전략
-
그리디 알고리즘은 탐욕 선택 속성(greedy choice property), 최적 부분 구조(optimal substructure) 특성을 가지는 문제들을 해결하는 데 강점을 가짐
-
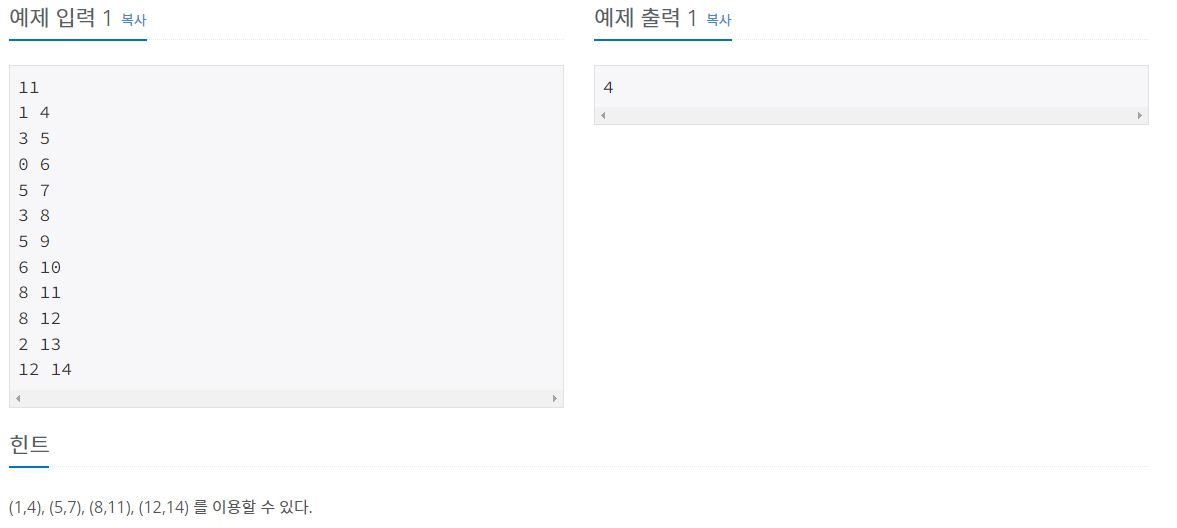
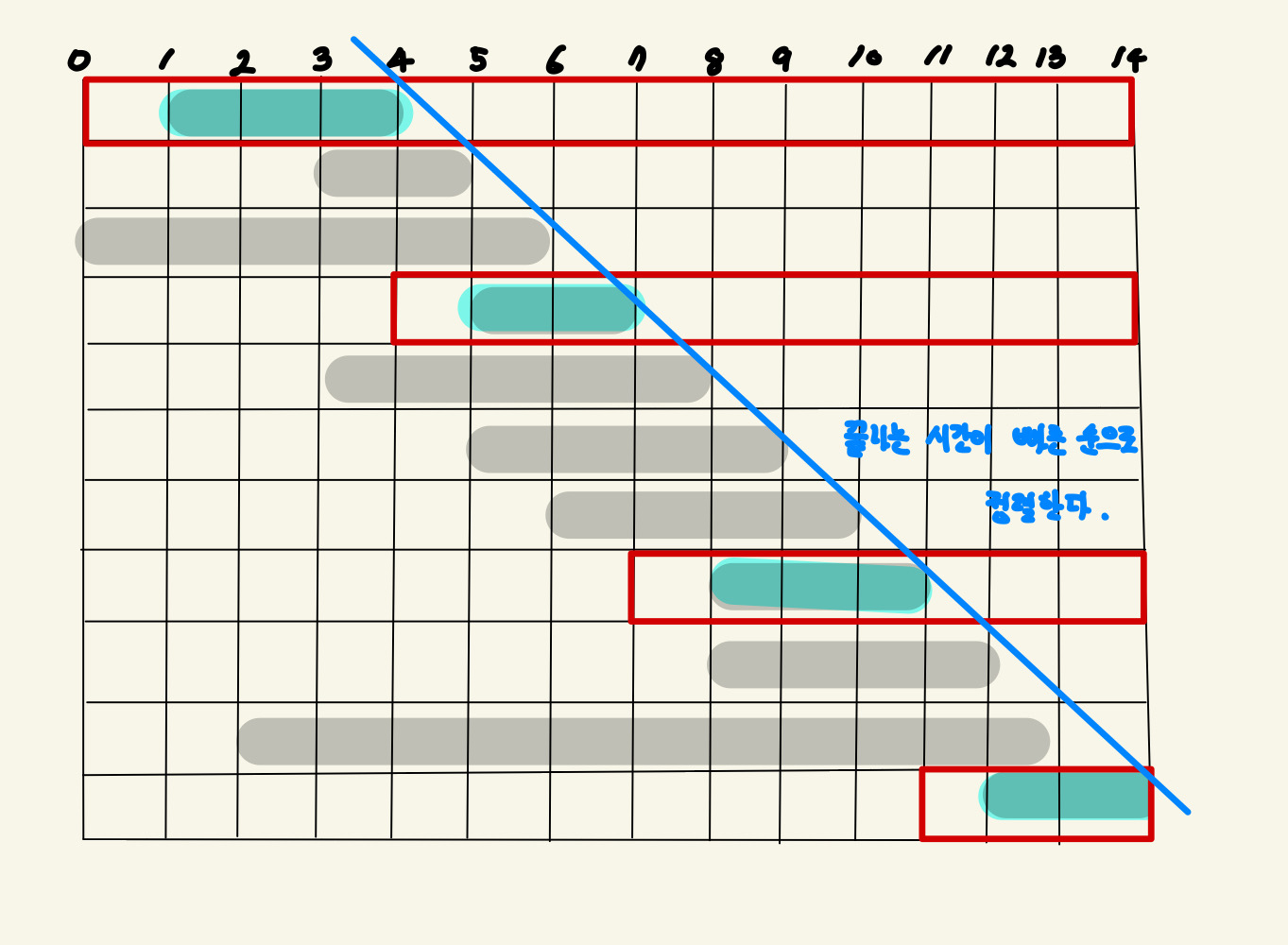
이 문제에서 회의를 마치는 시간이 가장 빠른 회의를 가장 높은 우선 순위로 정렬하면 예약된 회의를 제외하고 남는 시간이 가장 많다 -> 결국 이게 최적 부분 구조
-
즉 한번의 선택이 다음 선택에는 전혀 무관한 값이며 매 순간의 최적해가 문제에 대한 최적해가 된다
정답코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Time implements Comparable<Time>{
int start;
int end;
public Time(int s, int e) {
start = s;
end = e;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Time o) {
if(this.end == o.end) {
return this.start - o.start;
}
return this.end - o.end;
}
}
public class MeetingRoom {
static Time [] timeline;
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int time = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
timeline = new Time[time];
for(int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
String [] in = br.readLine().split(" ");
int s = Integer.parseInt(in[0]);
int e = Integer.parseInt(in[1]);
Time t = new Time(s,e);
timeline[i] = t;
}
Arrays.sort(timeline);
int result = 0;
int now_e = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
if (now_e > timeline[i].start)continue;
result++;
now_e = timeline[i].end;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}