A Multi-Task Benchmark for Korean Legal Langhage Understanding and Judgement Prediction
paper-study
1. Introduction
- Previous Legal Export Systems
- Useful on certain areas
- Deep Learning Based Approach
- Legal Judgement Prediction
- Legal Content Generation
- Legal Text Classification
- Legal Event Detection
- Legal Information Extraction
- Legal Contract Review and QA
- LBOX
-
Large Scale Korean legal AI benchmark
- precedent corpus
- classification tasks (Case Name, Statute)
- judgement prediction task (LJP-Criminal, Civil)
- summarization task
-
pre-trained LCUBE (decoder only, based on GPT-2)
- doesn't have advantage on summarization task
-
2. Background
2.1 Korean Legal System
-
Three-tiered (District, High and the Supreme Court)
-
rooted in civil law system (vs. common law system)
2.2 Korean Precedent
-
Structure of Korean Precedent
-
meta information
-
gist of claim from plaintiffs in a civil case
-
ruling
-
reasoning
-
facts
-
claims
-
reasoning
-
decisions
-
-
-
The Redaction Process
- Anonymizing
-
Precedent Disclosure Status
- Courts' decision should be pubshed via online service
3. LBOX Open Datasets
3.1 Structuring Raw Data
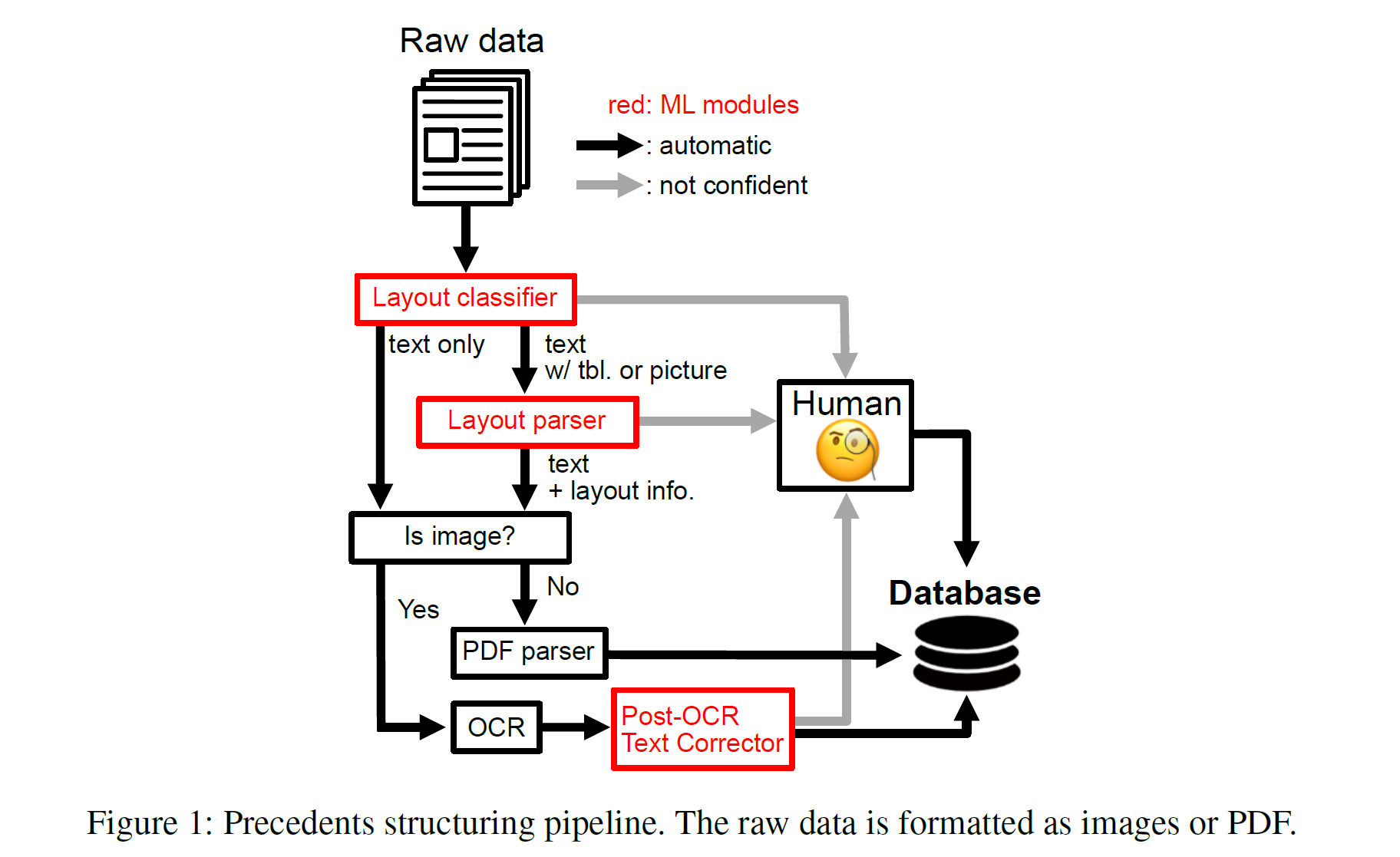
-
Document Images and PDF precedents are available
-
Preprocessing pipeline
- Layout Classifier (based on ResNet)
- Layout Parser (based on Mask-R-CNN)
- OCR
- Custom Language Model to correct OCR errors
- Human annotation for low-confidence instances
-
JSON format
- meta information
- ruling
- gist of claim
- appeal
- reasoning
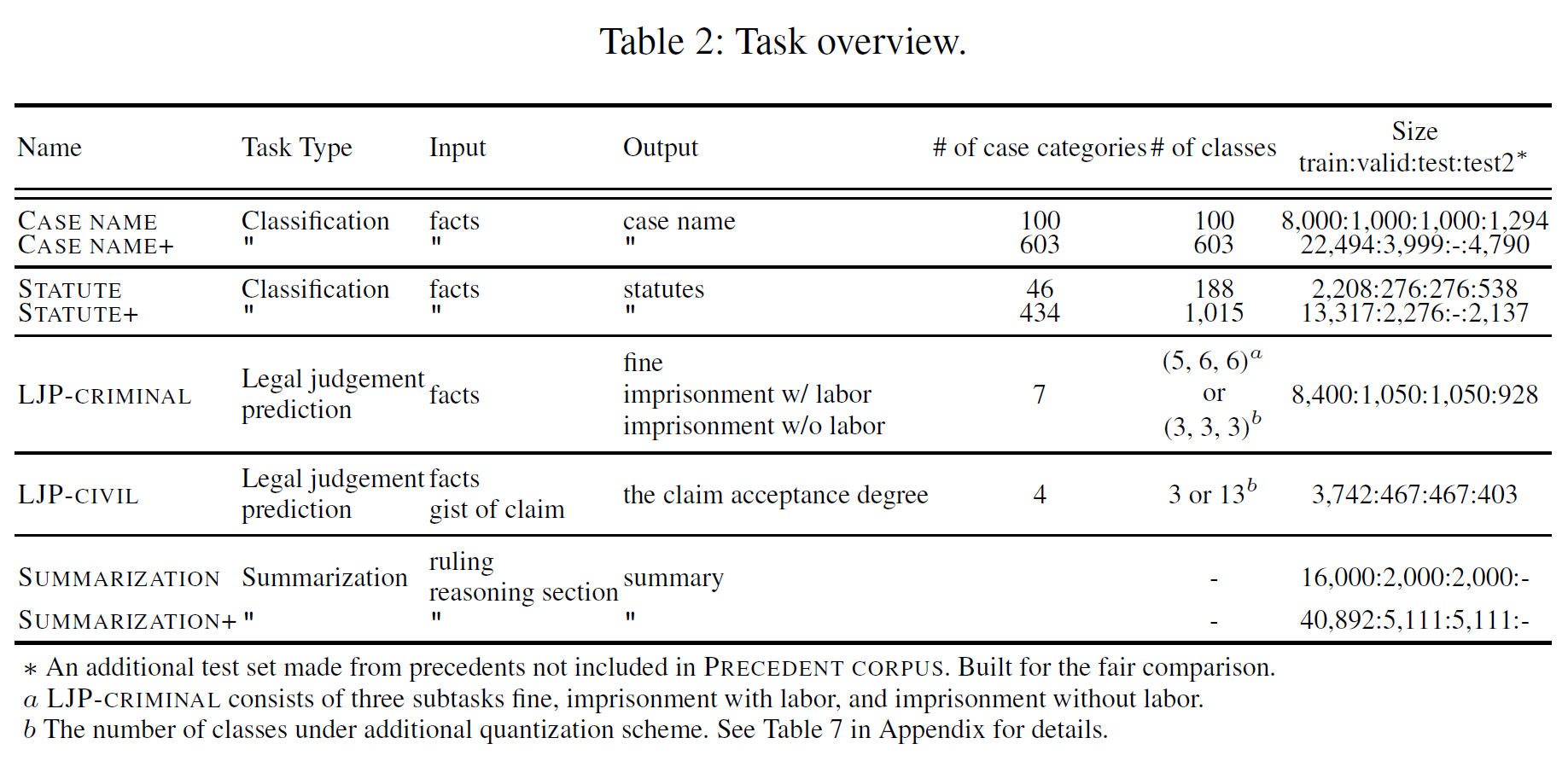
3.2 Datasets
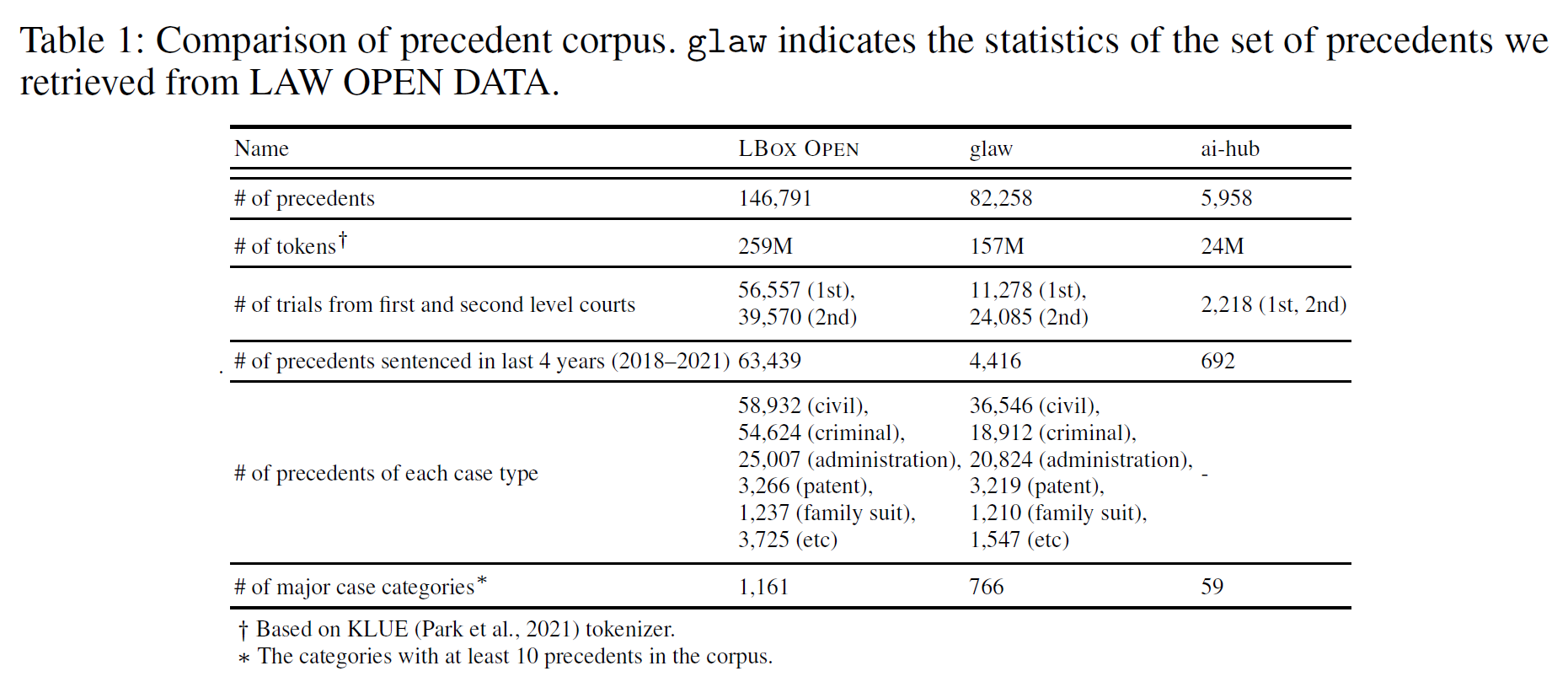
- Precedent Corpus
- AI Hub 6k + LAW OPEN DATA 82k + Internal 65k
- 57% of LAW OPEN DATA consist of the trials of the Supreme Court (no factual issues)
- Case Name
- 10k facts + case name
- Statute
- facts + statute
- LJP-Criminal
- facts + punishments(fine, imprisonment with labor, imprisonment without labor)
- Level 0 (type of punishment)
- Level 1 (degree of punishment in 3-scale, null/low/high)
- Level 2 (5-scale for fine, 6-scale for imprisonment)
- Level 3 (exact number) Regression!
- LJP-Civil
-
fact + gist of claim + degrees of claim acceptance
-
claim acceptance degree
- claimed money from the gist of claim
- approved money from ruling section
- approved money / claimed money
-
Level 1 (rejection / partial approval / full approval)
-
Level 2 (13 categories)
-
mt5-small + prompt-tuning for parsing expression (money provider / receiver / amount / litigation cost)
-
- Summarization
- Supreme Court Decisions Report + Summary of Decision
- Ruling and Reasoning section
4. Experiments
4.1 Model Training
-
Nvidia A6000, RTX3090 or RTX6000
-
lr 3e-5 to 1e-4
-
batch 8 to 60, AdamW
-
finetuning experiments with errorbar were repeaded 3 times
-
google/mt5-small for fine-tuning
-
GPT-2 from scratch (LCUBE), Modu and Wiki corpora
-
byte-level BPE
-
50K for base and 100K for medium
-
compared KoGPT2 and LCUBE
4.2 Task Setting
- text generation following
4.3 Metric
-
Case Name, Statiute, LJP-Civil : Examt Match
-
LJP-Criminal : F1 of individual fields
5. Results

- Domain specific corpus is critical in the classification and the summarization tasks
-
pretrain with Precedent Corput only also performed well in domain adaptation
-
in summarization task, LCUBE doesn't have an advantage over other models
- this might be from the architecture difference between encoder-decoder model and decoder only model
- LCUBE generated ~40% fewer tokens ROUGE score is low
-
- Domain adaptation is not helpful on legal judgement prediction tasks
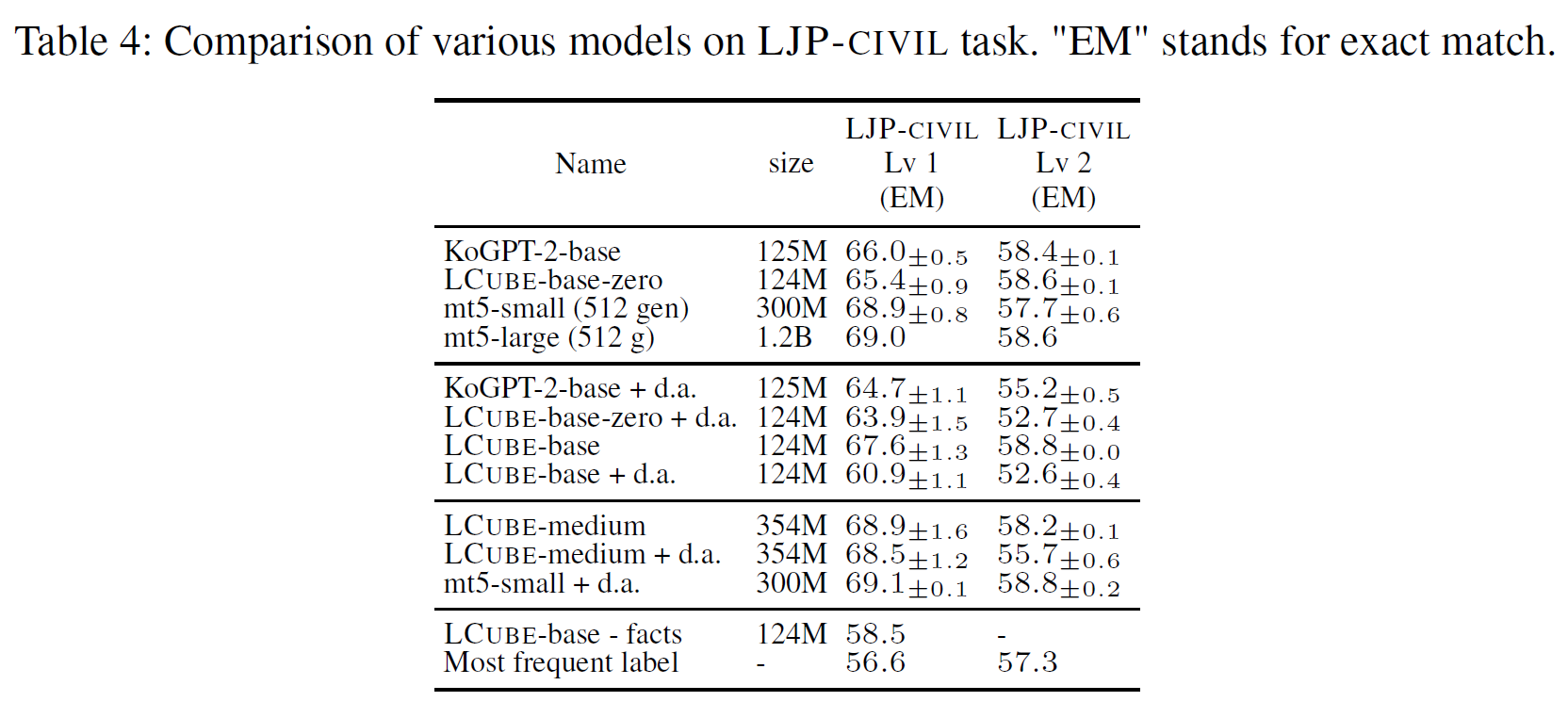
- In LJP-Civil, without the facts, the model performance is close to a dummy baseline
- Legal judgement prediction is challenging
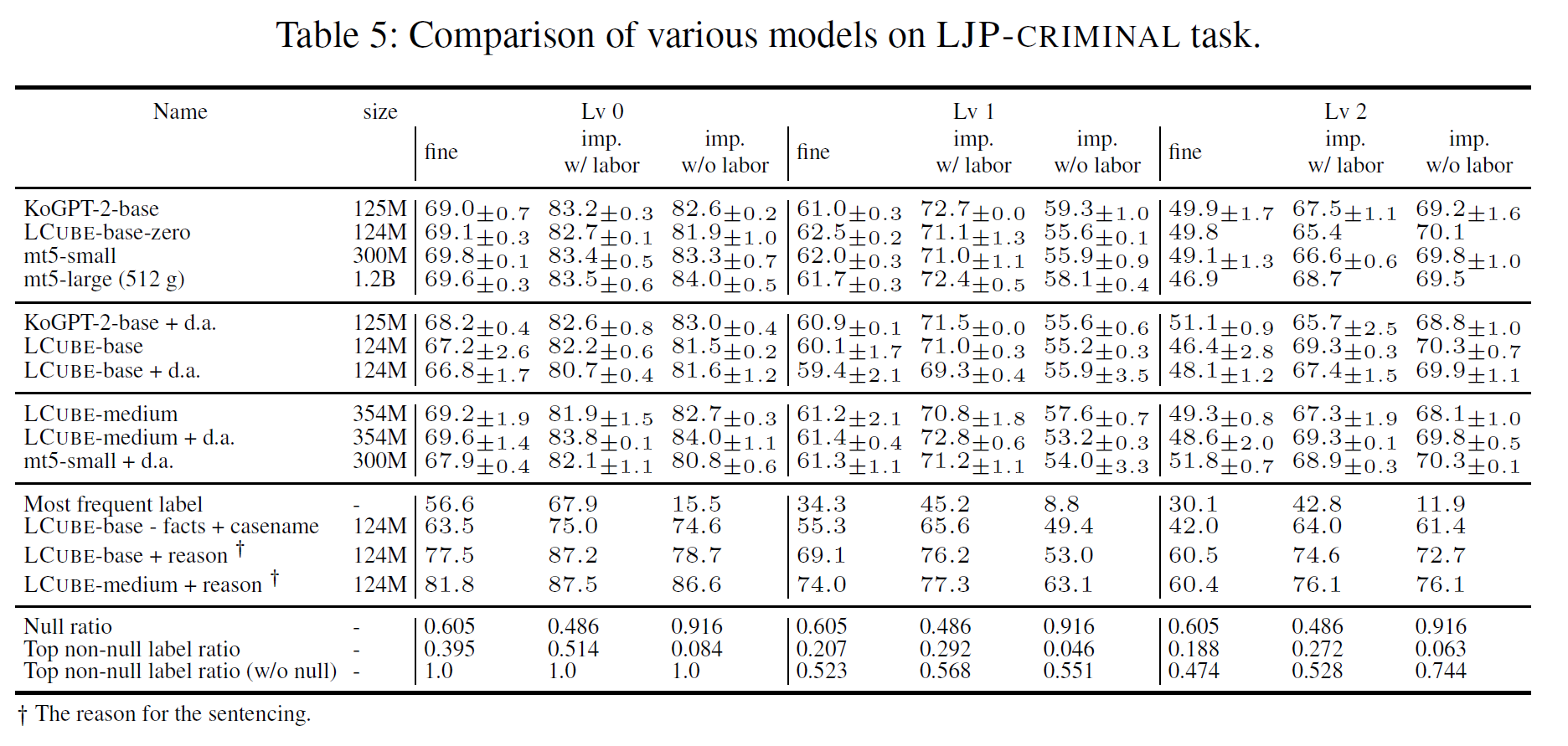
- There is no one superior model
6. Conclusion
-
the first large-scale Korean legal AI benchmark and legal language model LCUBE
-
only considered precedents from the first level courts
- for simplicity in legal reasoning
-
didn't used plaintiffs and defendants claims
-
difficult to separate the claims from reasoning sections without error
-
didn't consider many important legal applications of AI
