Roles
functions of nodes in a network
measured by structural behaviors
example: centers of stars, members of cliques 파벌, peripheral nodes 주변 노드
A collection of nodes which have similar positions in a network, similarity of ties, need not in direct
vs. Communities/Groups: well-connected to each other
Structral equivalence
have the same relations to all other nodes, both nodes have tie to k
1. Discovering Structural Roles in Networks
importance
RoIX: automatic discovery of structural roles
Unsupervised learning approach, no prior knowledge-required
assign mixed-membership of roles to each node, scales linearly in # edges
RoIX: Approach Overview
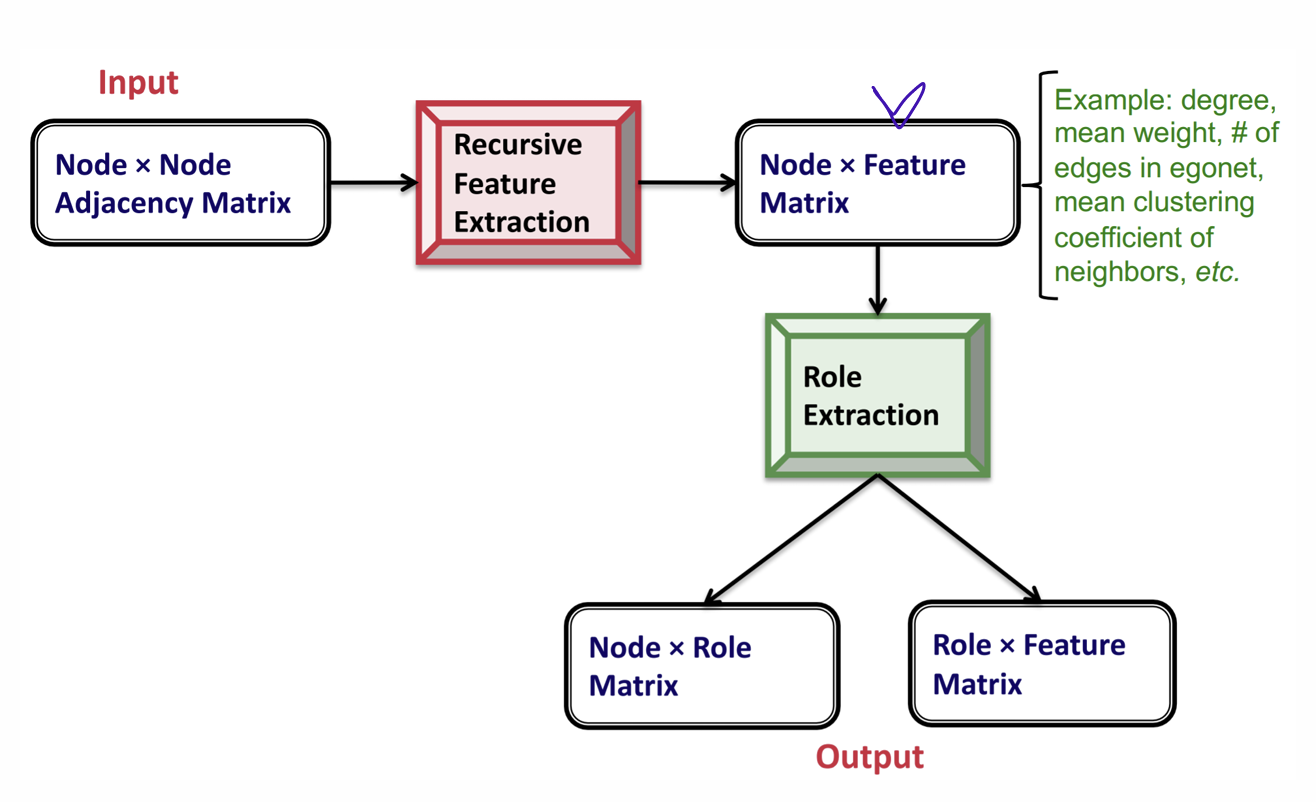
egonet: 자아
Recursive Feature Extraction
turns network connectivity into structural features
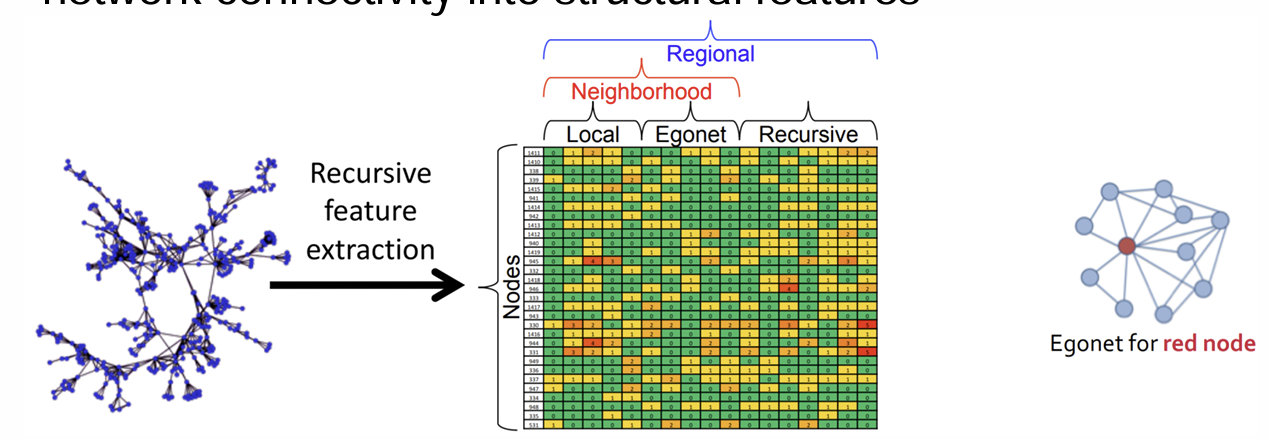
• Neighborhood features: What is a node’s connectivity pattern? 연결 패턴
• Recursive features: To what kinds of nodes is a node connected? 연결된 노드의 종류
Idea: Aggregate features of a node and use them to generate new recursive features
- Base set of a node’s neighborhood features: base set
• Local features: All measures of the node degree: node degree
If network is directed, include in- and out-degree, total degree
If network is weighted, include weighted feature versions
• Egonet features: Computed on the node’s egonet:
Egonet includes the node, its neighbors, and any edges in the induced subgraph
on these nodes
#(within-egonet edges),
#(edges entering/leaving egonet)
start with the base set of node features and use the set of current node features to generate additional features:
aggregate functions: mean & sum
ex) compute means and sums over all current features, including other recursive features and repeat
base set feature로 시작해서 추가적인 feature 생성
The number of recursive features grows exponentially:
reduce # of features using a pruning technique:
look for highly correlated pairs of features above a threshold, eliminate one
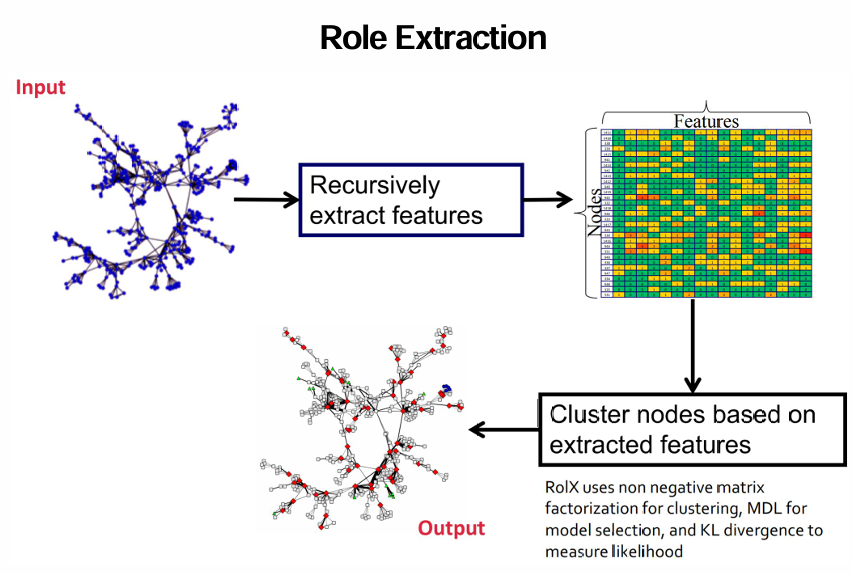
extract features, cluster based on features
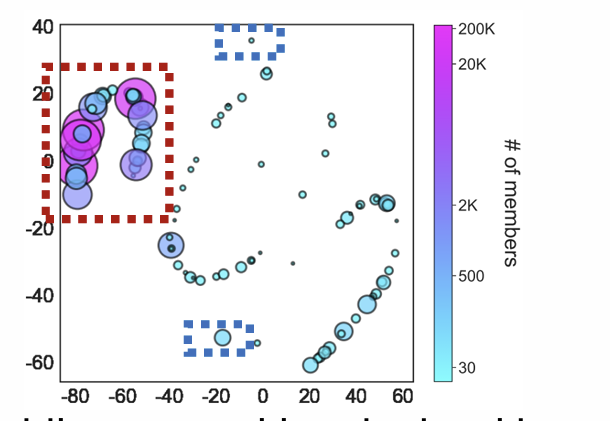
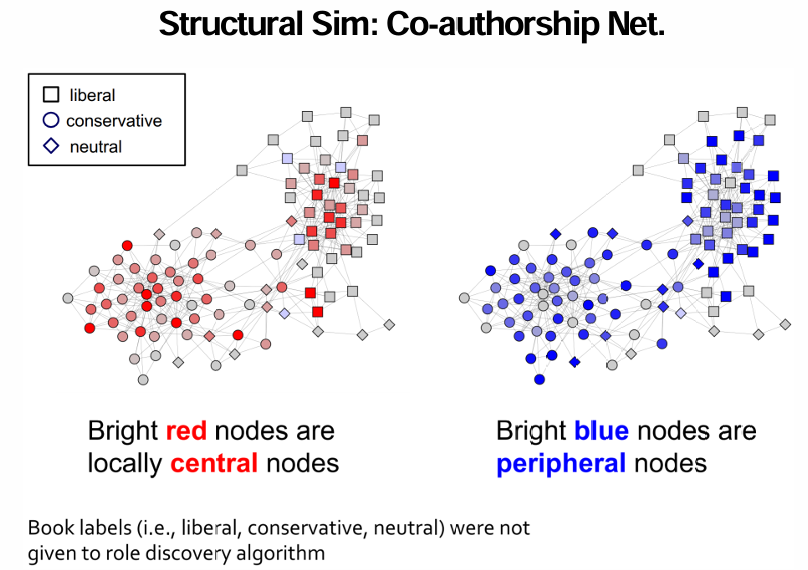
Application: Structural Similarity
Task: Cluster nodes
use RoIX to assign each node a distribution, determine similarity between nodes
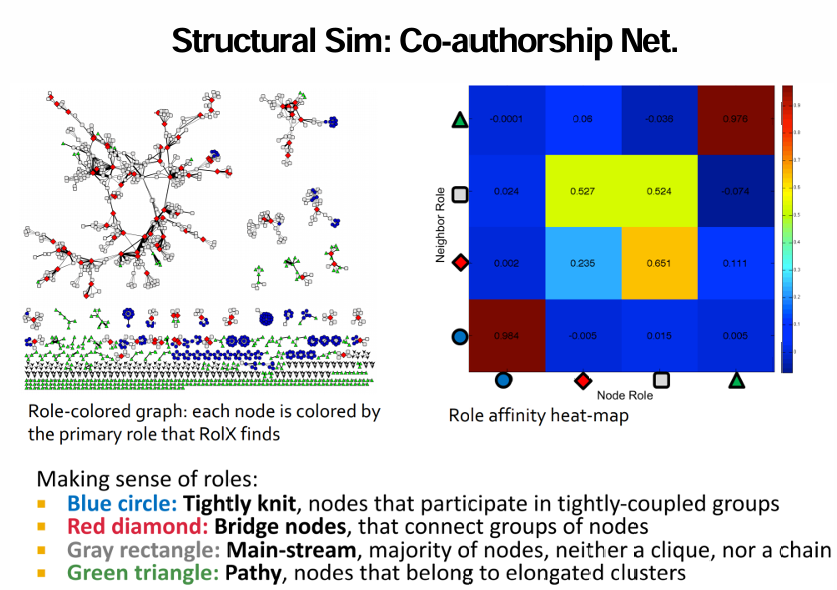
blue- 엄청 모여있는 그룹
red- bridge
gray- 일반
green- 길쭉한 클러스터 이어줌
elongated: 길쭉한
peripheral: 주변의
2. Communities: Motivation
Why contacts were often acquaintances rather than close friends?
Granovetter's Answer
two perspectives on friendships:
structural: span different parts of the network
interpersonal: strong or weak
span: 걸쳐있다
- Structural role: Triadic Closure = high clustering coefficient
같이 친구인 애 있으면(겹지인) 친구가 될 likelihood 증가
reason: B,C의 겹지인 A
B, C 둘다 A와 시간을 보내니 만날 확률 높음, 겹지인 있으니 신뢰, A가 disjoint relationships 유지하기 힘들어서 같이 데려오면 좋음 - connection between the social and sructural role of an edge
first point: Structure
Structurally embedded edges are also socially strong
Long-range edges spanning different parts of the network are
socially weak
second point: Information
Long-range edges 네트워크의 다른 부분의 정보를 모을 수 있게해줌
Structurally embedded edges 정보 중복
redundant: 중복된
-> structurallly embedded edges: socially strong, 정보 중복
Long-range edges: socially weak, 정보 유용
Edge Strength in Real Data
Edge Overlap
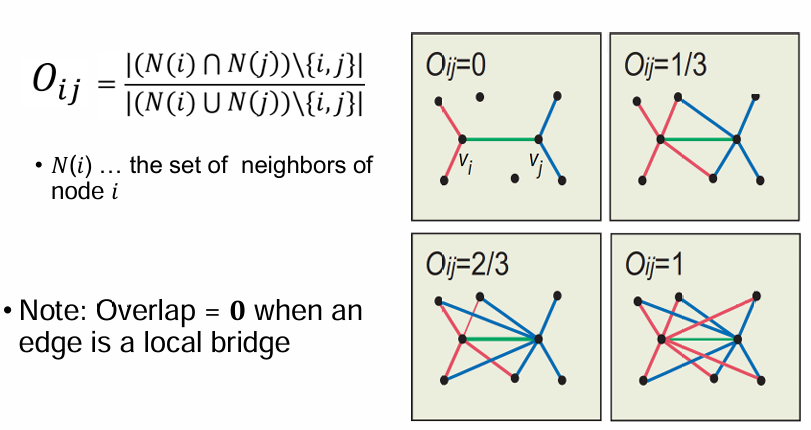
= neighbors 교집합/합집합
Strong ties are more embedded(higher overlap)
Link Removal by Overlap
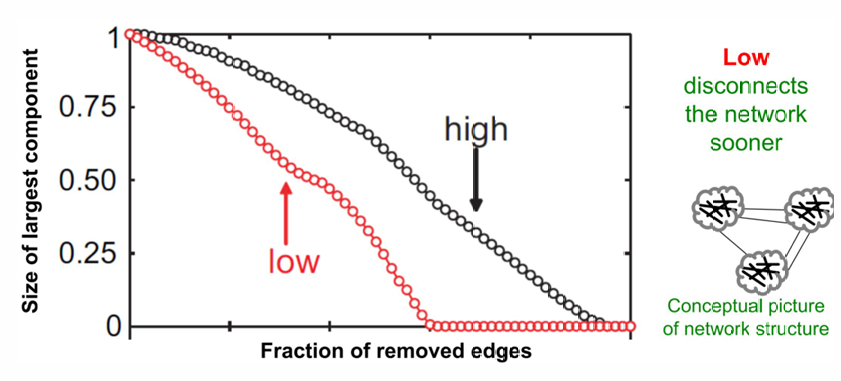
high overlap- edge 제거해갈 때 가장 큰 요소의 크기가 천천히 작아짐
Network Communities
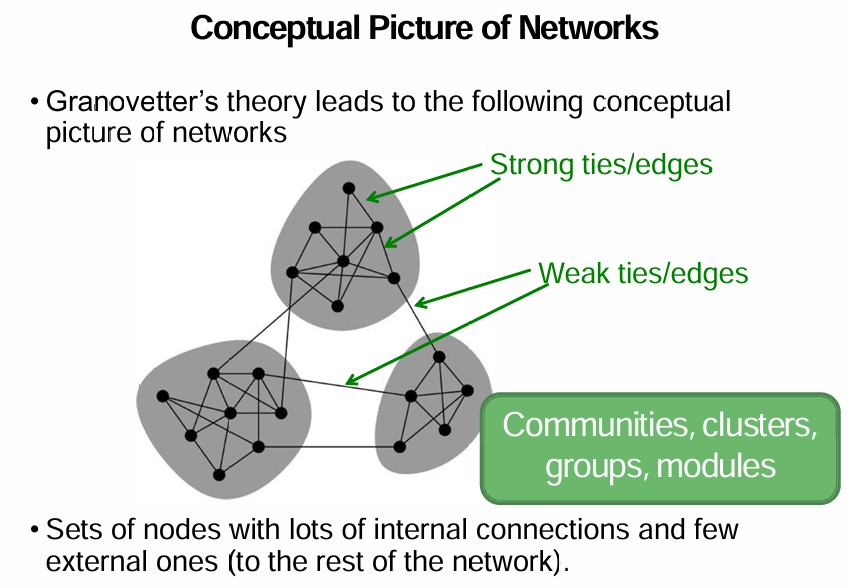
set of nodes with lots of internal connections and few external connections
Strong ties/ Weak ties
Not homogeneous- no equal #edges
Local clusters exist
skewed to a few nodes 치우치다
Week 4-2. Community Detection
Finding Network Communities
- Social Network Data
examples
Null Network Configuration Model
real network G, n nodes, m edges, rewired network G'
Same degree distribution but uniformly random connections, multigraph
- same # of edges G, G'증명
expected # of edges between nodes i, j of degree :
The expected number of edges in G'
Note:
Modularity
a measure of how well a network is partitioned into communities
given (a partitioning of the network) into (groups disjoint)

- Modularity values range [-1,1]
# edges within groups가 expected number 넘으면 양
0.3-0.7 넘으면 significant community structure
1. Newman Method
Edge Betweenness: # of shortest paths passing over the edge
Divisive hierarchical clustering based on the edge betweenness 분열적 계층적 군집화
works on undirected unweighted networks
- steps:
Calculate betweenness of edges
Remove edges with highest betweenness
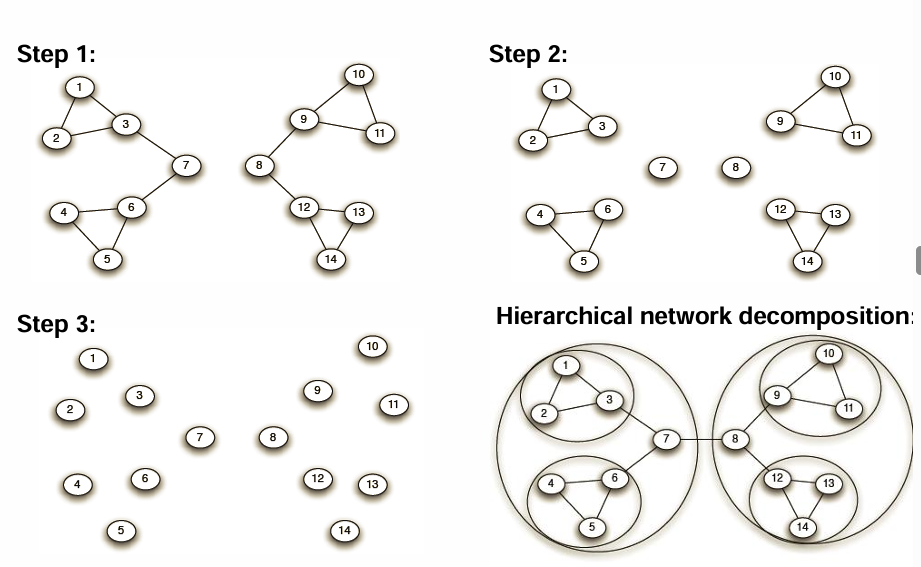
Connected components are communities
Gives a hierarchical decomposition of the network
Repeat 1-5
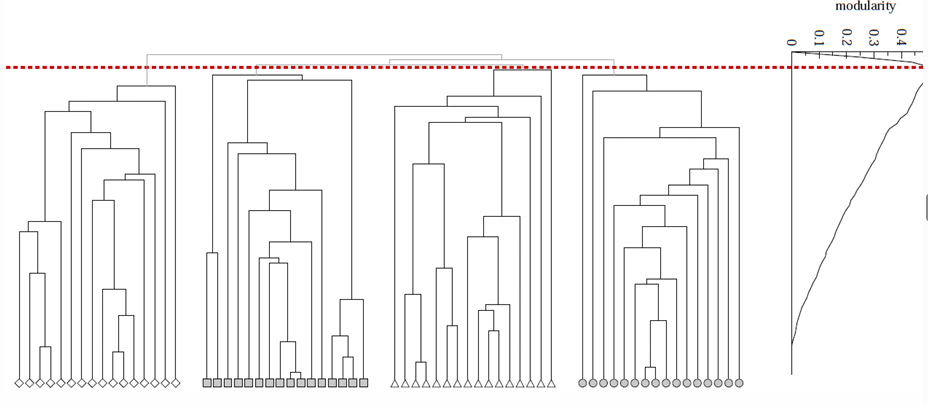
→ Find the best clusters based on threshold of modularity
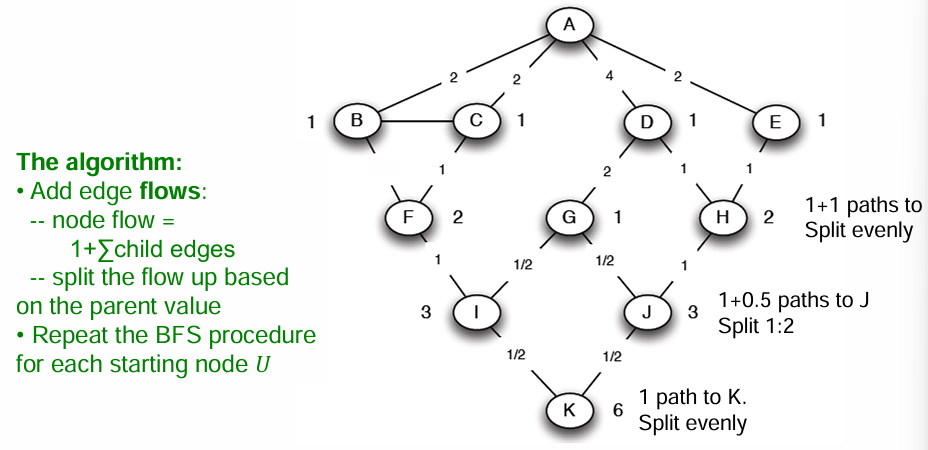
Compute Edge Betweenness
randomly selected node, conduct BFS(breath first search)
count the # of shortest paths from A to all other nodes of the network
Compute betweenness by working up the tree from the lowest layers of the tree
if multiple paths, count them fractionally
랜덤으로 선택된 노드로 다른 모든 노드와의 최소 거리 수를 센다
낮은 층부터 betweenness 계산
The algorithm: node flow = 1 + child edges, parent value 기반으로 split the flow up
repeat BFS for each starting node U
Hierachical network decomposition
decide clusters with the highest modularity
2. Louvain Algorithm
Greedy algorithm for community detection
O(nlogn)
support weighted graphs
provides hierarchical communities
large networks- fast, high modularity
greedily maximizes modularity
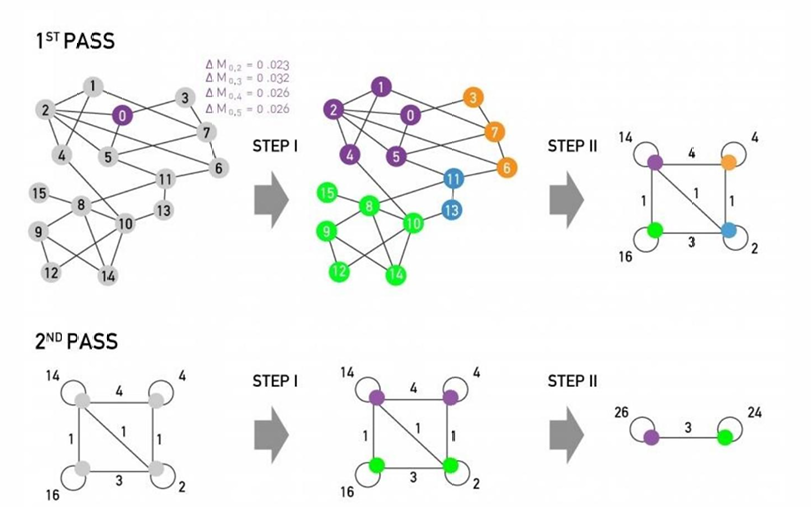
pase 1- Partitioning
: only local changes to node-communities memberships로 modularity is optimized
put each node into a distinct community
each node i two calculation:
Compute the modularity delta() when putting node i into the community of some neighbor j
Move i to a community of node j that yields the largest gain in
runs until no movement yields a gain- local maxima of modularity
node를 community에 놓음, 이웃 j node의 community로 옮길 때 modularity의 변화량이 가장 큰 곳으로 감, 더이상 gain이 없을 때까지 이동
- Modularity Gain
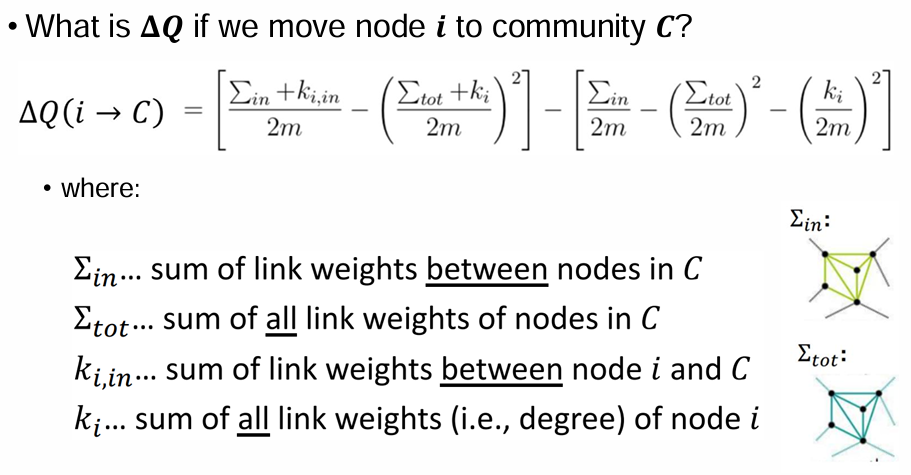
: C의 between nodes의 link weights합
: C의 노드들의 모든 link weights 합
: node i, C 사이의 link weights의 합
: node i의 모든 link weights
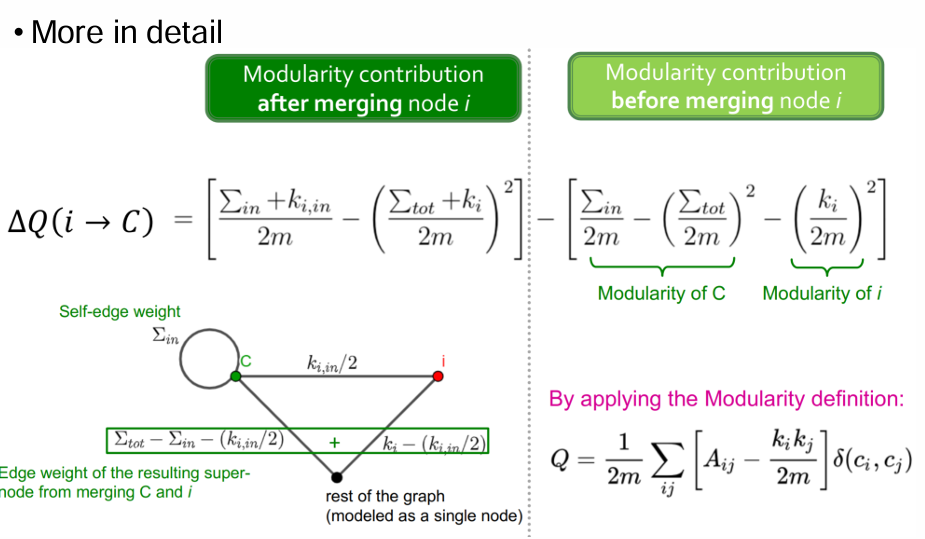
phase 2- Reconstructing
: The identified communities are aggregated into super-nodes
super-nodes끼리 one edge만 있으면 이어진거임
두 super-nodes 사이 edge의 weight는 모든 edges의 weights의 합
- Pseudo-code Description

Week5-1. Community Detection Examples
1. Pin Recommendation
Modeling Image Propagation as Tree
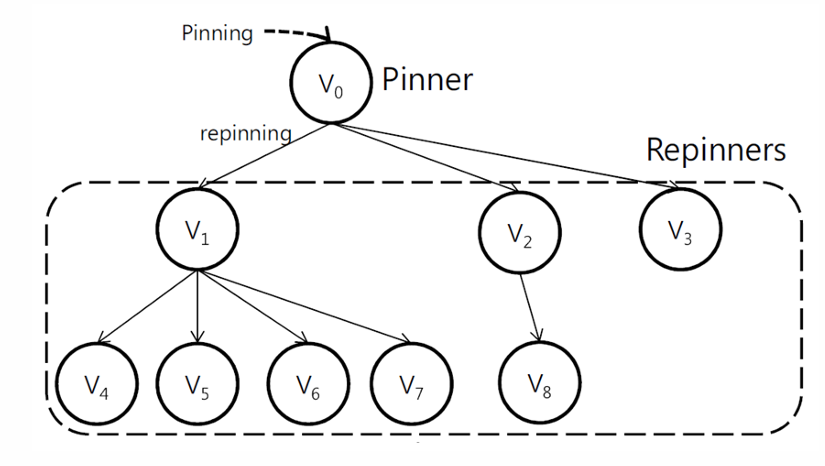
significant correlation between # repinners and pin's influence itself(pins, followers/original pin, pin-Tree)
Interest Graph in Pinterest
relations among users
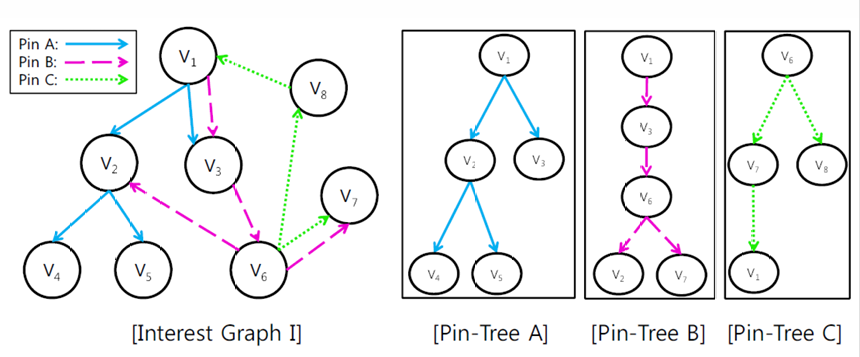
Community Analysis in Interest Graph
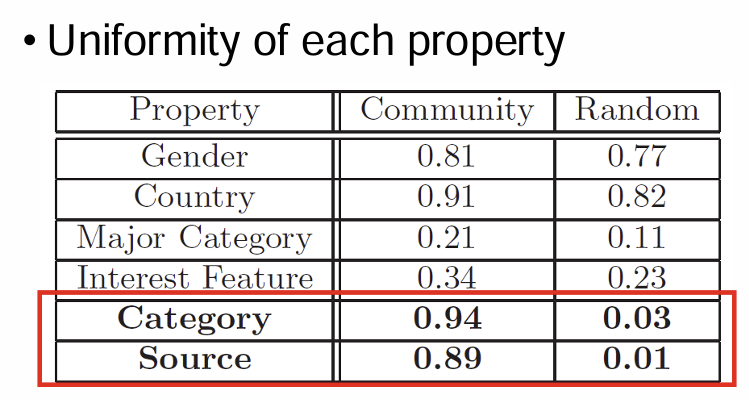
- Uniformity in the same community:
같은 community의 임의의 두 사람이 same property를 가질 확률
Properties: User's similarity-gender, Shared interests- category, source
- trace-driven simulation: candidate pin list -> validate actually consumed
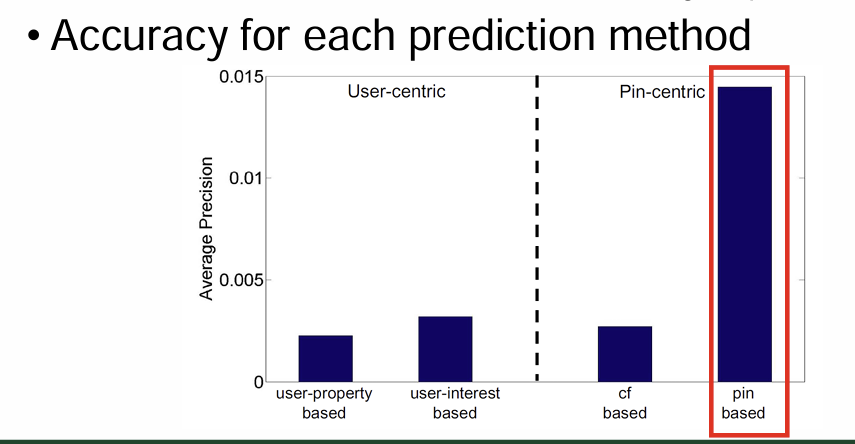
Prediction on Pin Consumption
Prediction methods
- User-centric
User-property-based: gender
User-interest-based: (C1,C2...) - Pin-centric
CF-based: (item-to-item) collaborative filtering technique
Pin-based: properties of pin(category, source) + collective opinions of other users(likes of original pin)
2. Video Recommendation
NOTE: Bipartite Graph Projection
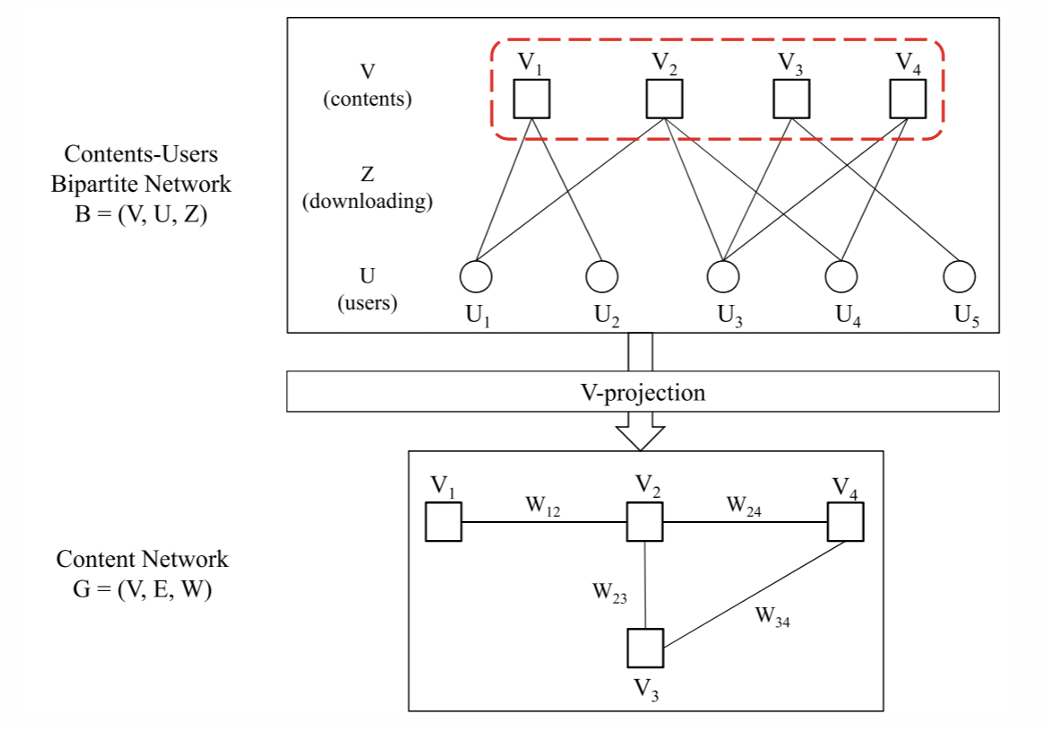
Key Insights of EDA
Similarity analysis among the members in the same community
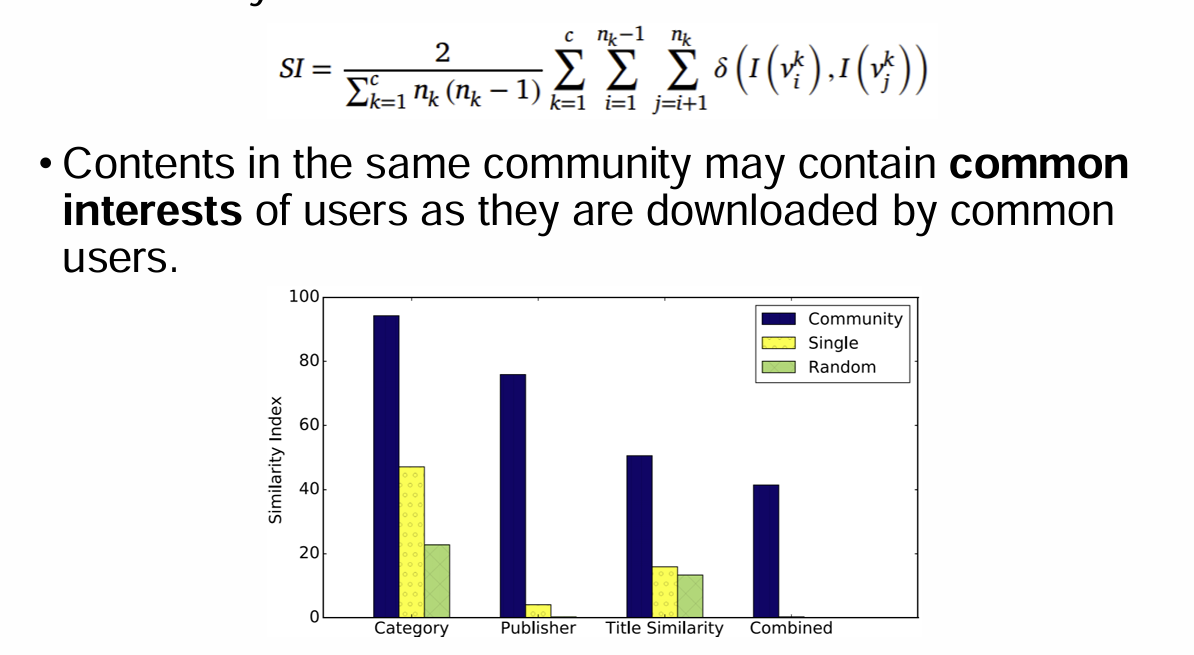
contents in the same community 는 같은 user한테 다운받아져서 user의 common interests를 포함할지도 모른다
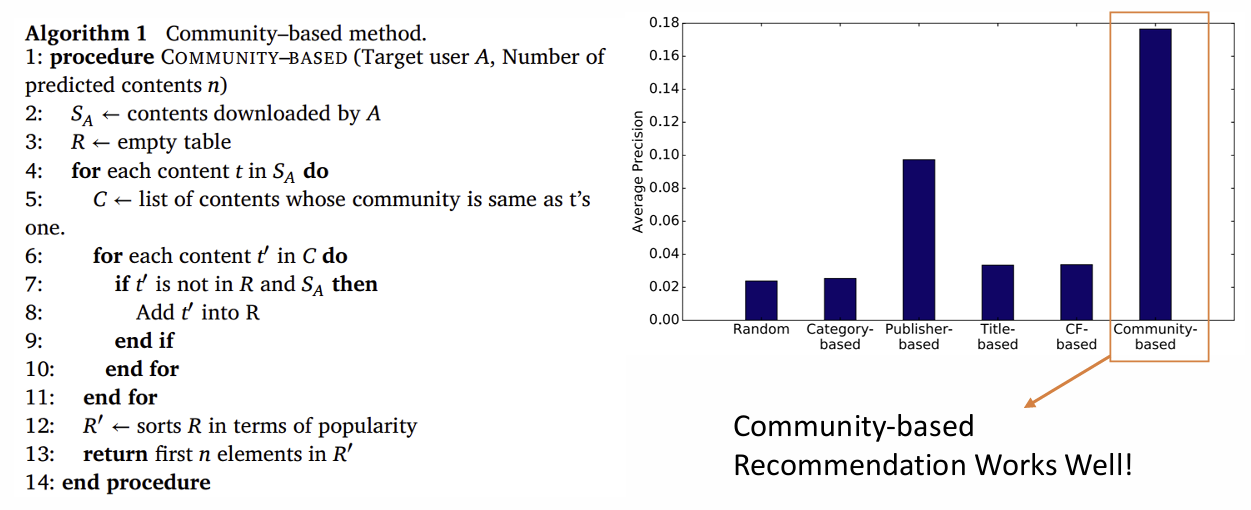
A가 다운받은 contents , t와 같은 community에 있는 contents
t'가 , 빈 테이블 R에 없으면 R에 넣기, C 다 쓸 때까지 반복
popularity로 sort R -> R'
return first n elements in R'
3. Community Detection Applications
Social Support for Mental Health
mental status 드러내기 힘듦 -> online social support
anonymity, connection beyond acquaintance, interaction with less restriction on space and time
-
Methodology: Dataset Construction
collect support-seeking posts, replies
assign Informational Support, Emotional Support scores based on BERT-based classification model -
Methodology: Graph Modeling
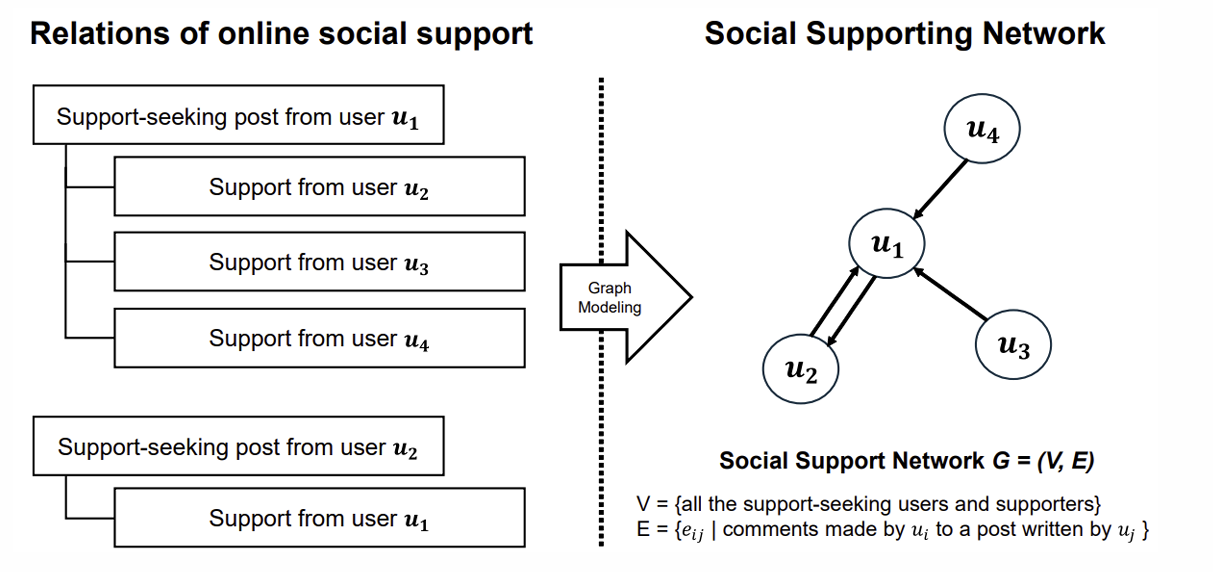
- Key Result on Community Analysis
Community detection(Louvain), LDA,
t-SNE of keywords embeddings (w2v) of communities
Big cross-subreddit communities deals with general MH topics(anxiety, depression,...)
small communities cover specific topics(hair pulling, cyber-bullying,...)