Kong, X., Huang, J., Tung, Z., Guan, J., & Huang, M. (2021). Stylized story generation with style-guided planning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.08625.
- contribution: first stylized story generation(pilot study)
Introduction
-
story generation의 main task: enhancing coherence, introducing commonsense knowledge etc
-
style에 대한 연구는 부족: 글의 작성 목적에 따라 style이 달라질 수 있으므로 중요함
-
본 연구에서는 emotion-driven(국문의 형용사, 관형사에 대응), event-driven(국문의 동사에 대응)으로 style을 나누어 generation
-
emotion-driven stories의 keyword는 NRCLex로부터, event-driven stories의 keyword는 NLTK 이용해 동사 추출
-
2-step model: keyword distribution 예측 -> keyword distribution으로부터 generation
-
새로운 metrics 제안: lexical level, semantic level
Method
- objective: input sentence with style(, or ) -> output
- planning -> generation의 순서
- total loss 를 최소화
planning
- output y에 등장할 가능성이 있는 keyword distribution을 구하는 것: 가능한 모든 선택지의 keyword(set )를 대상으로 계산
keyword distribution , 는 encoder의 last layer를 context vector로 사용- loss function: ground-truth keyword distribution()과 predicted keyword distribution()의 cross entropy loss 사용
generation
- output word 를 예측하기 위해 planning에서 도출된 keyword distribution(), input word set(), output word() 이용
- : planning의 keyword distribution을 고려하지 않은 단어집합()에서의 distribution
- : gate vector indicating weight of keyword distribution()
- loss function: 정답의 negative log-likelihood()
Experiment
- ROCStories corpus 사용: 첫 번째 문장을 제시하고, 이후 4개 문장을 구성
- BartForConditionalGeneration을 사용해 tokenizing, encoding 등 수행
- 고유명사를 male/female/neutral로 mask해 generalize하였음
- baseline: GPT-2, BART
keywords
- keyword를 word-emotion lexicon으로 mapping: e.g. favorite -> joy
참고: NRCLex - emotional keywords: selected emotion labels: fear, anger, surprise, sadness, disgust, joy
- event keywords: NLTK로 동사 추출, 하위 IDF keyword 제외
style annotation
- 각 story별로 emotional, event의 keyword 등장횟수()를 normalize하여() emotional keyword, event keyword의 등장빈도를 비교
- story 안에서 emotional, 또는 event keyword의 절대적인 빈도가 낮거나(threshold ), 두 style의 빈도 차이가 크지 않으면(threshold ), 'other'로 분류
evaluation & result
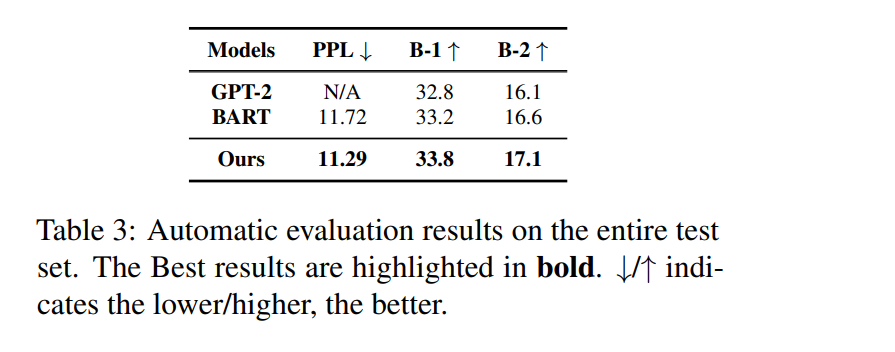
(1) perplexity
(2) BLEU: n-gram overlap evaluation
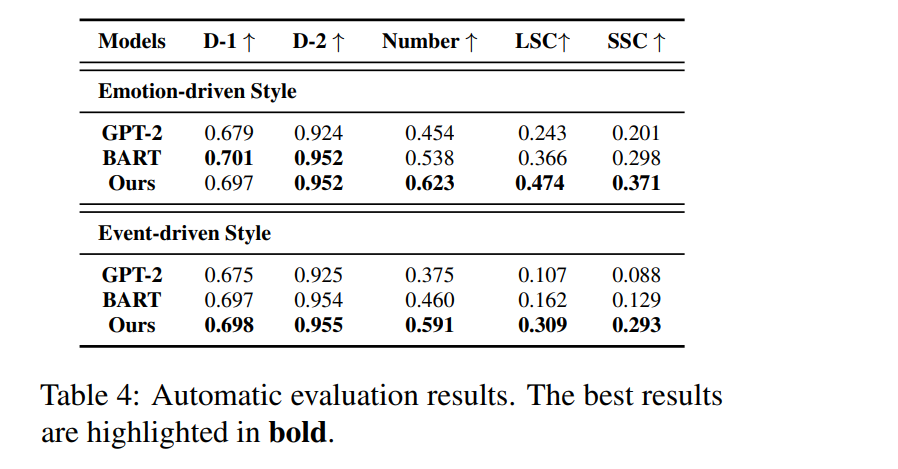
(3) Distinct: generation diversity(percentage of unique n-grams)
(4) Numbers of Stylistic Keywords: evaluation on consistent stylistic keywords of generated stories
(5) Lexical Style Consistency(LSC): (stylistic keywords consistency를 유지한 stories)/(total generated stories)
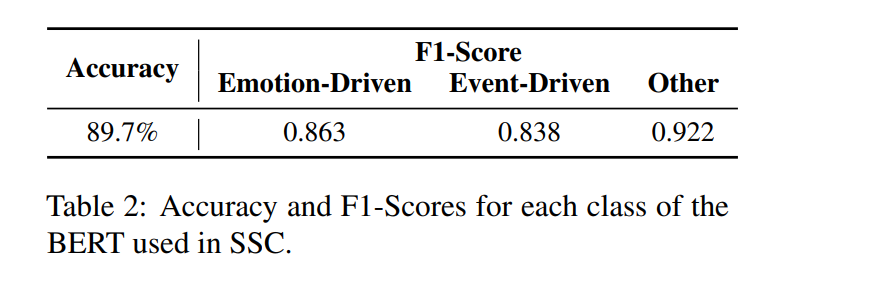
(6) Semantic Style Consistency(SSC): BERT(base) finetune하여 story style을 emotion/event/others로 분류할 수 있게 학습하고, training set에 대해 golden truth의 bert-classified consistency와 generated stories의 style consistency를 비교해 F1-Socre, accuracy 계산
- 결과: baseline에 비해 human-written stories와 overlap 높고, lower perplexity 보여줌
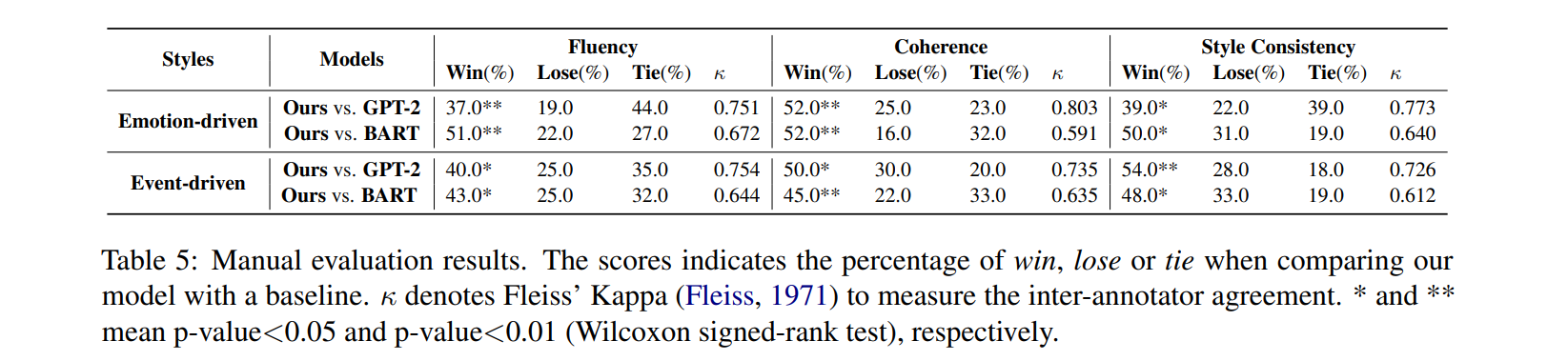
lexical, semantic style consistency, more number of keywords than baselines, comparable diversity with baselines - AMTurk 이용한 human evaluation: 정답과 generated stories 사이에서 fluency, coherence, style consistency에 대해 3 annotators가 win/lose/tie를 매김
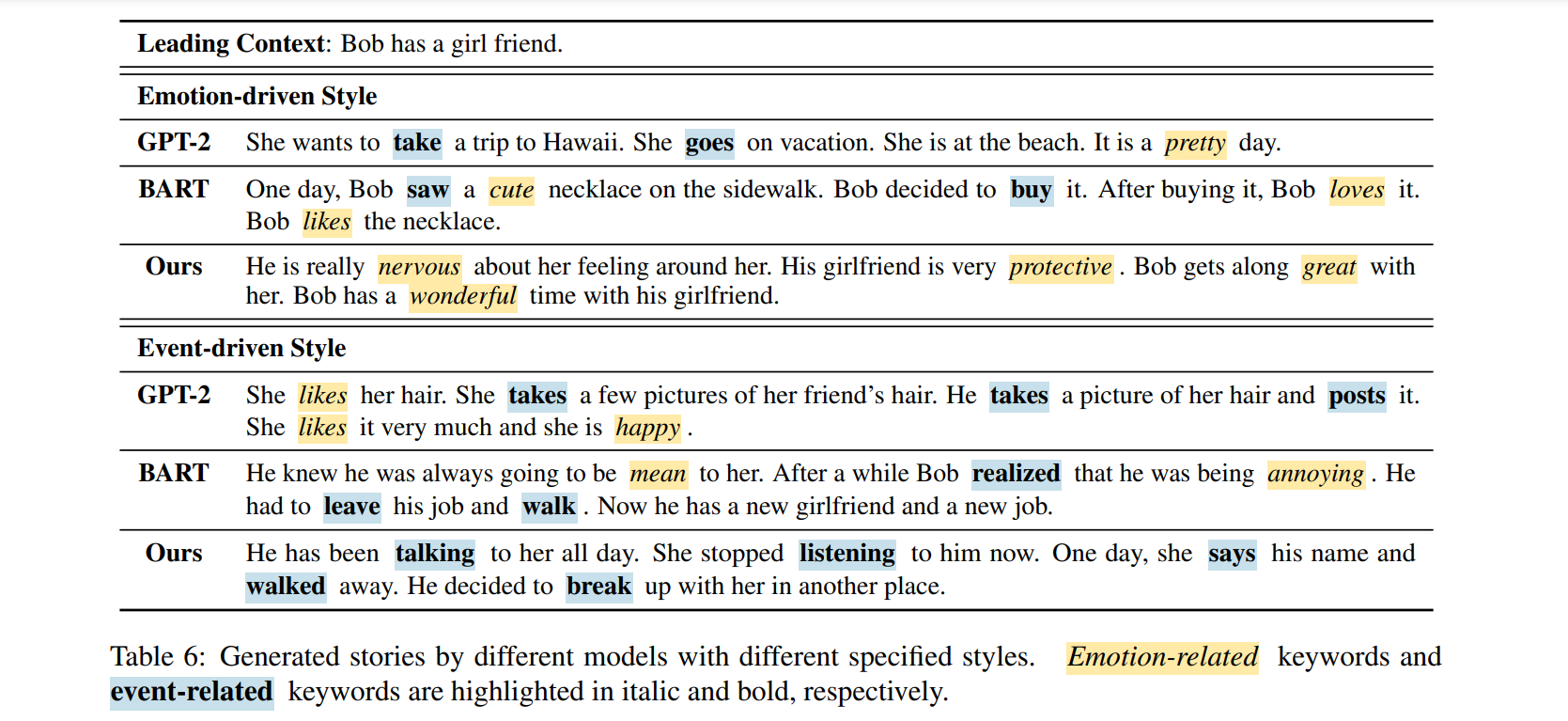
- example inference below
Conclusion & Opinion
- pilot study on a new task: stylized story generation(emotion & event)
- baseline에 비해 준수한 performance
- legal QA에서 같은 내용의 다른 표현방식의 답변을 제공하는 것에도 사용할 수 있을까..?
- pilot study라 experiment 규모 작은데, 후속 연구 찾아보자
- 는 무엇을 의미..?