자료 구조
- 데이터에 효율적으로 접근하기 위해 선택되는 데이터의 조직 및 저장 형식
- 데이터 값들의 모음, 이들간의 관계, 데이터에 적용될 수 있는 연산의 모음
- 알고리즘 시간에 확인 가능
분류
- 정적 자료 구조 : 크기가 고정된 자료 구조(배열)
- 동적 자료 구조 : 크기가 변할 수 있는 자료 구조 (리스트, 스택, 큐)
선택 기준
- 데이터 접근 속도
- 메모리 사용 효율성
- 삽입 및 삭제의 효율성
- 순서 유지 여부
- 중복 데이터 허용 여부
컬렉션 프레임워크
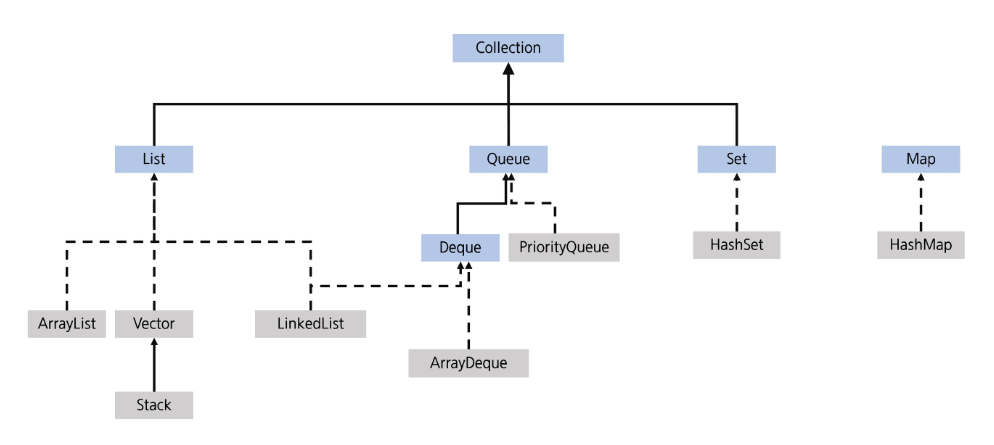
(푸른색 interface, 회색 class // 실선 - 상속, 점선 - 구현 )
- 다양한 자료 구조를 구현하여 제공
- 구성 요소 : 주요 인터페이스, 구현 클래스, 유틸리티 클래스로 구성
- 주요 인터페이스 : 전부 Generic을 사용해서 사용 제한 요소는 없다.
- Collection : List, Set, Queue 등 컬렉션의 상위 인터페이스
- List : 순서가 있는 컬렉션, 중복을 허용
- Set : 중복을 허용하지 않는 컬렉션
- Queue : FIFO 방식의 컬랙션
- Deque : 양쪽 끝에서 요소의 삽입, 삭제가 가능한 컬렉션
- Map <K, V> : 키-값 쌍으로 이루어진 요소의 컬렉션
- 주요 구현 클래스
- ArrayList : 동적 배열로 구현된 List
- 미리 배열을 만들어서, 크기가 변하는 경우 동적으로 관리
- LinkedList : 이중 연결 리스트로 구현된 List와 Deque
- Stack : LIFO(Last In First Out) 방식의 컬랙션
- HashSet : 해시 테이블 기반의 Set
- HashMap <K, V> : 해시 테이블 기반의 Map
- PriorityQueue : 힙(heap) 기반의 우선 순위 큐
- ArrayList : 동적 배열로 구현된 List
- 유틸리티 클래스
- Collections : 컬렉션 객체의 정렬, 검색 등을 위한 정적 메서드 제공- Arrays : 배열을 다루기 위한 유틸리티 메서드 제공
Collection 인터페이스
- List, Set, Queue 의 상위 인터페이스
List
- 순서가 있고, 중복을 허용한다. (배열과 유사)
- 내부적으로 배열을 이용하여 데이터를 관리
- 배열과 다르게 크기가 유동적으로 변함 (동적 자료구조)
- 배열을 다루는 것과 유사하게 사용할 수 있음.
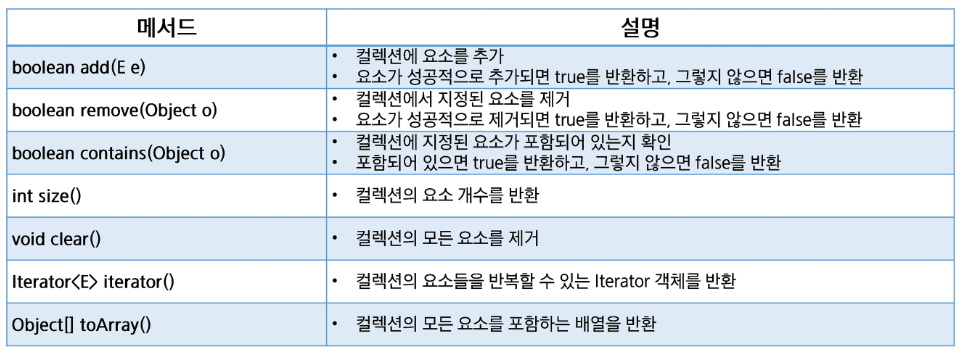
- 추가 :
add(element) - 조회 :
get(index),indetOf(찾고자 하는 내용) - 삭제 :
remove(index),remove(element),clear() - 수정 :
set(index, element)
- 배열로 변경 :
Product[] result = products.toArray(new Product[products.size()]);
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
names.add("luna");
names.add("max");
names.add("luna"); // 중복 허용
// 리스트가 비어있는지 확인
System.out.println(names.isEmpty());
// 수정
names.set(0, "Sting");
// 조회
names.get(0);
names.indexOf("max");
// 삭제
names.remove(0);
names.clear();
}- List 삭제의 특징
- List는 중복 값 삭제의 경우, 하나만 제거가 된다.
- 삭제하게 되는 경우, 리스트의 값은 하나씩 제거가 되는 것이다.
- 접근 속도는 빠르다.
- 데이터 삭제 시, 인덱스를 재조정하기 위해 전체 데이터를 옮기는 비효율성이 있다.
- 리스트의 중복 값 삭제를 위해 순회를 돌게 되는 경우,
삭제 시 사이즈와 인덱스 변경이 있으므로 뒤에서부터 값을 돌면 된다.
- LinkedList :
- 각 요소를 Node로 정의하고, Node는 다음 요소의 참조 값과 데이터로 구성
- 각 요소가 다음 요소의 링크 정보를 가지며, 연속적으로 구성될 필요가 없다.
Set
- 순서가 없지만, 중복을 허용하지 않는다.
- 빠른 속도와 효율적인 중복 데이터 제거 수단
- 동일성 판단 : hashcode && equals 메서드
- 단순 집합의 개념으로 정렬하려면 별도의 처리가 필요하다.
- 추가 :
add(element) - 조회 :
isEmpty(),contains(찾고자 하는 내용),size() - 삭제 :
remove(element),clear() - 변환 :
toArray()- Object 형 배열로 변환 /iterator()- iterator 인터페이스 객체 반환
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}public class settest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Person> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(new Person("luna", 3));
set.add(new Person("luna", 3));
System.out.println(set);
// equals는 동일하지만, new 사용으로 hashcode가 다르기 때문에 다른 값으로 된다.
}
}이런 경우, 동일한 값을 동일하게 처리하게 위해서는 Person class 에서 중복 값을 확인하는 메소드를 재정의 해야 한다.
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// 이름이 동일하면 hashcode가 동일하게 나올 수 있도록
return name.hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Person) {
Person p = (Person) obj;
return this.age == p.age;
}
return super.equals(obj);
}Map
- Key 와 Value를 하나의 Entry로 묶어서 데이터 관리
- 순서는 없으며, 키에 대한 중복은 없다.
- 속도가 빠름
- 추가 :
put(Key, value),putAll(Map<key, value> m- 기존 Collection 데이터 추가 - 조회 :
get(key),containsKey(key)- boolean 형 - 삭제 :
remove(key) - 변환 :
Set<Map.Entry<key, value>> entrySet(),keySet()- 모두 반환 가능
- map의 put은, key가 동일할 때, 덮어쓰기로 기존에 있던 값이 사라진다.
- Key로 구별이 되어야 함으로, 중복을 허용하지 않는다.
- 다만 값, value는 중복이 될 수 있다.
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map<키 자료형, 값 자료형>
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("luna", "cat");
map.put("max", "dog");
map.put("daisy", "cow");
map.put("toby", "cat");
map.put("luna", "dog"); // 중복의 key 값이 있으면, 그 뒤에 값이 수정된다.
// map 순회
// 1. keySet()
for(String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.printf("%s : %s \n", key, map.get(key));
}
// 2. entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.printf("%s : %s \n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}Queue
- LinkedList 구현체 사용
- FIFO, 가장 먼저 들어온 값이, 가장 먼저 빠져나간다.
- 추가 :
offer(element),add(element) - 가장 앞에 있는 데이터 조회 :
peek() - 가장 앞에 있는 데이터 꺼내기 :
poll() - 값의 여부 :
isEmpty()
public class QueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
//while 문과 함께 사용 가능
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
}Stack
- stack 클래스 사용, 인터페이스가 없다.
- LIFO, 가장 먼저 들어온 값이, 가장 나중에 빠져나간다.
- 추가 :
push(element) - 가장 위(마지막에 들어온) 데이터 조회 :
peek() - 가장 마지막에 들어온 데이터 꺼내기 :
pop() - 값의 여부 :
isEmpty()
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
// 값을 꺼내지 않고, 조회만 할 때
System.out.println(stack.peek()); //3
System.out.println(stack.peek()); //3
System.out.println(stack.peek()); //3
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
// 3, 2, 1 순서로 나옴
}
}Deque
- 구현체 ArrayDeque, LinkedList를 사용
- Array 의 경우, 실제로 배열을 갖고 리스트를 만드는 것이다.
- 중간에 삭제나 추가가 빈번하게 일어나면 어려움 조회는 가장 빠르게 할 수 있다. - LinkedList 의 경우, 초회는 느리지만, 중간에 삭제나 추가의 속도가 빠르다.
- Array 의 경우, 실제로 배열을 갖고 리스트를 만드는 것이다.
- 양쪽 끝에서 자유롭게 삭제, 삽입이 가능
- 추가 :
addFirst(element),addLast(element) - 제거 :
removeFirst(),removeLast() - 조회 :
peekFirst(),peekLast() - 비어있는지 여부 :
isEmpty()
public class DequeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addFirst(1);
deque.addFirst(2);
deque.addLast(3);
deque.addFirst(4);
System.out.println(deque);
// 4, 2, 1, 3
}
}컬렉션의 정렬
- 요소들을 특정 기준에 맞추어 오름차순 또는 내림차순으로 배치하는 것
- 순서를 가지는 Collection들만 정렬 가능하다. (예 : list)
- Collections 의 sort()를 이용한 정렬
- Comparable interface
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class SortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 순서가 있는 자료 구조만 가능
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
names.add("daisy");
names.add("luna");
names.add("max");
names.add("alice");
System.out.println(names);
// [daisy, luna, max, alice]
Collections.sort(names);
System.out.println(names);
// [alice, daisy, luna, max]
}
}- 알파벳은 오름차순으로, 수의 크기대로 오름차순 정렬 가능
public class SortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 순서가 있는 자료 구조만 가능
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>();
persons.add(new Person("daisy", 3));
persons.add(new Person("luna", 5));
persons.add(new Person("max", 6));
persons.add(new Person("alice", 2));
System.out.println(persons);
Collections.sort(persons);
System.out.println(persons);
}
}이와 같이 사용자 정의 class의 경우 기본적으로 정렬이 불가능하다.
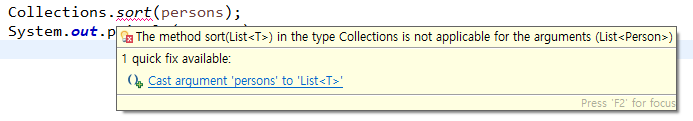
사용자 정의 class에 비교 비교 기준을 만드는 방법
comparable 클래스 사용
- class를 정의하는 class 내부에 작성
public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo<Person o>{
return this.age - o.age;
// 양수 : 자리 바꿈
// 음수 : 자리 그대로
// 0 : 동일 위치
}- 나이를 비교하여, sort를 진행할 수 있게 하였다.
Comparator
- 객체가 Comparable을 구현하고 있지 않거나, 사용자 정의 알고리즘으로 정렬하려는 경우
public class PersonComparator implements Comparator<Person>{
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
}이렇게 작성 후에는 Collections.sort(persons, new PersonComparator()); 으로 쓰면 된다.
- 1회성 정의
Collections.sort(persons, new PersonComparator<String>(){
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
});- 람다 표현식
Collections.sort(persons, (o1, o2) -> {
return Integer.compare(o1.length(), o2.length());
});