트리 구조
- 트리(Tree) : Node와 Branch를 사용해서, 사이클(원형)을 이루지 않도록 구성한 데이터 구조이다.
- 이진 트리(Binary Tree) 형태의 구조를 가장 많이 사용하며, 탐색(검색) 알고리즘 구현을 위해 많이 사용된다.
트리 용어
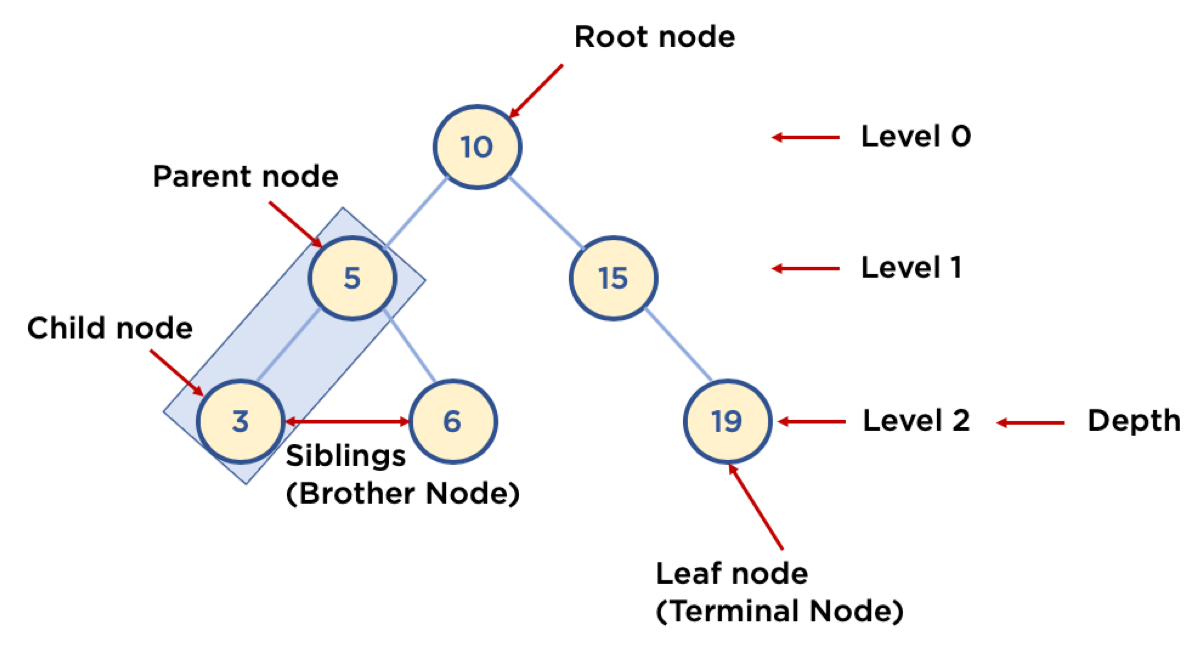
Node : 트리에서 데이터를 저장하는 기본 요소(데이터, 연결된 다른 노드에 대한 Branch 정보)Root Node : 트리 맨 위에 있는 노드Level : 최상위 노드를 Level 0으로 정했을 때, 하위 Branch로 연결된 노드의 깊이를 나타낸다.Parent node : 어떤 노드의 하위 레벨에 연결된 노드Child Node : 어떤 노드의 상위 레벨에 연결된 노드Leaf Node : Child Node가 하나도 없는 노드Sibling : 동일한 Parent Node를 가진 노드Depth : 트리에서 node가 가질 수 있는 최대 Level
이진 트리
- 이진 트리 : 노드의 최대 Branch가 2인 트리이다.
이진 탐색 트리

- 이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree) : 이진 트리에 추가적인 조건이 있는 트리
- 왼쪽 자식 노드는 부모 노드보다 작은 값, 오른쪽 자식 노드는 부모 노드보다 큰 값을 가진다.
이진 탐색 트리의 장점과 용도
- 장점
- 배열을 사용하여 탐색할 때보다 시간 복잡도가 줄어든다. -> O(logn)
- 동적으로 데이터 집합 크기가 바뀌고 순서가 바뀌어도 문제가 발생하지 않는다.
- 용도 : 데이터 검색(탐색)
이진 탐색 트리의 시간 복잡도와 단점
- 시간 복잡도
- 이진 탐색 트리의 노드가 n개라면, 트리의 높이(Depth)인 h=log2n에 수렴한다.
즉, 시간 복잡도는 O(logn)이다.
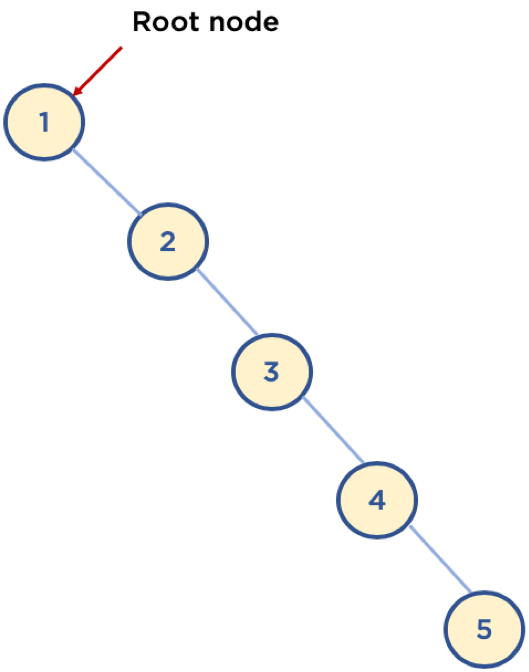
- 단점
- 평균 시간 복잡도는 O(logn)이다. 하지만 이것은 트리가 균형 잡혀 있을 때의 시간 복잡도이다.
- 다음 예시와 같이 구성되어 있을 경우, 연결 리스트와 동일한 성능을 보여준다. O(n)
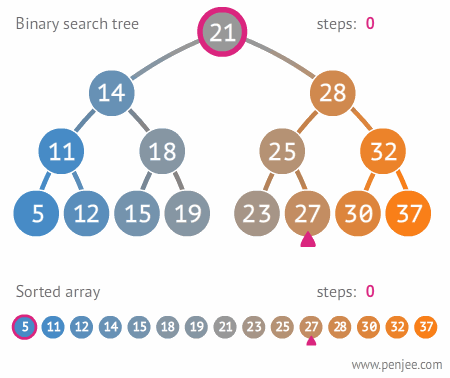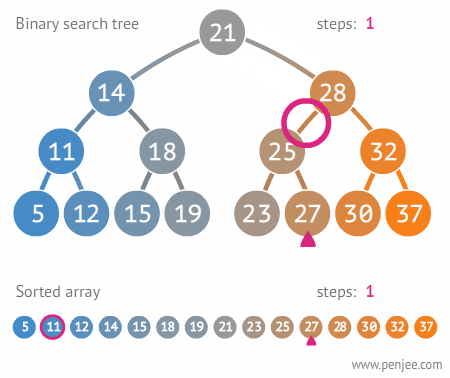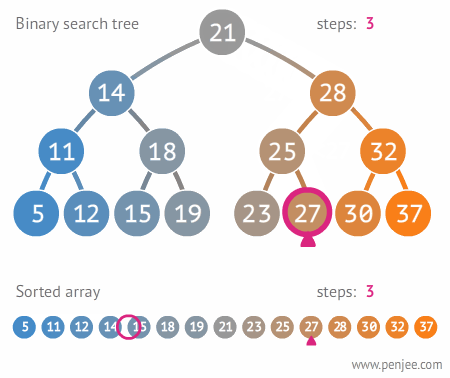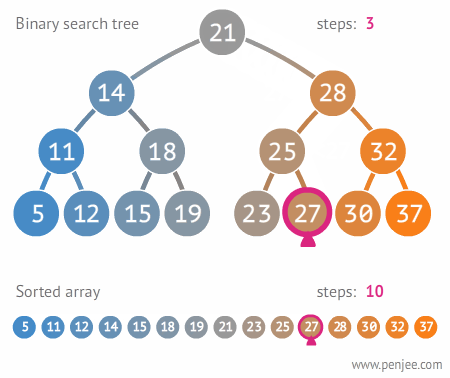
이진트리와 정렬된 배열간의 탐색 비교
이진 탐색 트리 구현
이진 탐색 트리에 데이터 넣고 탐색해보기
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BinarySearchTree:
def __init__(self, head):
self.head = head
def insertNode(self, value):
self.current_node = self.head
while True:
if self.current_node.value > value:
if self.current_node.left != None:
self.current_node = self.current_node.left
else:
self.current_node.left = Node(value)
break
else:
if self.current_node.right != None:
self.current_node = self.current_node.right
else:
self.current_node.right = Node(value)
break
def searchNode(self, value):
self.current_node = self.head
while self.current_node:
if self.current_node.value == value:
return True
elif self.current_node.value > value:
self.current_node = self.current_node.left
else:
self.current_node = self.current_node.right
return False
head = Node(5)
BST = NodeMgmt(head)
BST.insertNode(10)
BST.insertNode(1)
BST.insertNode(4)
BST.insertNode(6)
print(BST.searchNode(1))
print(BST.searchNode(-1))
True
False





.png)