BeautifulSoup for web data_네이버 금융
html.parser : html을 읽는 해석기, 엔진
prettify() : html 출력을 들여쓰기 화면으로 출력
from urllib.request import urlopen : 웹주소(url)로 접근 시 urllib.request 모듈 필요
from urllib.request import urlopen
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
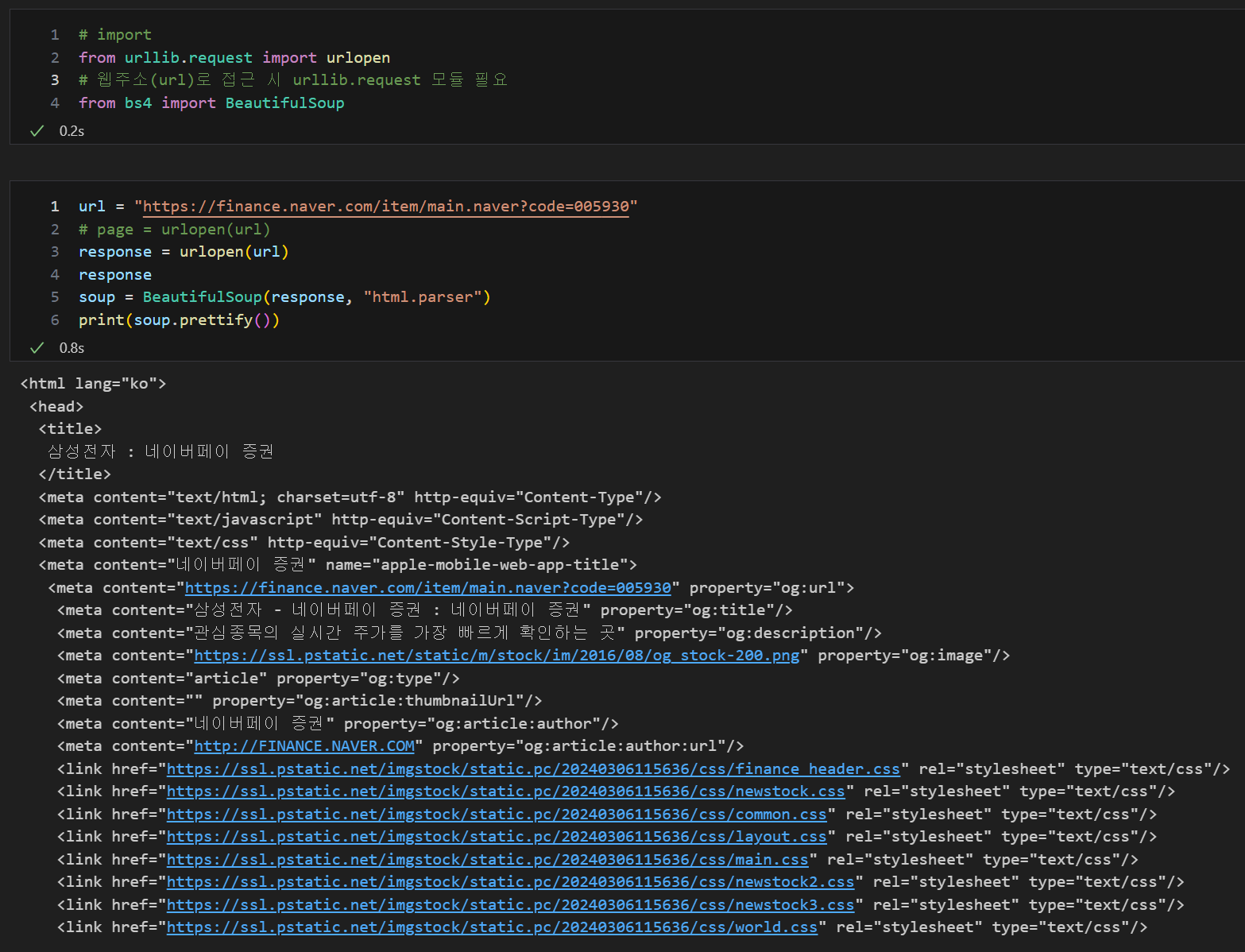
url = "https://finance.naver.com/marketindex/exchangeDetail.naver?marketindexCd=FX_USDKRW"
response = urlopen(url)
response
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify())
크롬 개발자 도구 : f12
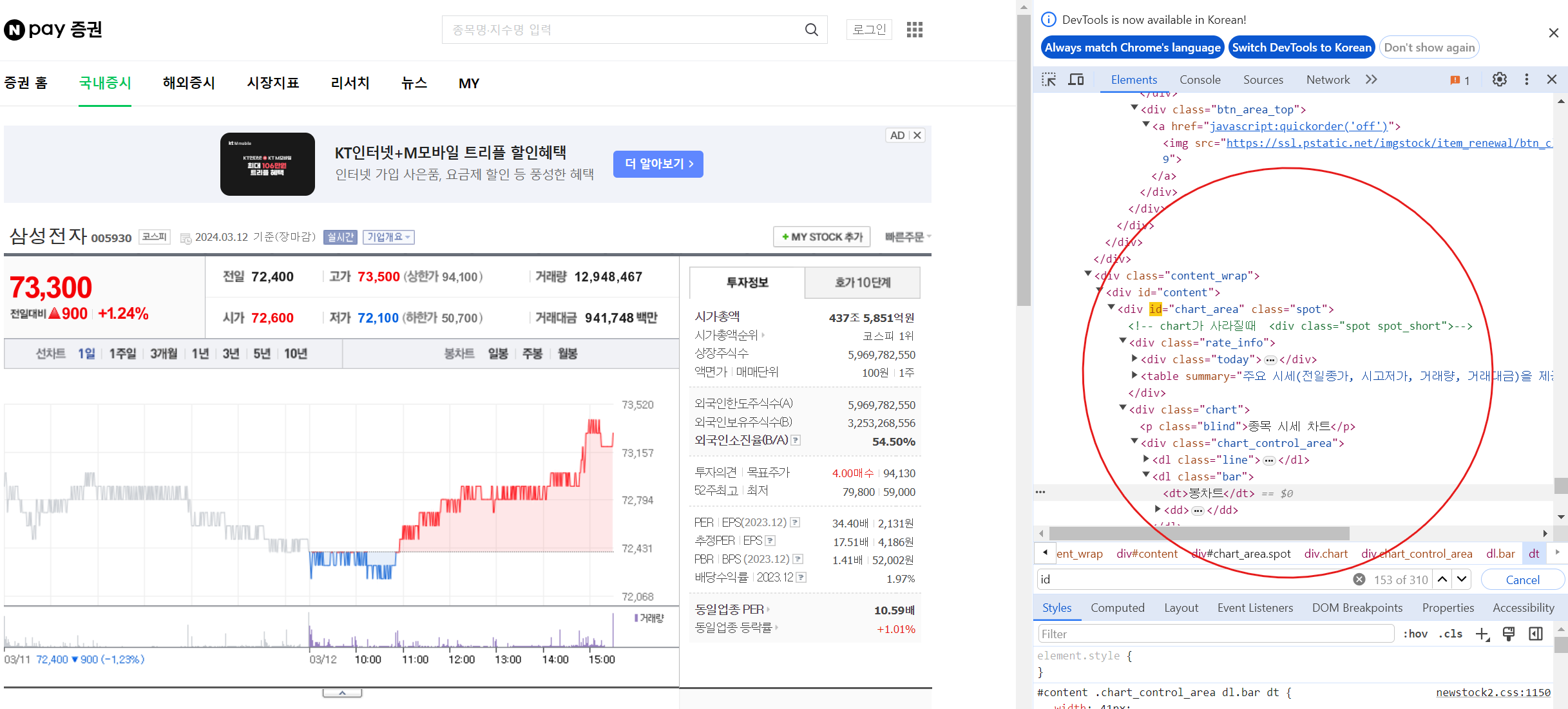
개발자 도구에서 태그값 찾기 : ctrl + shift + c
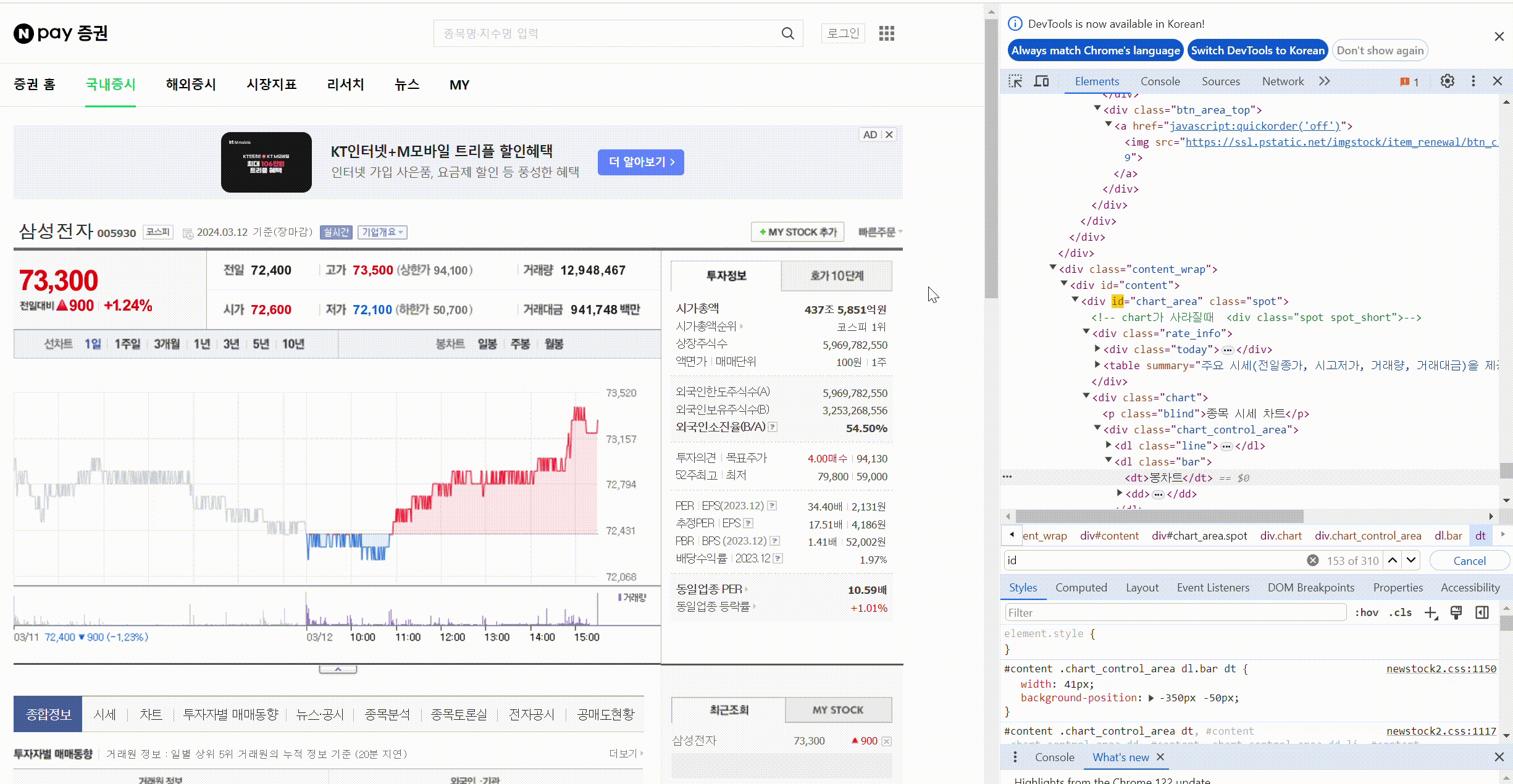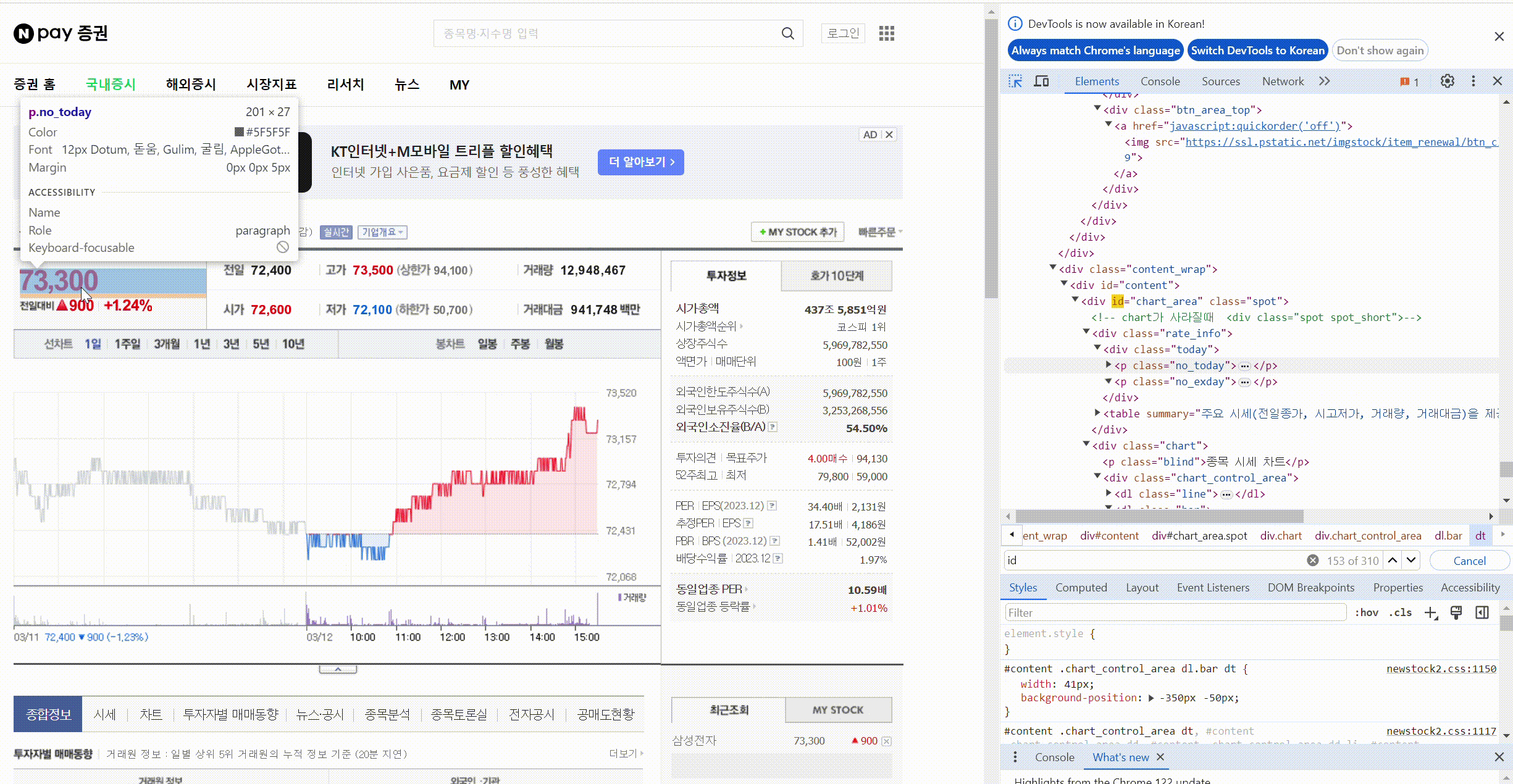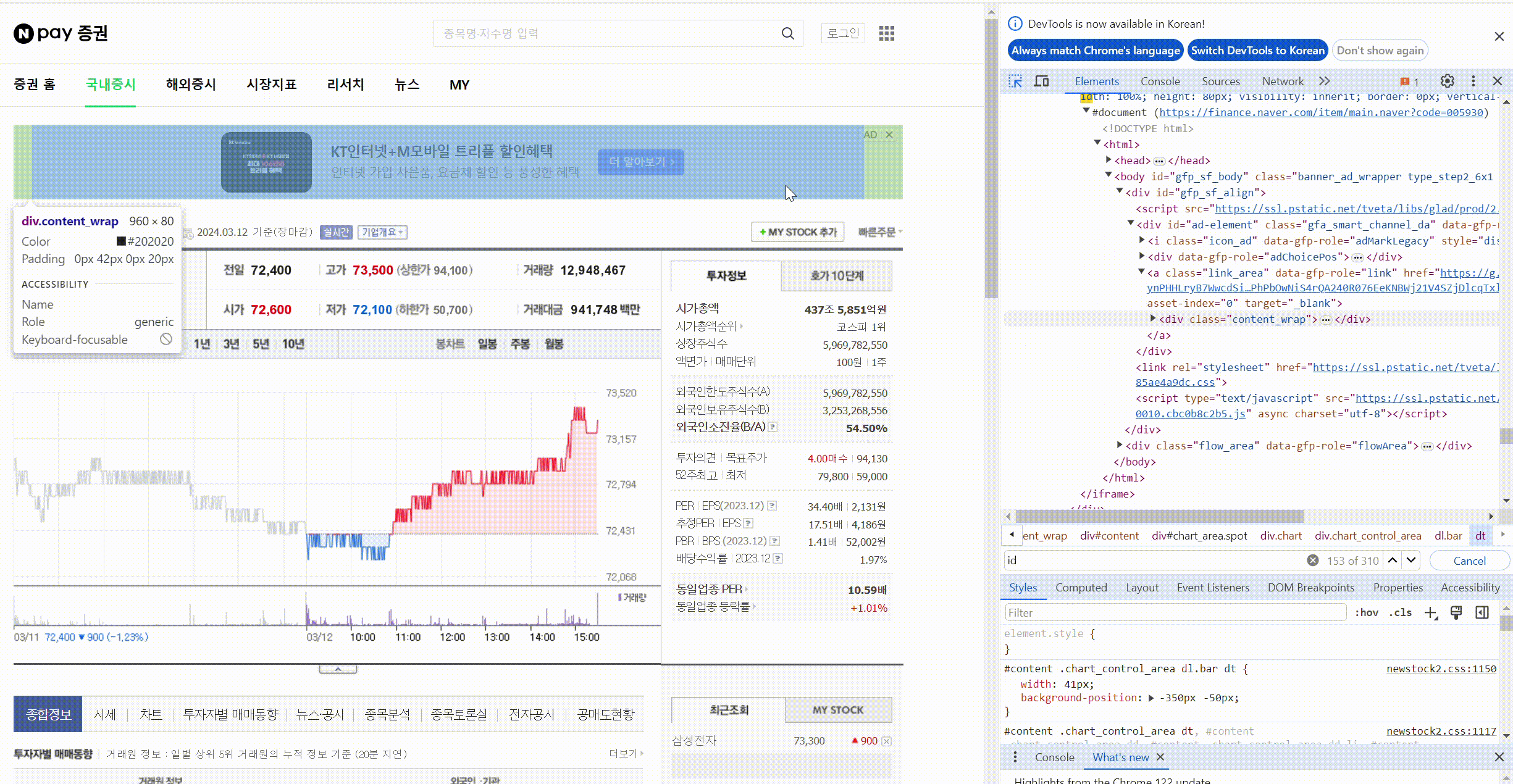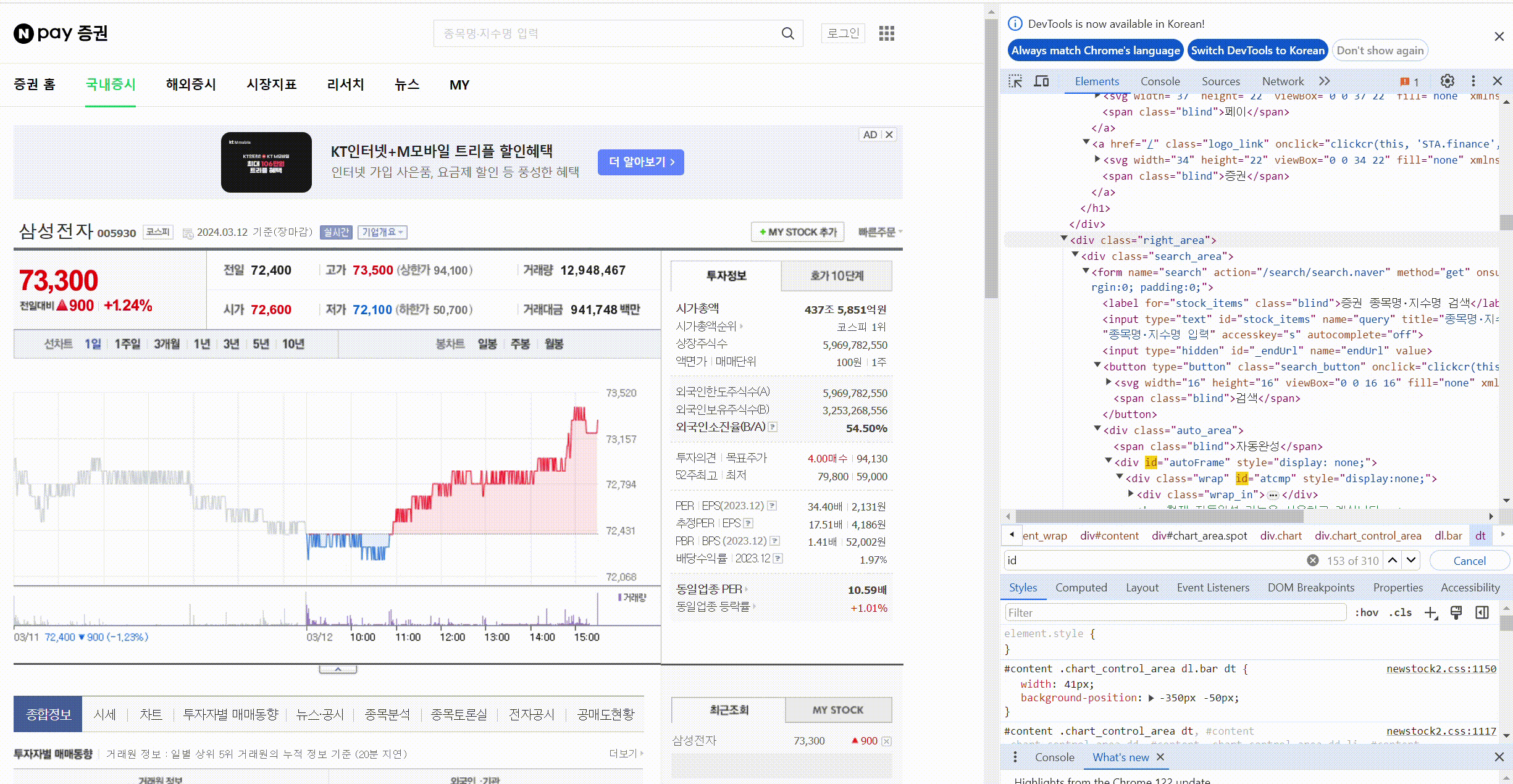
태그로 원하는 값 찾기(태그와 속성값), find(태그값, 속성값)
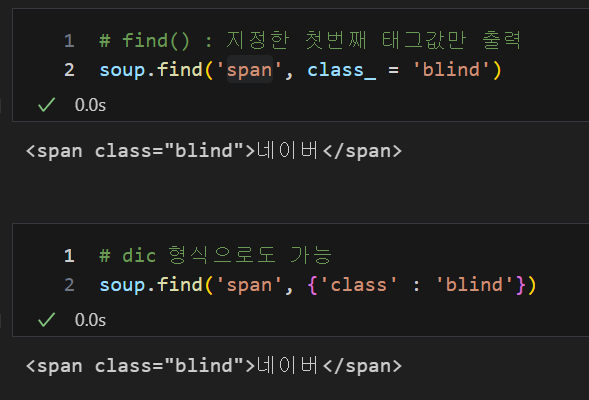
find() : 지정한 첫번째 태그값만 출력
파이썬 예약어와 겹치지 않게 사용, class, id, def, list, str, int, tuple... 사용 시 " _ "(언더바) 사용
soup.find('span', class_ = 'blind')
soup.find('span', {'class' : 'blind'})
태그로 원하는 값 찾기(태그와 속성값), find_all(태그값, 속성값)
find_all() : 지정한 모든 태그값 출력, 삼성전자의 주식 금액 찾기
soup.find_all('span', 'blind'), len(soup.find_all('span', 'blind'))
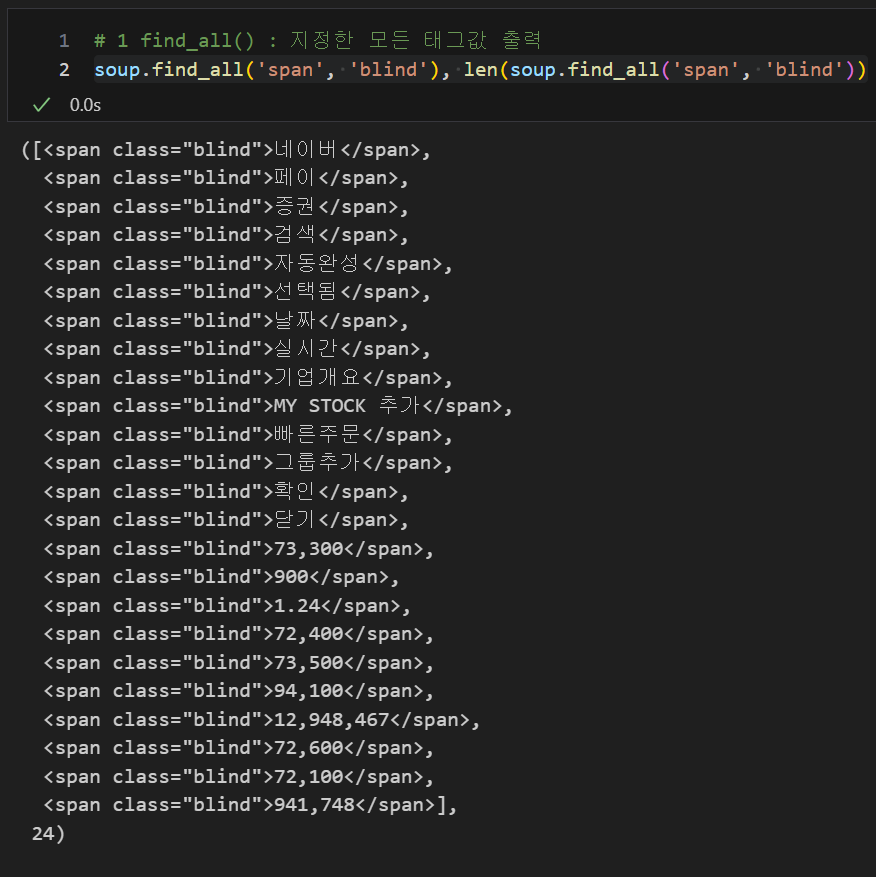
리스트의 순서 확인을 통하여 원하는 값 찾기
soup.find_all('span', 'blind')[14]
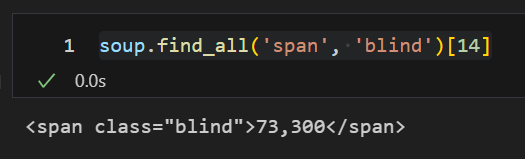
텍스트값 얻기, .text / .string / .get_text()
soup.find_all('span', 'blind')[14].text
soup.find_all('span', 'blind')[14].string
soup.find_all('span', 'blind')[14].get_text()
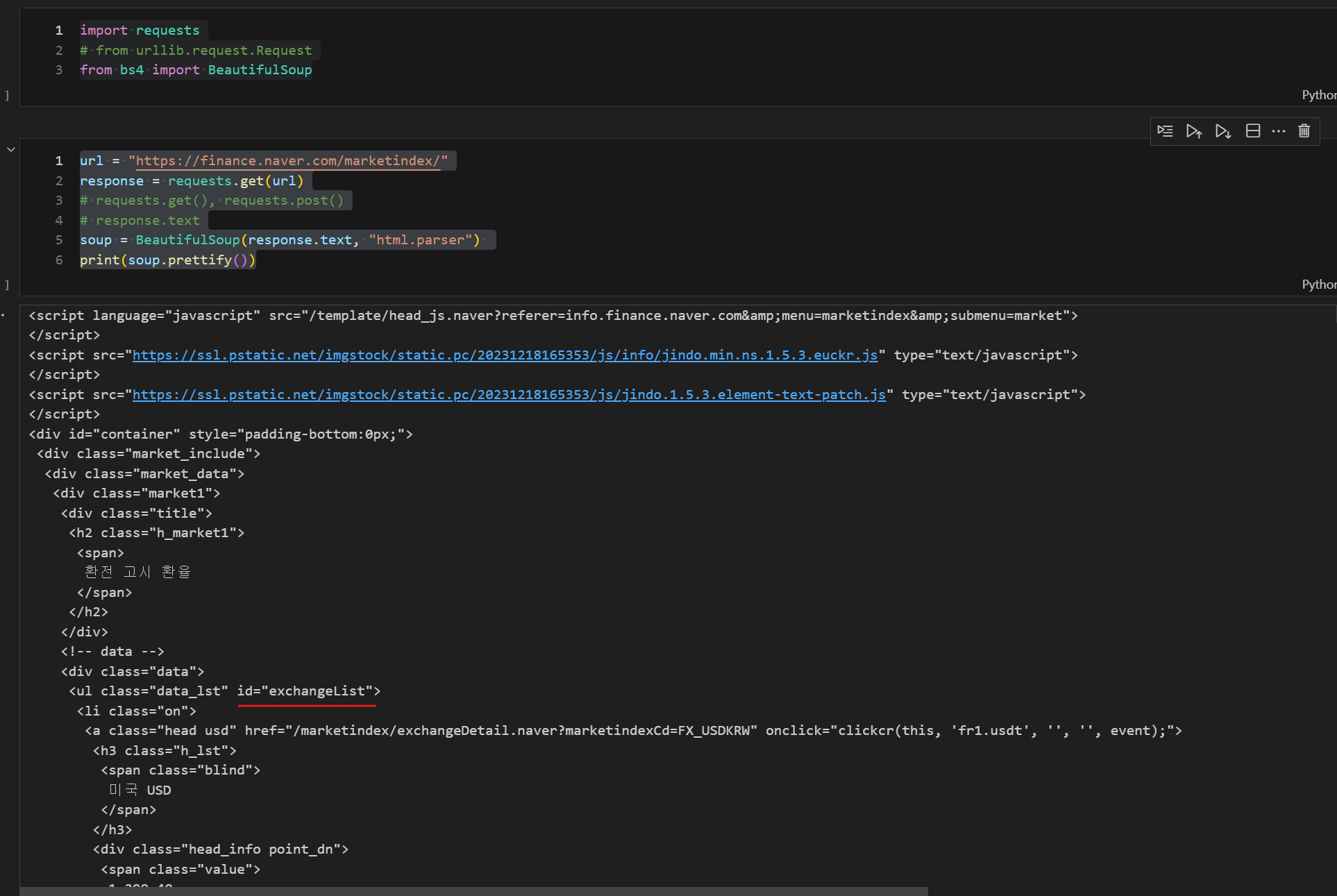
urlopen이외 request로 url 읽어오기
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "https://finance.naver.com/marketindex/"
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify())
태그로 원하는 값 찾기(태그와 속성값), select
select은 find_all과 같은기능
"id"는 "#" 으로 "class"는 "." 으로 표현
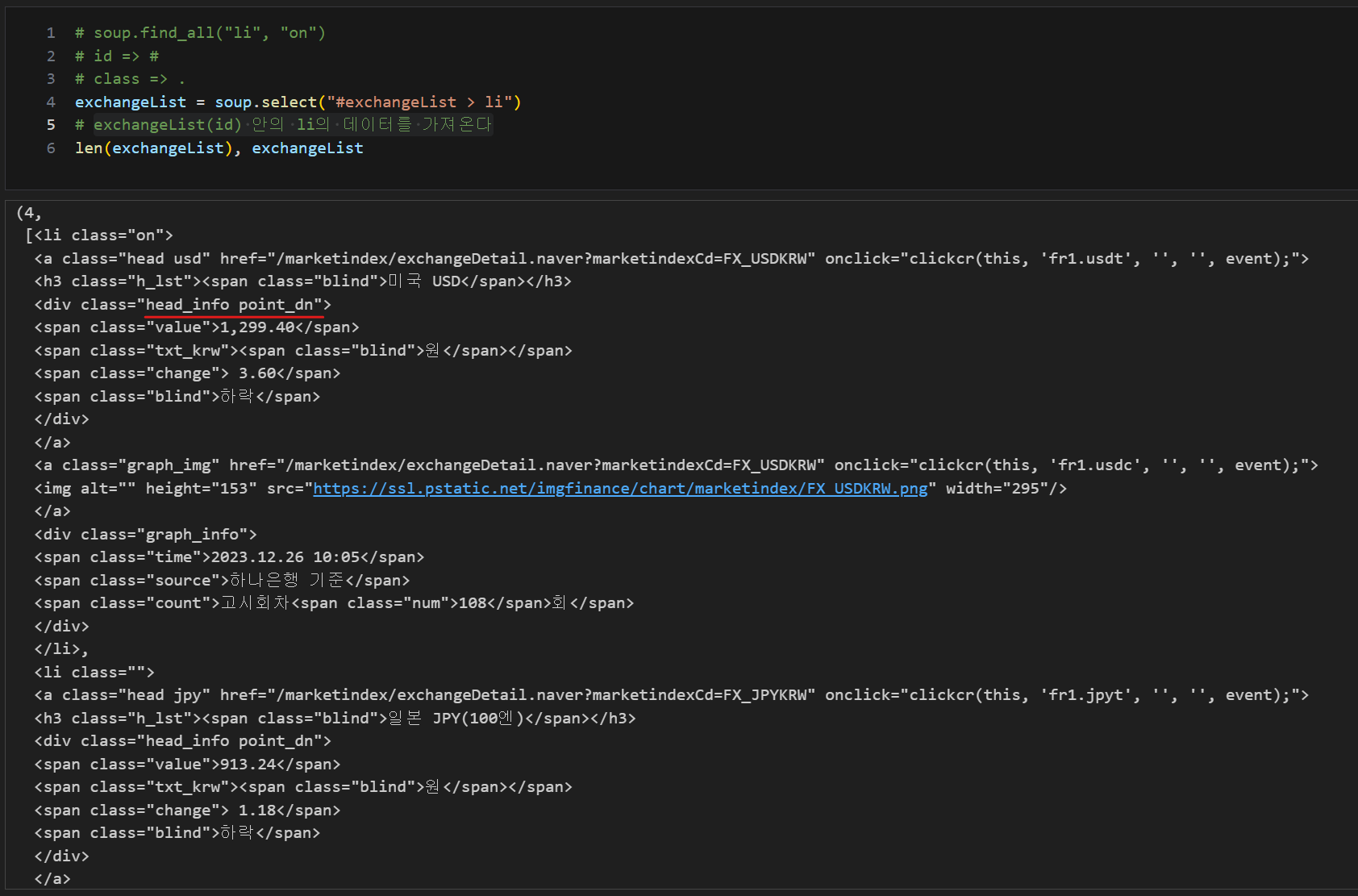
id인 exchangeList 를 이용하여 하위 값 가져오기, exchangeList(id) 안의 li의 데이터를 가져온다
exchangeList = soup.select("#exchangeList > li")
len(exchangeList), exchangeList
태그로 원하는 값 찾기(태그와 속성값), select_one
select_one은 find와 같은기능
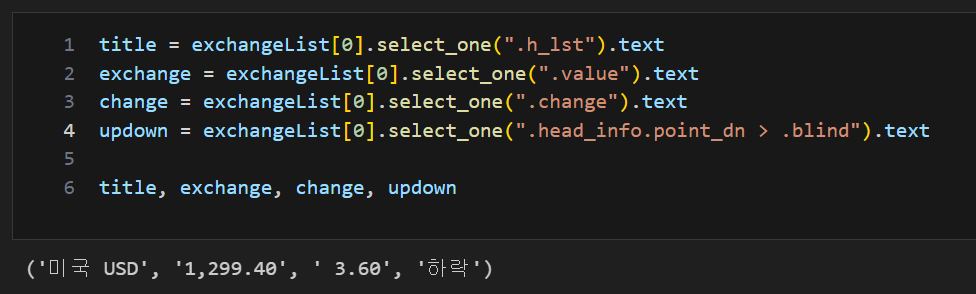
updown의 경우 head_info.point_dn(class) 안의 blind(class)의 데이터를 가져온다
title = exchangeList[0].select_one(".h_lst").text
exchange = exchangeList[0].select_one(".value").text
change = exchangeList[0].select_one(".change").text
updown = exchangeList[0].select_one(".head_info.point_dn > .blind").text
findmethod = soup.find_all("ul", id="exchangeList")
findmethod[0].find_all("span", "value")
list 데이터, append() : list 제일 뒤에 추가
movies.append("타이타닉")
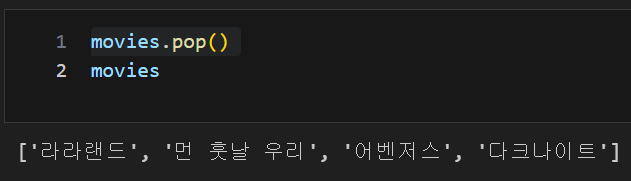
list 데이터, pop() : 리스트 제일 뒤부터 자료를 하나씩 삭제
movies.pop()
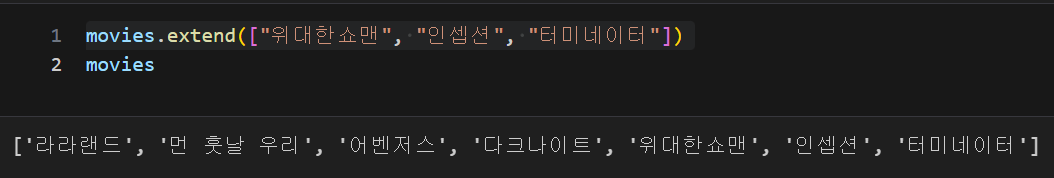
list 데이터, extend() : 제일 뒤에 자료 추가
리스트 형식을 넣어도 개별 데이터로 추가
movies.extend(["위대한쇼맨", "인셉션", "터미네이터"])
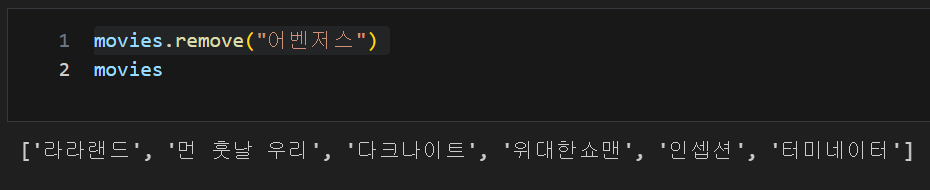
list 데이터, remove() : 자료를 삭제
movies.remove("어벤저스")
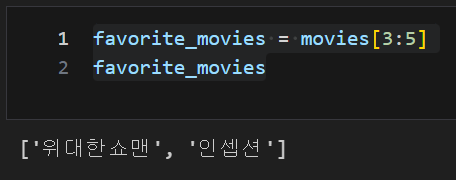
list 데이터, 슬라이싱 : [n:m] n번재 부터 m-1까지
favorite_movies = movies[3:5]
favorite_movies
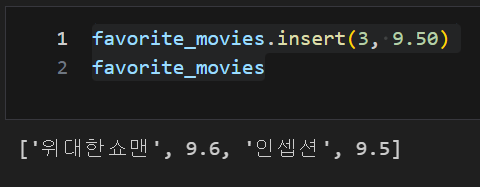
list 데이터, insert : 원하는 위치에 자료를 삽입
favorite_movies.insert(3, 9.50)
favorite_movies
시카고 맛집데이터
- 분석할 페이지가 메인페이지 하나와 분석할 각각의 페이지로 구성되어 있는데 메인페이지의 주소가 있는 분석 페이지와 없는 분석 페이지로 구분되어 별도로 url을 분리
- from fake_useragent import UserAgent를 통한 자동화 프로그램 여부 확인 후 접속 -> ua = UserAgent()
chrome_user_agent = ua.chrome # Chrome 브라우저의 사용자 에이전트
from urllib.request import Request, urlopen
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url_base = "https://www.chicagomag.com/"
url_sub = "Chicago-Magazine/November-2012/Best-Sandwiches-Chicago/"
url = url_base + url_sub
ua = UserAgent()
chrome_user_agent = ua.chrome
req = Request(url, headers={"user-agent": chrome_user_agent})
html = urlopen(req)
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify())
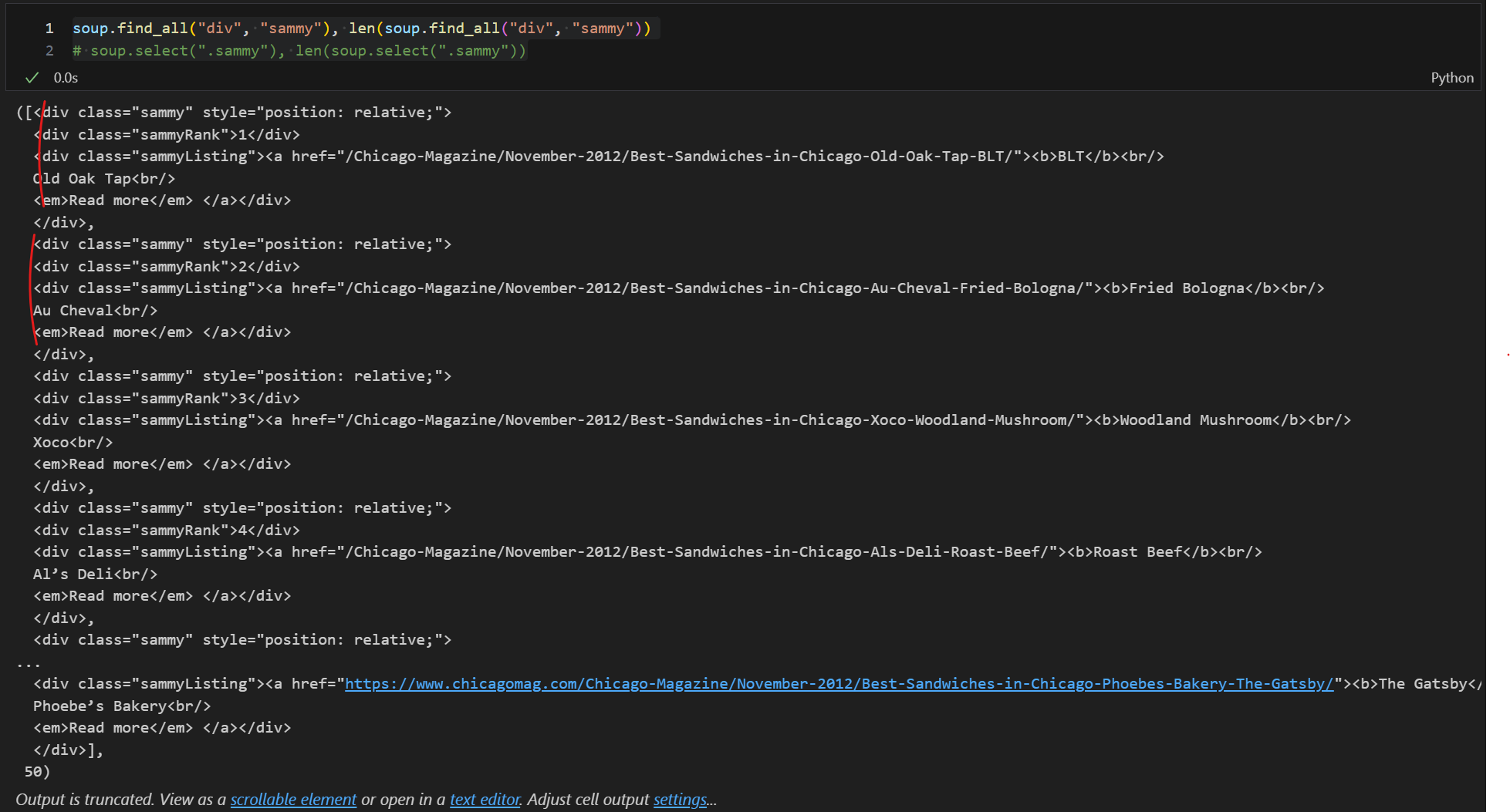
태그 및 속성을 이용한 원하는 값 위치 찾기, find_all
soup.find_all("div", "sammy"), len(soup.find_all("div", "sammy"))
위치를 변수로 담고 원하는 값 찾기
type이 bs4.element.Tag인 것은 beautifulSoap의 find, find_all 기능을 내부적으로 또 쓸 수 있다
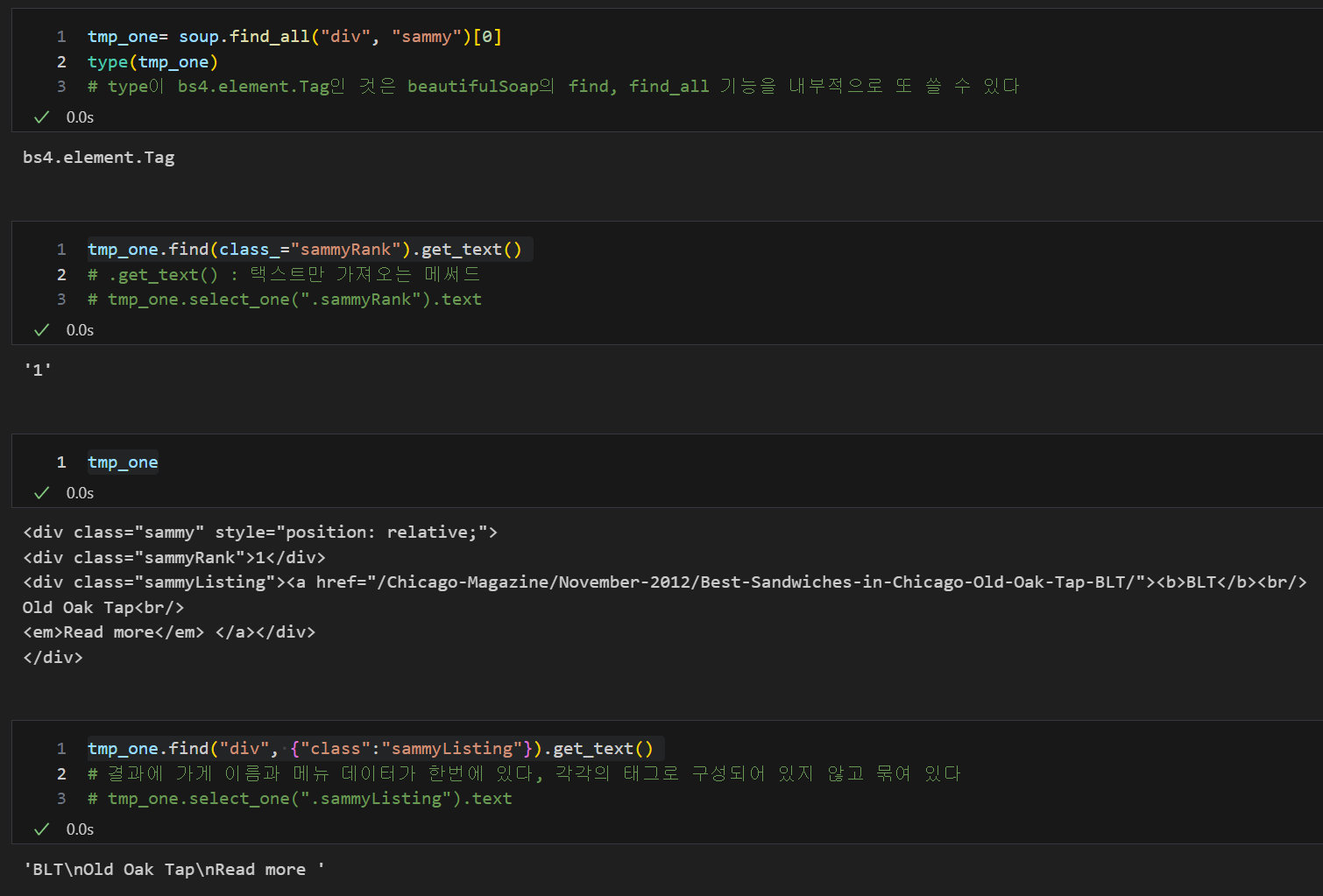
tmp_one= soup.find_all("div", "sammy")[0]
type(tmp_one)
tmp_one.find(class_="sammyRank").get_text()
tmp_one
tmp_one.find("div", {"class":"sammyListing"}).get_text()
re, 패턴을 '매칭'하여 매칭되는 것을 다른 것으로 '치환'하거나 매칭된 것을 '분리'
- 're'는 정규 표현식을 사용하기 위한 모듈
- 파이썬은 re 모듈을 지원하기에 간단히 import해서 사용
- 여기선 split을 사용하여 단어를 나누기 위해 사용
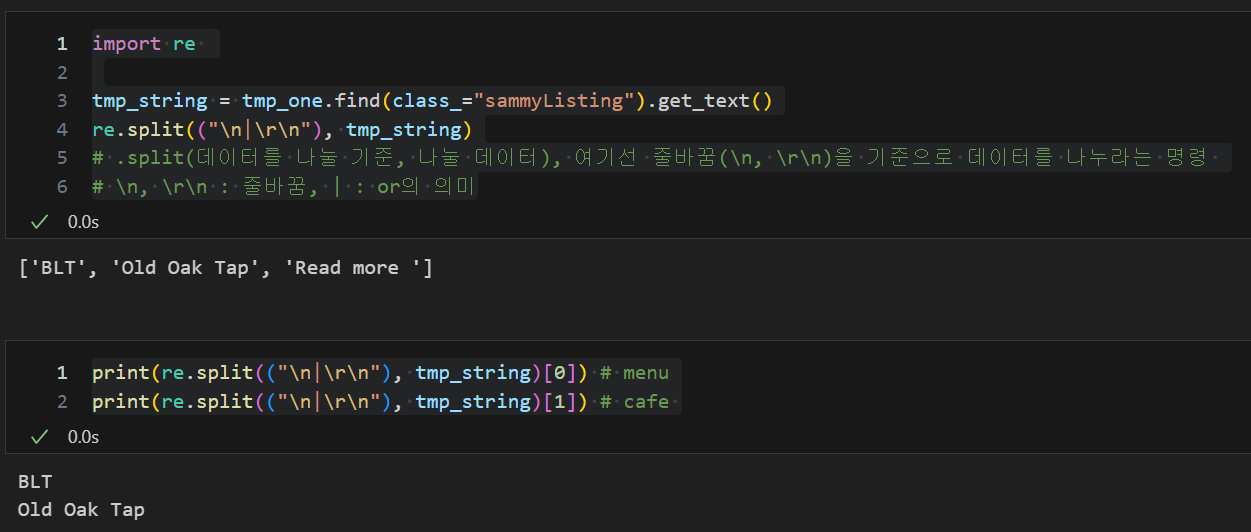
import re
tmp_string = tmp_one.find(class_="sammyListing").get_text()
re.split(("\n|\r\n"), tmp_string)
print(re.split(("\n|\r\n"), tmp_string)[0])
print(re.split(("\n|\r\n"), tmp_string)[1])
상대주소 절대주소 대응을 위해 urllib.parse의 urljoin 사용
상대주소 및 절대주소 대응 후 for문을 통하여 원하는 값들을 리스트화하고 데이터 프레임 생성
- 시카고 매거진이 이 페이지에서 연결하는 하위 50개 페이지의 주소가 상대주소와 절대주소를 혼용하고 있다
- urljoin(절대주소, 가져온 주소) : 가져온 주소가 상대주소라면 앞의 절대주소와 같이 붙이고 만약 가져온 주소가 절대주소라면 앞의 절대 주소를 붙이지 않는다
from urllib.parse import urljoin
url_base = "http://www.chicagomag.com"
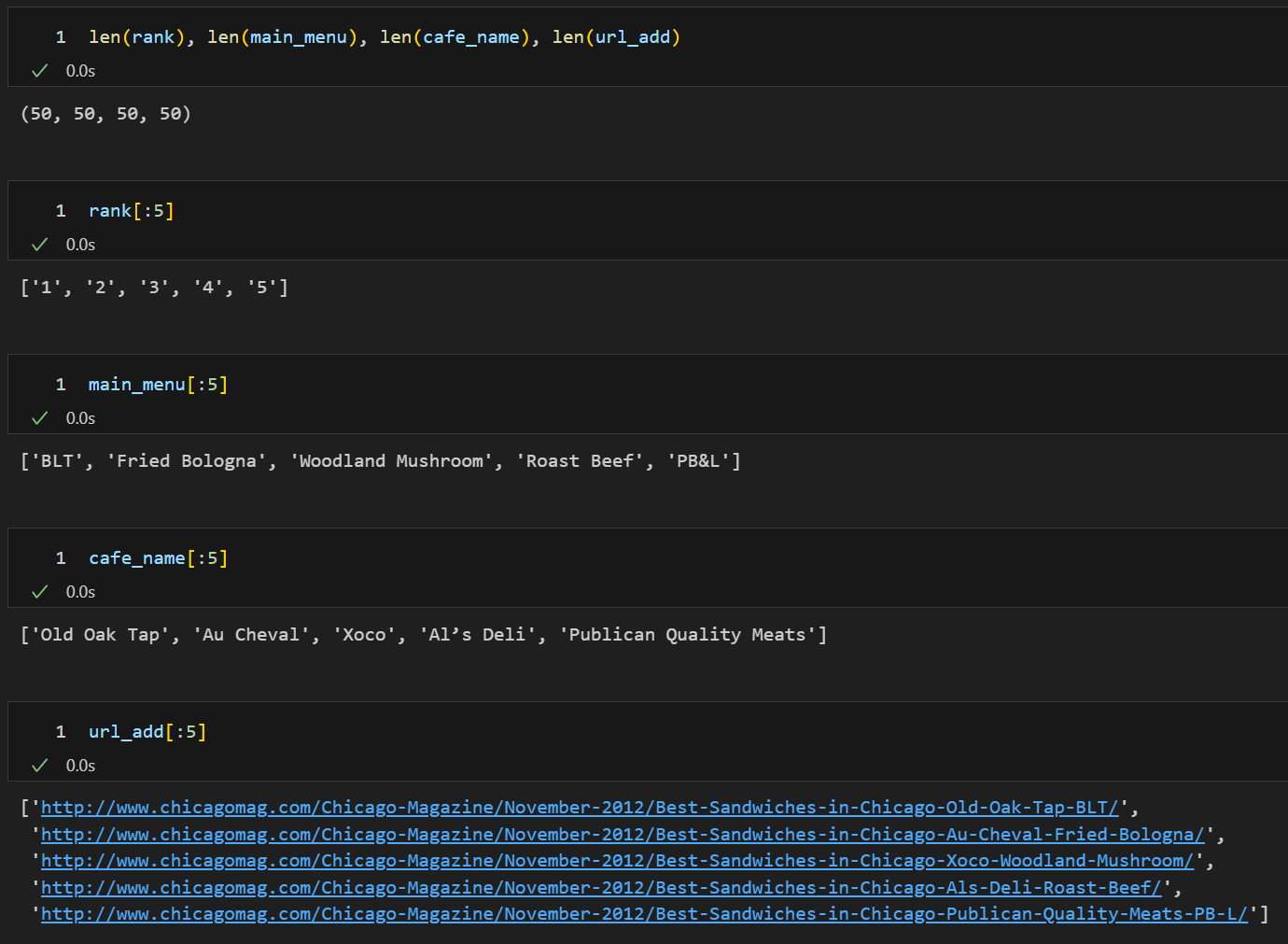
rank = []
main_menu = []
cafe_name = []
url_add = []
list_soup = soup.find_all("div", "sammy")
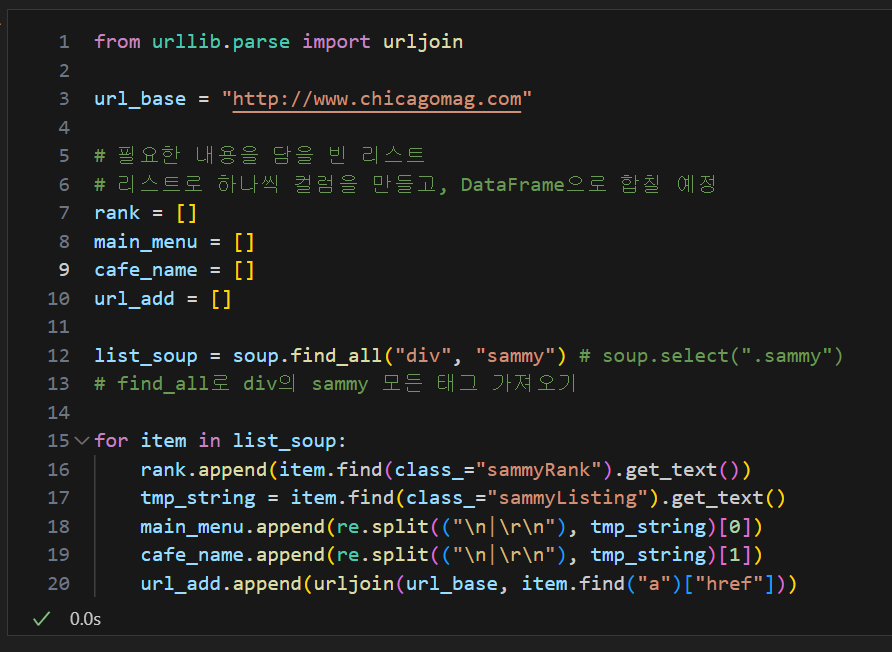
for item in list_soup:
rank.append(item.find(class_="sammyRank").get_text())
tmp_string = item.find(class_="sammyListing").get_text()
main_menu.append(re.split(("\n|\r\n"), tmp_string)[0])
cafe_name.append(re.split(("\n|\r\n"), tmp_string)[1])
url_add.append(urljoin(url_base, item.find("a")["href"]))
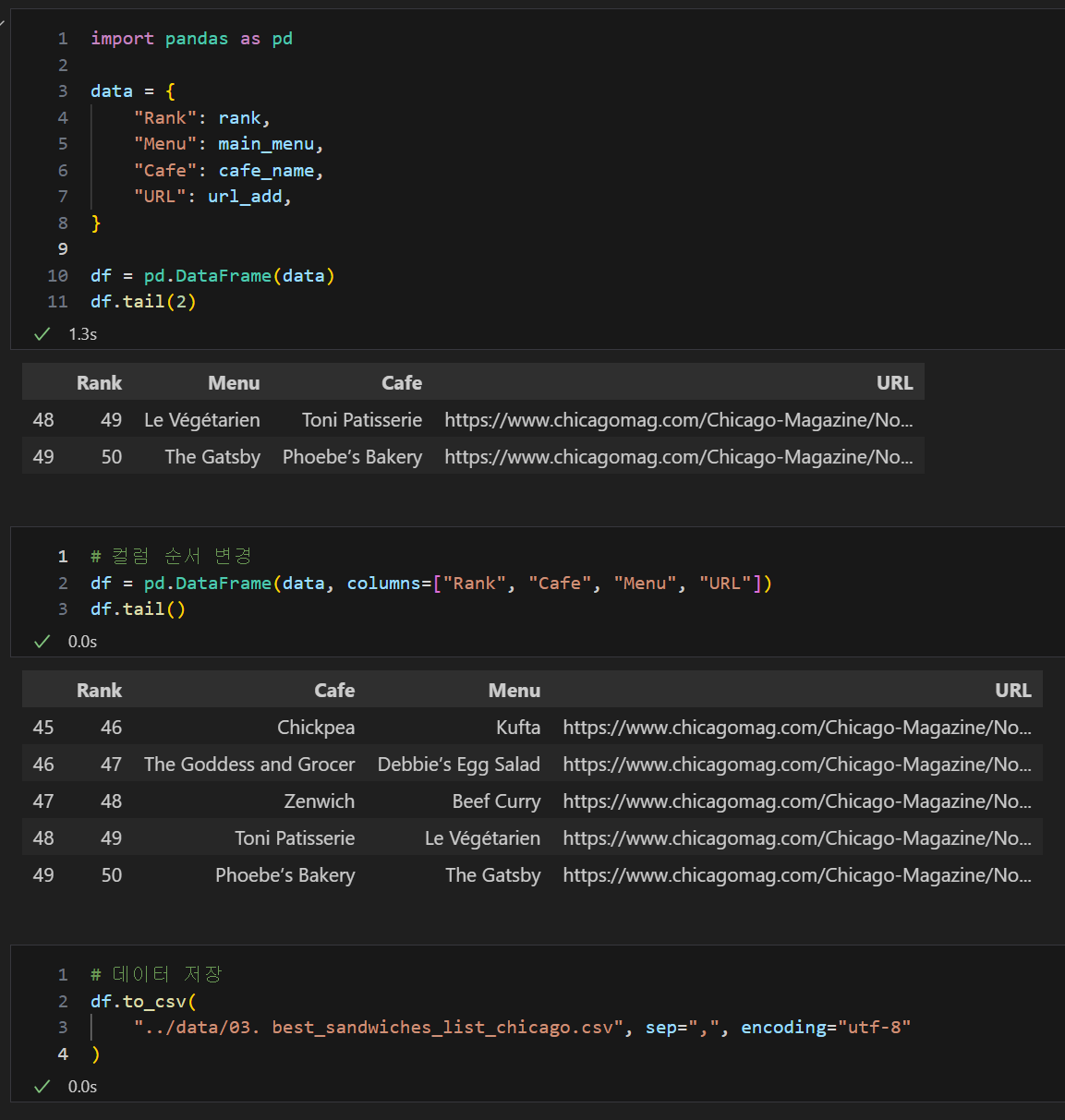
data = {
"Rank": rank,
"Menu": main_menu,
"Cafe": cafe_name,
"URL": url_add,
}
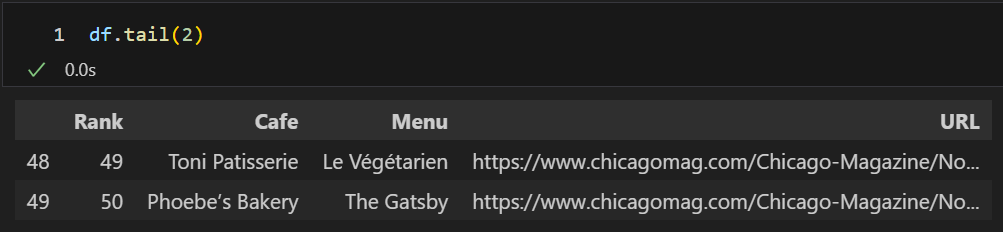
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.tail(2)
URL 주소를 이용한 하위 정보 가져오기
Request로 주소 접근 및 자동화프로그램 여부 전달 후 urlopen 사이트 접속, 원하는 정보 위치 찾기
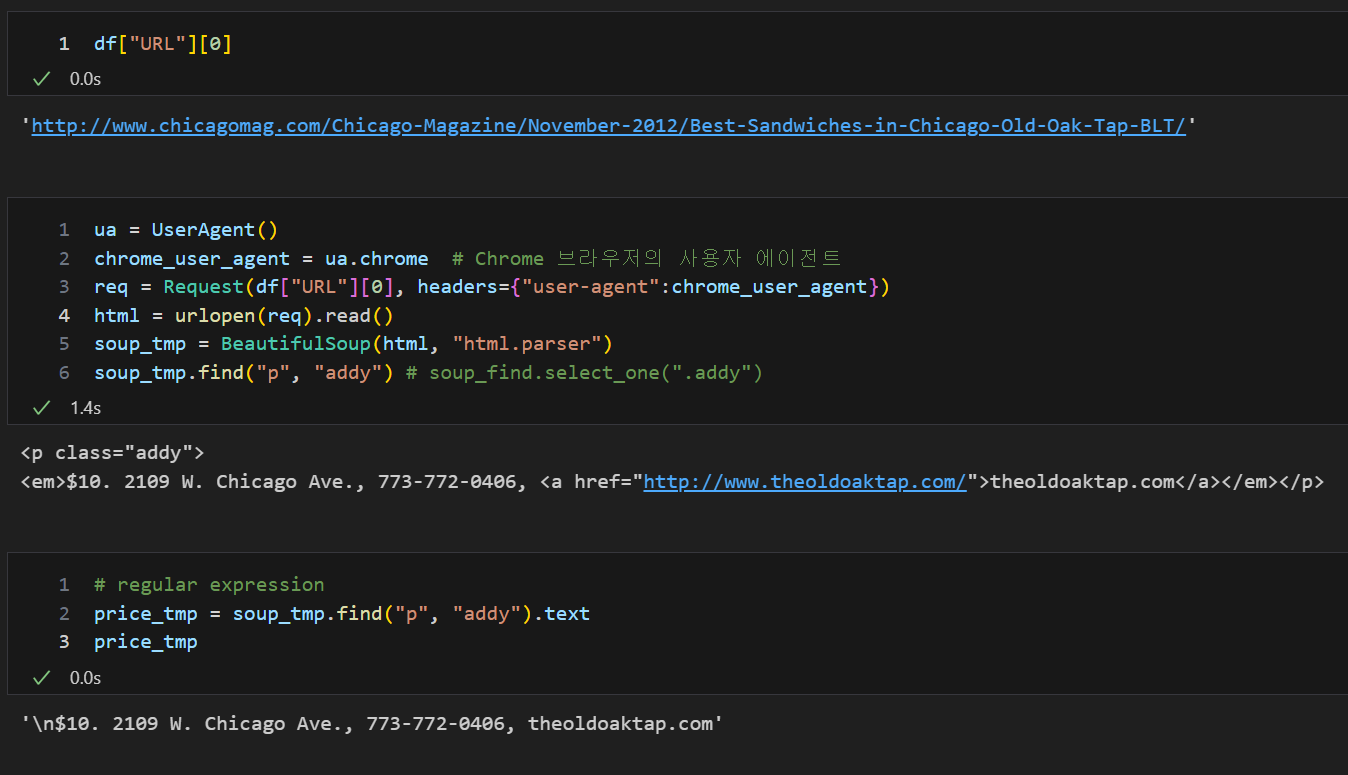
df["URL"][0]
ua = UserAgent()
chrome_user_agent = ua.chrome
req = Request(df["URL"][0], headers={"user-agent":chrome_user_agent})
html = urlopen(req).read()
soup_tmp = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
soup_tmp.find("p", "addy")
price_tmp = soup_tmp.find("p", "addy").text
price_tmp
re를 이용한 원하는 값 출력
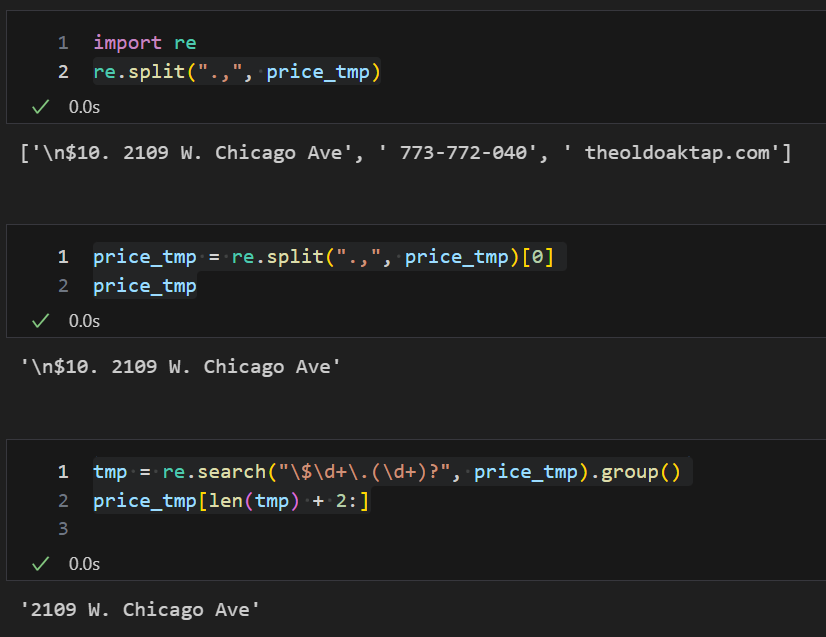
re.split(".,", price_tmp)
price_tmp = re.split(".,", price_tmp)[0]
price_tmp
tmp = re.search("\$\d+\.(\d+)?", price_tmp).group()
price_tmp[len(tmp) + 2:]
for문과 iterrows를 이용하여 부가 정보 리스트 만들기
tqdm : for문의 진행사항과 작업시간 확인
from tqdm import tqdm
price = []
address = []
for idx, row in tqdm(df.iterrows()):
ua = UserAgent()
chrome_user_agent = ua.chrome
req = Request(row["URL"], headers={"user-agent":chrome_user_agent})
html = urlopen(req).read()
soup_tmp = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
gettings = soup_tmp.find("p", "addy").get_text()
price_tmp = re.split(".,", gettings)[0]
tmp = re.search("\$\d+\.(\d+)?", price_tmp).group()
price.append(tmp)
address.append(price_tmp[len(tmp)+2:])
print(idx)

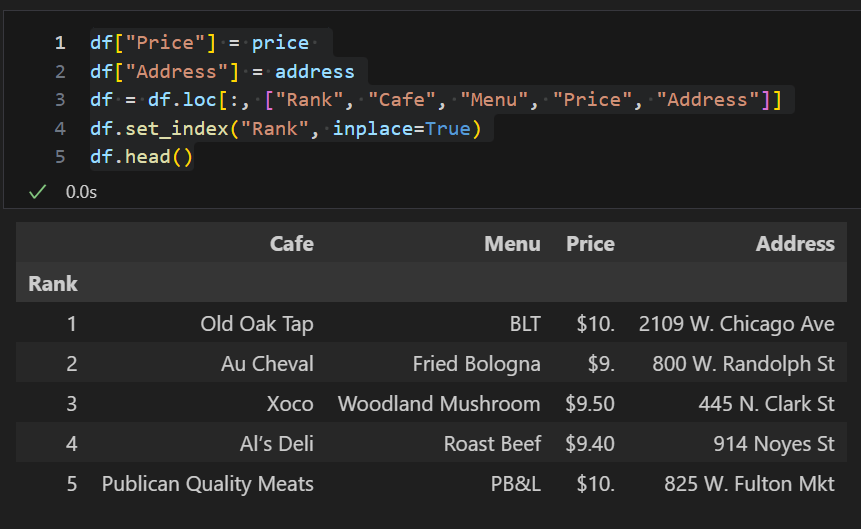
데이터프레임 수정
df["Price"] = price
df["Address"] = address
df = df.loc[:, ["Rank", "Cafe", "Menu", "Price", "Address"]]
df.set_index("Rank", inplace=True)
df.head()