해시 테이블 구조
Hash Table : key 에 value 를 저장하는 데이터 구조이다.
- key를 통해 데이터를 바로 받아올 수 있어서 속도가 빠르다.
- 파이썬의 딕셔너리
{} 가 해시 테이블이다.
- 배열로 미리 해시 테이블 사이즈만큼 생성 후에 사용한다.
해시 테이블 시간복잡도
- 충돌이 없는 경우 :
O(1)
- 충돌이 모두 발생하는 경우 :
O(n)
해시 테이블 용어
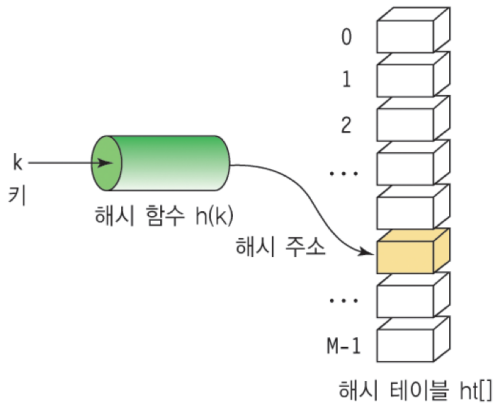
Hash : 임의 값을 고정 길이로 변환하는 것이다.Hash Table : key값으로 연산을 하여 직접 접근이 가능한 데이터 구조이다.Hashing Function : key값으로 연산을 하여 데이터 위치를 찾을 수 있는 함수이다.Hash valueorHash Address : key값을 해싱 함수로 연산하여 해시 값을 반환받고, 이것으로 해시 테이블에서 해당 key에 대한 데이터 위치를 일관성있게 찾을 수 있다.slot : 한 개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 공간이다.
해시 테이블 장단점 및 용도
- 장점
- 데이터 저장/읽기 속도가 빠르다.(=검색속도가 빠르다.)
- 해시는 키에 대한 데이터가 있는지 확인이 쉽다.(=중복확인이 쉽다.)
- 단점
- 일반적으로 저장공간이 좀 더 필요하다.
- 여러 키에 해당하는 주소가 동일할 경우 충돌을 해결하기 위한 추가 자료구조가 필요하다.
- 용도
- 검색이 많이 필요한 경우
- 저장, 삭제, 읽기가 빈번한 경우
- 캐시 구현할 경우(중복확인이 쉽기 때문이다.)
해시 테이블 구현
리스트를 활용하여 해시 테이블 구현
hash_table = list(0 for _ in range(8))
def get_key(data):
return hash(data)
def hash_func(key):
return key % 8
def save_data(data, value):
hash_address = hash_func(get_key(data))
hash_table[hash_address] = value
def read_data(data):
hash_address = hash_func(get_key(data))
return hash_table[hash_address]
save_data('Lee', '01011112222')
save_data('Kim', '01033334444')
save_data('Park', '01055556666')
save_data('Kang', '01077778888')
print(read_data('Park'))
충돌 해결 알고리즘
Chaining 기법
Open Hashing : 해시 테이블 저장공간 외의 공간을 활용하는 기법- 충돌이 발생하면, 연결 리스트 자료구조를 활용하여 연결 리스트로 데이터를 연결시켜 저장하는 기법이다.
hash_table = list(0 for _ in range(8))
def get_key(data):
return hash(data)
def hash_func(key):
return key % 8
def save_data(data, value):
index_key = get_key(data)
hash_address = hash_func(index_key)
if hash_table[hash_address] != 0:
for index in range(len(hash_table[hash_address])):
if hash_table[hash_address][index][0] == index_key:
hash_table[hash_address][index][1] = value
return
hash_table[hash_address].append([index_key, value])
else:
hash_table[hash_address] = [[index_key, value]]
def read_data(data):
index_key = get_key(data)
hash_address = hash_func(index_key)
if hash_table[hash_address] != 0:
for index in range(len(hash_table[hash_address])):
if hash_table[hash_address][index][0] == index_key:
return hash_table[hash_address][index][1]
return None
else:
return None
save_data('Lee', '01011112222')
save_data('Lem', '01033334444')
save_data('Leo', '01055556666')
print(read_data('Leo'))
print(hash_table)
01055556666
[[[-3493608407143804680, '01011112222'], [3139630669677575136, '01033334444'], [-4679829885639949944, '01055556666']],
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0]
Linear Probing 기법
Close Hashing : 해시 테이블 저장공간 안에서 충돌 문제를 해결하는 기법- 충돌이 발생하면, hash address의 다음 address부터 맨 처음 나오는 빈공간에 저장하는 기법이다.
hash_table = list(0 for _ in range(8))
def get_key(data):
return hash(data)
def hash_func(key):
return key % 8
def save_data(data, value):
index_key = get_key(data)
hash_address = hash_func(index_key)
if hash_table[hash_address] != 0:
for index in range(hash_address, len(hash_table)):
if hash_table[index] == 0:
hash_table[index] = [index_key, value]
return
elif hash_table[index][0] == index_key:
hash_table[index][1] = value
return
else:
hash_table[hash_address] = [index_key, value]
def read_data(data):
index_key = get_key(data)
hash_address = hash_func(index_key)
if hash_table[hash_address] != 0:
for index in range(hash_address, len(hash_table)):
if hash_table[index] == 0:
return print("해당 데이터는 저장되지 않았습니다.")
elif hash_table[index][0] == index_key:
return hash_table[index][1]
else:
return print("해당 데이터는 저장되지 않았습니다.")
save_data('Lee', '01011112222')
save_data('Lem', '01033334444')
save_data('Leo', '01055556666')
read_data('L')
print(hash_table)
해당 데이터는 저장되지 않았습니다.
[0, 0, 0, [-5753092057274981677, '01055556666'], [8054465307741704620, '01033334444'], 0, 0, [5247878448664773471, '01011112222']]
빈번한 충돌을 개선하는 기법
- 해시 함수를 재정의 및 해시 테이블의 저장공간을 확대 한다.
hash_table = list(0 for _ in range(16))
def hash_func(key):
return key % 16


.png)