Week 5-2. PageRank
1. PageRank
assigns a PageRank(- score, measure of importance) to each webpage
graph = web
nodes = web pages
edges = hyperlinks
navigational(page to page) -> transactional(post, comment, like)
- idea: LINKs as Votes
in-coming links, from important pages(recursive) important
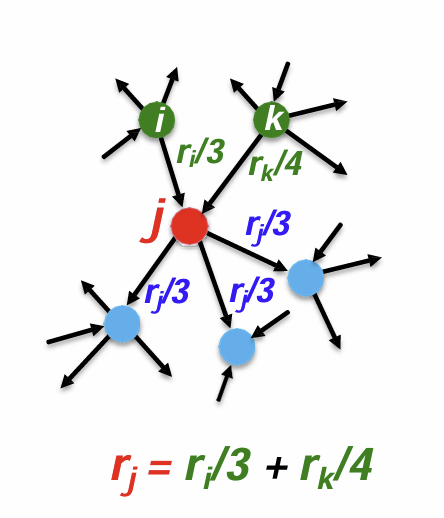
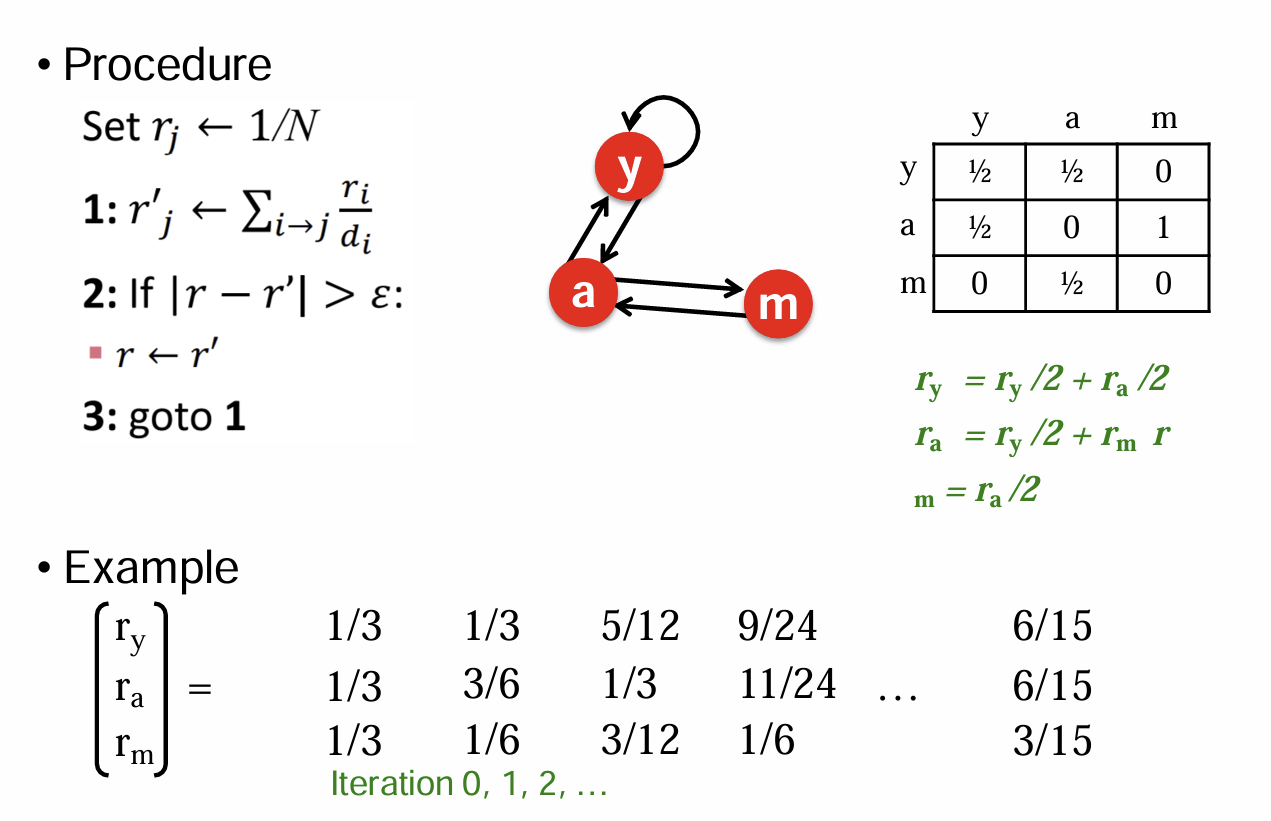
Beginning of PageRank: The "FLOW" Model
each link's vote, source page의 importance와 비례
page i with importance out-links- votes
page j rank : sum of the votes on in-links
PageRank: Matrix Formulation
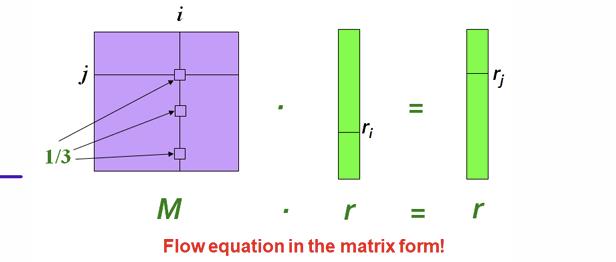
- Stochastic adjacency matrix M
page j has out-links
if j -> i, then
columns sum to 1 - Rank vector r: an entry per page
: importance score of page i
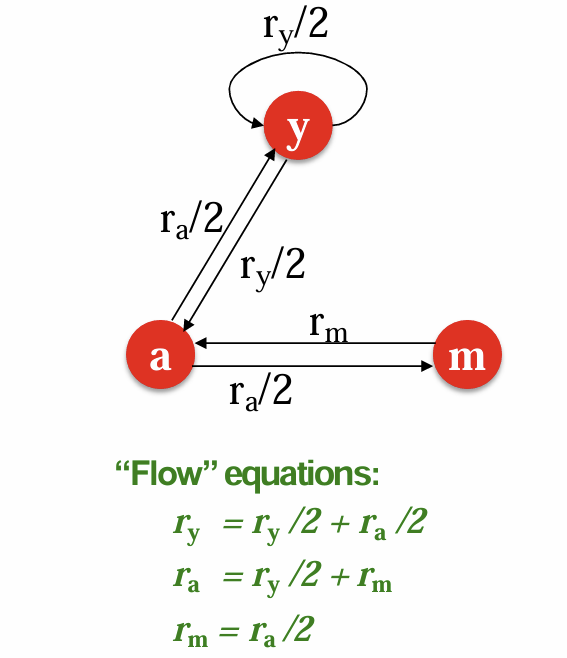
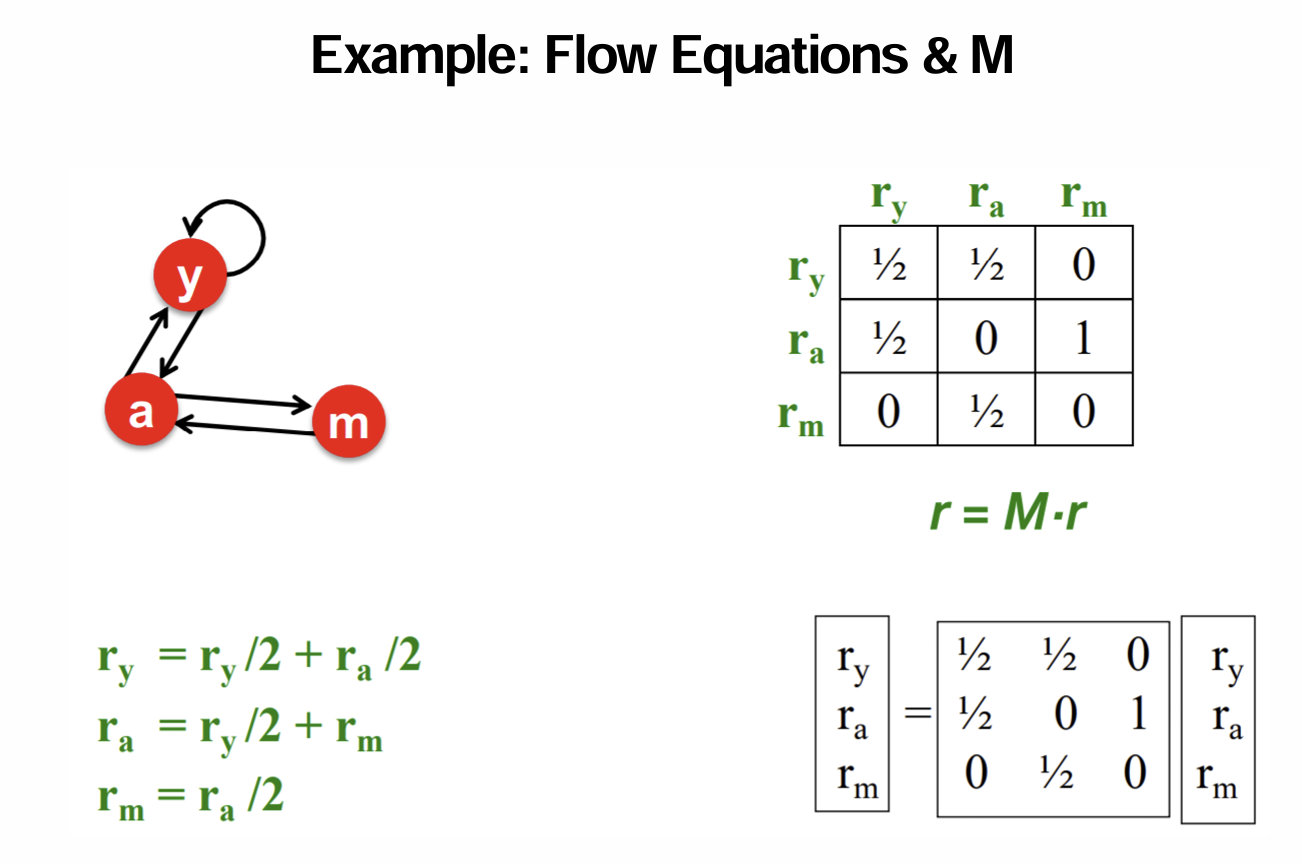
- The flow equations
2. Solving PageRank
Gaussian elimination -> bad, too much cost
Power Iteration
n nodes, initialize, iterate, repeat until convergence
L1 norm

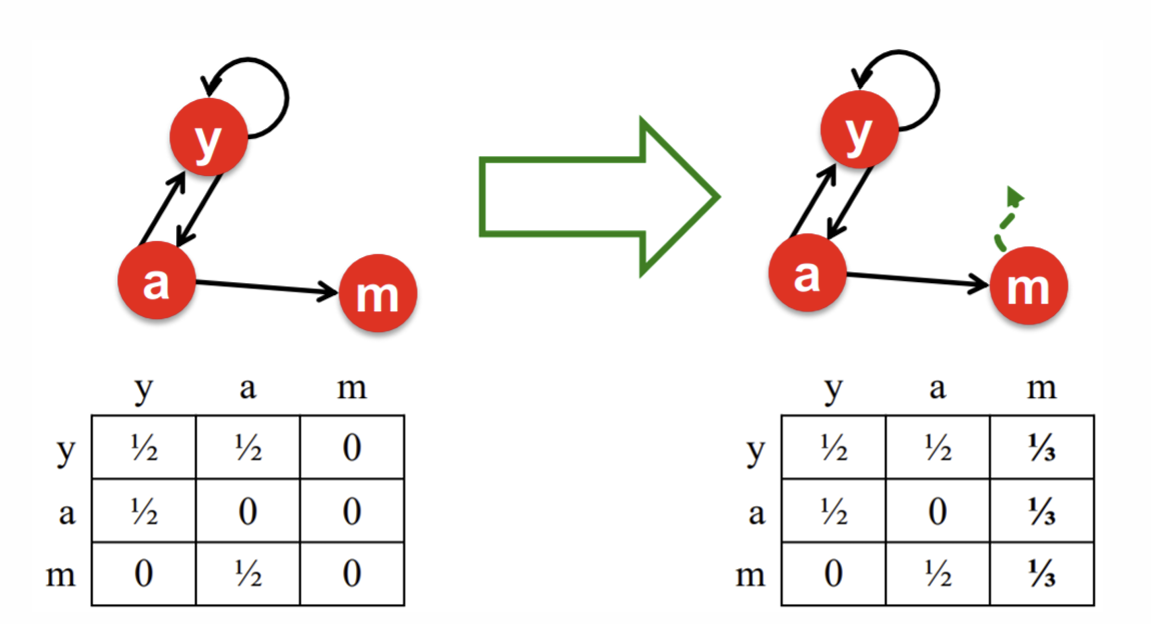
Two Problems: Dead Ends & Spider Traps
Dead ends: no out-links
Spider traps: all out-links are within the group
Solution: Teleports
- For Spider traps: random surfer
prob follow a link at random
prob jump to a random page - For dead-end: follow random teleport links with total probability 1.0 from dead-ends
adjust matrix accordingly
000이면 무조건 random teleport
Final Solution: Random Teleports
-
PageRank equation
-
Google Matrix G
recursive problem:
power method still works
= 0.8,9 (5 steps on average to jump)

3. Topic Specific PageRank
Modified Scenarios with Topic-Specific PageRank
1. Model the web as a graph
2. Compute the importance of webpages with PageRank
3. Web-search query
The user types the query “Trojan”
4. Identify relevant webpages
Find webpages relevant to “Trojan”
-> compute the importance of webpages based on their relevance to a topic
5. Show them to the user
Webpages with high generic -> topic-specific PageRank will be presented first
Goal: Evaluate Web pages by how close they are to a particular
topic, e.g. “sports” or “history”
search queries answered based on the interests of a user, e.g. “sports” or “history”
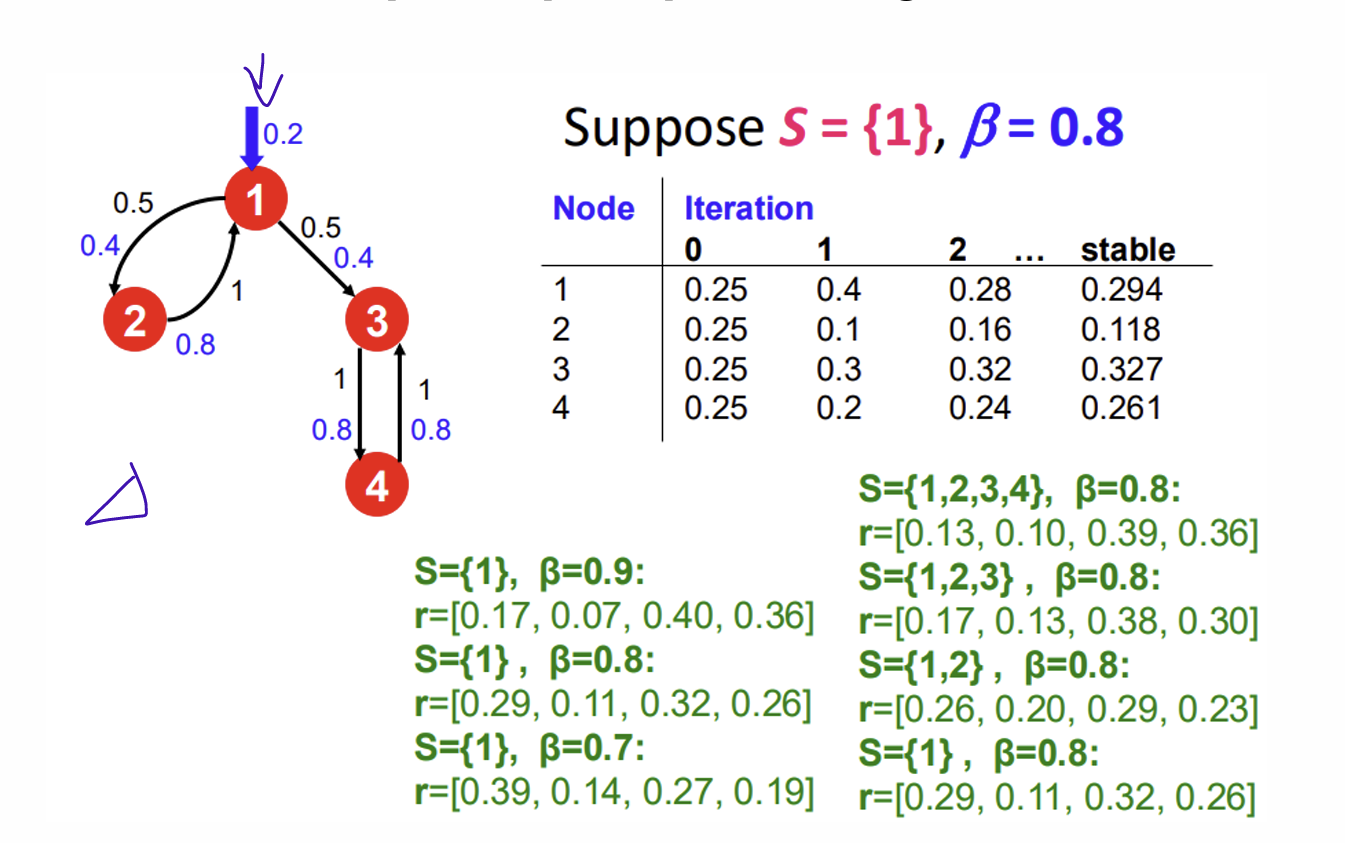
How to Compute: Topic-Specific Teleportation
idea: Bias the random walk
When teleports, pick a page from a set S
S contains only relevant pages
For each teleport set S, we get a different vector
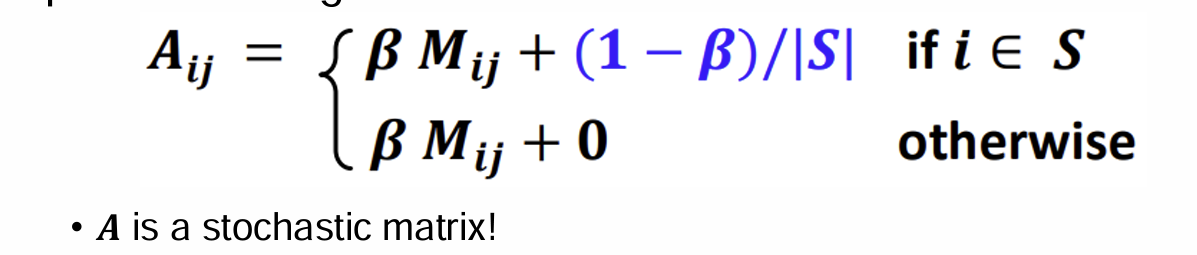
안 외워도 됨
Which topic ranking to use: user can pick, classify query into a topic, context of the query, user context
