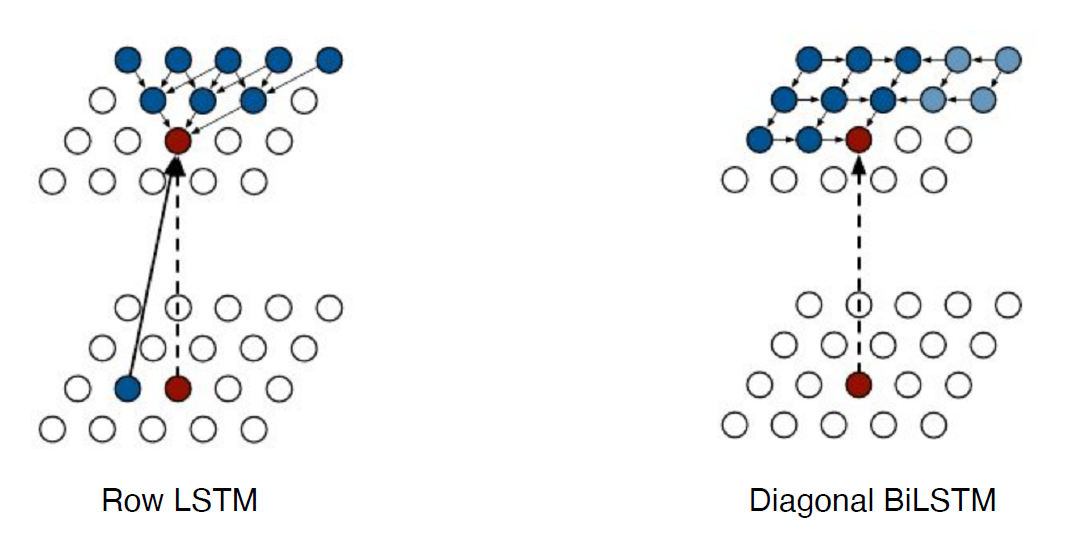
- chain ordering에 따라 다음과 같은 두 가지의 model architecture를 가짐
- Row LSTM : i번째 픽셀을 만들 때 위쪽의 정보 활용
- Diagonal BiLSTM : bidirectional LSTM 활용하되 ordering 기준 이전 정보 모두 활용