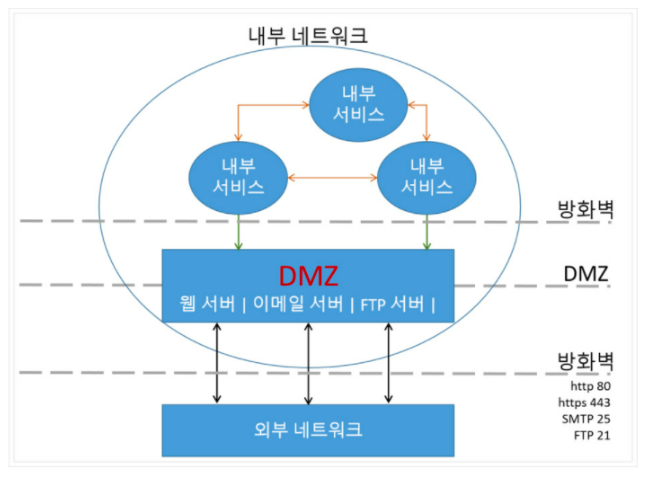
Firewall(방화벽) 은 무엇인가?
- 인터넷과 같은 외부 네트워크에 연결되어 있는 내부 네트워크의 중요한 정보 및 자원을 외부 네트워크를 통한 불법적인 침입으로부터 안전하게 보호하기 위한 시스템
- 외부로부터 내부 네트워크를 보호하기 위해 강력한 접근 제어를 제공하는데, 이를 위해 외부망과 내부망의 구성을 위한 별개의 네트워크를 갖고 있음
- 외부망 사용자가 내부망에서 제공하는 서비스를 이용하려면 반드시 방화벽 시스템을 통과해야함
- 단점으로는 해킹과 같은 외부에서 공격하는 경우는 막을수 있지만, 내부에서 공격하는 경우에는 매우 약한 특징이 있음
DMZ 는 무엇인가?
- 기관들은 보안의 목적으로 폐쇄 형태의 내부 네트워크(LAN: Local Area Network)만 사용하여 각종 인트라넷이나 내부 시스템을 운영하는 방법도 있지만, 이러면 외부 네트워크로는 단절되어서 웹 검색이나 이메일링, DNS사용, FTP 등의 기본적인 인터넷 서비스를 사용할 수 없다.
- 따라서 내부 네트워크에 존재하지만, 외부에서 접근할 수 있는 특수한 네트워크인 DMZ 를 사용함
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 는 무엇인가?
- 일종의 가상 네트워크 센터 (Virtual Private Cloud)
- IP 주소 범위 선택, 서브넷 생성, 라우팅 테이블 및 네트워크 게이트웨이 구성 등 가상 네트워킹 환경
내부 IP 사용 - 각각 방화벽 존재 -> 외부 접속은 차단해주고 같은 VPC(default)내에서 내부 접속은 가능
출처:
https://velog.io/@ko1586/Firewall-DMZ-%EB%AD%94%EB%8D%B0
https://velog.io/@yjin/FirewallDMZVPC
https://velog.io/@ko1586/Firewall-DMZ-%EB%AD%94%EB%8D%B0
(영문 해석)
What is a DMZ Network?
-
In computer security, a DMZ Network (sometimes referred to as a “demilitarized zone”) functions as a subnetwork containing an organization's exposed, outward-facing services. It acts as the exposed point to an untrusted networks, commonly the Internet.
-
The goal of a DMZ is to add an extra layer of security to an organization's local area network. A protected and monitored network node that faces outside the internal network can access what is exposed in the DMZ, while the rest of the organization's network is safe behind a firewall.
When implemented properly, a DMZ Network gives organizations extra protection in detecting and mitigating security breaches before they reach the internal network, where valuable assets are stored.
What is a VPC?
- A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a secure, isolated private cloud hosted within a public cloud.
- VPC customers can run code, store data, host websites, and do anything else they could do in an ordinary private cloud, but the private cloud is hosted remotely by a public cloud provider. (Not all private clouds are hosted in this fashion.)
- VPCs combine the scalability and convenience of public cloud computing with the data isolation of private cloud computing.
Imagine a public cloud as a crowded restaurant, and a virtual private cloud as a reserved table in that crowded restaurant. Even though the restaurant is full of people, a table with a "Reserved" sign on it can only be accessed by the party who made the reservation. Similarly, a public cloud is crowded with various cloud customers accessing computing resources – but a VPC reserves some of those resources for use by only one customer.
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DMZ_(computing)
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-a-virtual-private-cloud/
https://www.barracuda.com/glossary/dmz-network
