에러 (Error)
- 컴파일 에러 : 컴파일 도중 컴파일러가 발견하는 오류 (문법적 오류)
- 런타임 에러 : 컴파일은 성공적으로 진행이 되었으나, 프로그램 실행 중 발생하는 비정상적 종료 오류
- 논리적 에러 : 컴파일도 되고 프로그램도 실행이 되었지만, 프로그램이 의도대로 동작하지 않는 오류.
→ 프로그램이 실행되고 종료되었지만, 결과가 예상과 다른 경우
예외(Exception)
- 프로그래머가 적절한 코드를 통해 대비할 수 있는 오류
- ex) 클래스 형 변환 실패, 파일 읽기 실패
예외의 종류
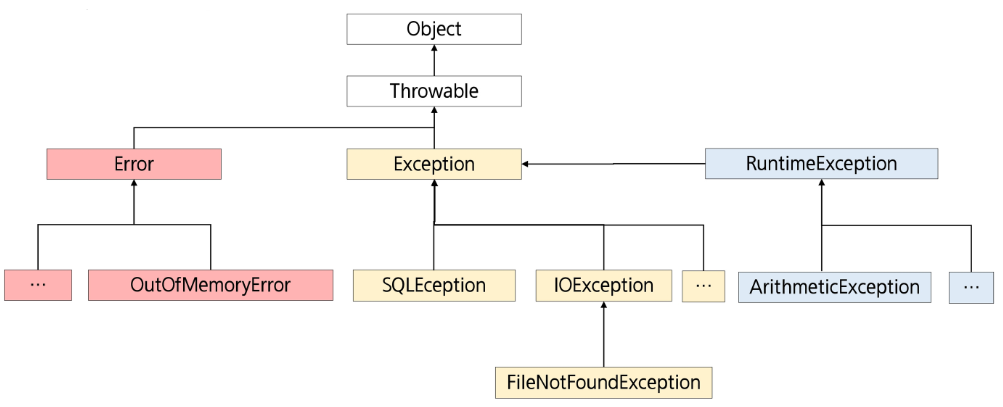
→ 붉은 색은 처리하지 않아도 된다.
- 체크 예외 : 컴파일 시점, 예외처리가 요구되는 예외 (컴파일 자체를 수행하지 않는다.)
ex. IOException, SQLException - 언체크 예외 : 실행 시점에서 발생하는 예외로, 컴파일러가 예외 처리를 강제하지 않음
ex. NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundesException
예외처리
- 예외 발생 시, 프로그램의 비정상 종료를 막고 정상적인 실행 상태를 유지하는 것.
- 예외의 감지 및 예외 발생 시 동작할 코드 작성 필요
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1. Unchecked Exception
- RuntimeException 자손
- 저장하는 순간, 이클립스에서 컴파일 수행
- 일단 실행은 되지만, 컴파일 시점 이후에 확인된다.
- 컴파일러가 예외 처리를 강제하지 않는다.
*/
int[] num = {10};
System.out.println(num[2]);
/*
2. Checked Exception
- Exception 자손 중에서, RuntimeException 자손은 아닌 애들
- 붉은 에러 표시로 보여준다. -> 컴파일 자체가 수행되지 않았다.
- 실행이 불가능하다.
*/
Class.forName("Hello");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}예외처리 키워드

- try : 예외 발생 가능성 있는 코드를 포함하는 블록
- catch (예외처리) : 예외 발생 시 실행 코드 블록, 괄호 생략 불가능 / catch하지 못하면 종료
- finally : 예외 발생 여부와 상관 없이 실행
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {10};
try {
System.out.println("1번 코드");
System.out.println(nums[2]); // 예외 발생 가능 코드
System.out.println("정상의 경우 출력");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("인덱스 범위 초과 에러");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally 출력");
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}1번 코드
인덱스 범위 초과 에러
finally 출력
프로그램 종료
다중 예외처리
- catch 를 여러 개 작성하여, 여러 종류의 예외를 처리할 수도 있다.
- 혹은,
catch (AExceoption | BException e) { }로 작성할 수 있다. - 예외 처리의 변수 명은 동일해도 괜찮다. 해당 블록에서 사용하는 변수 명이 되므로.
-
예외 객체에 해당하는 catch 문장을 찾을 때는 다형성 적용
-
상속 관계에서 상위 타입의 예외가 먼저 선언되는 경우, 뒤의 catch 블록은 동작할 기회가 없다.
-
상속 관계에서는 작은 범위에서 큰 범위 순으로 정의
-
예외 메세지를 확인하며, 프로그램 정상 종료 진행하는 방법
System.out.print(e.getMassage());e.printStackTrace();
-
catch에서 처리가 안 되는 예외가 있더라도, finally 구문은 진행 후 프로그램이 강제 종료가 된다.
-
try 메서드 내부에서
return;구문을 작성하더라도, finally는 진행 후에 main 메서드가 종료된다.
public class TryCatchTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {10};
try {
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println(nums[0]);
System.out.println("2");
return;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("3");
} finally {
System.out.println("4");
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
}1 2 4
예외 던지기 (throws)
- 예외를 처리하는 것이 아닌, 나를 호출한 곳으로 전달하여 처리하도록 하는 것
- 다형성 처리가 가능하다.
public class ThrowsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method1();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
method2();
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName("Hello");
}
}
- 프로그램의 시작점인 main method 에도 throw 하게 되면, 예외는 처리되지 않은 채 남게 된다.
이 경우, 비 정상적인 종료가 된다. - CheckedException 이 발생한다면 반드시 throws를 해줘야 하지만,
- UncheckedException은 원래 컴파일러가 봐주는 예외라서 쓰지 않아도 된다.
메서드 재정의와 throws
- 자식 클래스의 메서드는 부모 클래스의 메서드와 동일하거나 좁은 범위의 예외를 throws 할 수 있다.
- 자식 클래스의 메서드가 부모 클래스의 메서드보다 더 넓은 범위의 예외를 throws 하는 것은 허용되지 않는다.
- 자식이 부모의 기능을 숨길 수 없는 것처럼, 자식이 부모의 예외보다 큰 걸 던질 수는 없다.
class Parent{
void methodA() throws IOException{ }
void methodB() throws ClassNotFoundException{ }
}public class Child extends Parent {
@Override
void methodA() throws FileNotFoundException{ }
@Override
void methodB() throws Exception{ }
}자동 자원 반납 구문
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt");
// 메인 로직 작성
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}- 자원을 반납하게 되는 경우, finally에서 진행하여 코드가 길어지기도 했다.
- 다만, try 안에서 내가 쓸 자원을 명시하게 되는 경우, finally에서 쓰지 않고도 close()가 호출된다.
- 해당 부분은 AutoCloseavle 이라는 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스여야 가능하다.
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInpuStream("test.txt")) {
// 메인 로직 작성
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}사용자 정의 예외
- 기존에 정의된 예외 이외에 사용자가 직접 정의 예외를 작성할 수 있다.
- 대부분 Exception 또는 RuntimeException 클래스를 상속 받아 작성.
- Checked Exception 활용 : 명시적 예외 처리 또는 throws 필요
- 코드는 복잡해지지만, 처리, 누락 등 오류 발생 가능성은 줄어든다.
- Runtime Exception 활용 : 묵시적 예외 처리 가능
- 코드가 간결해지지만 예외 처리, 누락 가능성이 발생한다.
- Checked Exception 활용 : 명시적 예외 처리 또는 throws 필요
public class FruitNotFoundException extends Exception {
FruitNotFoundException(){}
FruitNotFoundException(String name){
// super : 현재 부모 class인 Exception의 생성자를 호출한다는 뜻
super(name + "에 해당하는 과일이 없습니다.");
}
}public class UserExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method1();
} catch (FruitNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void method1() throws FruitNotFoundException {
// 처리 진행 ... ing
// 예외 발생 !
// 예외를 직접 발생 시킬 때는 throw 키워드 사용
throw new FruitNotFoundException("사과");
}
} 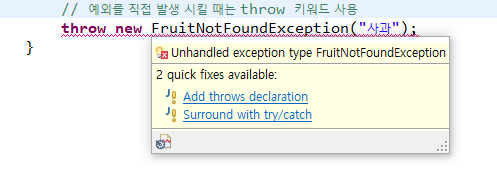
throw 사용하면 throw declaration을 진행하라고 한다.
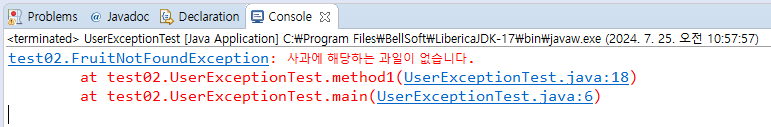
콘솔 창에 위와 같이 뜬다.
public class FruitNotFoundException2 extends RuntimeException {
FruitNotFoundException2(){}
FruitNotFoundException2(String name){
// super : 현재 부모 class인 Exception의 생성자를 호출한다는 뜻
super(name + "에 해당하는 과일이 없습니다.");
}
}- RuntimeException 과 같이 예외 처리가 필수적이지 않은 것을 정의하게 되는 경우,

실행 시에도, throws 나 try catch 를 작성하지 않아도 된다.