Week 7. ML with Graph
1. Fundamentals of ML/DL
ML <P, T, E> performance, task, experience
Machine Learning
learns patterns by training on previous data, makes prediction on unseen cases
- process in general
Extract/select/generate features
Select candidate ML models
Train the model with features(x) and target variable (y)
Evaluate the model by testset(Acc, AUC)
conduct feature engineering- , reduce dimension of the features
Process of Feature Extraction: Hand-Crafted
biased
comes from intuition
rigorous:
(cycle)
-> think possible features -> Investigate relations(data mining) -> Vertify & measure degree of importance(w/ ML Model) ->
data mining: basic statistics, graph modeling...
- features: Graphlets, graph kernels, ...
Process of Feature Extraction: Automatic
use raw data
Deep Learning
- features: Node embedding
node u -- learn a neural network, f:u -> -->Feature representation, embedding
:representation learning
2. Tasks for Graph ML
Types of Graph ML Tasks
Node level
Edge-level
Graph-level prediction, Graph generation
Community(subgraph level)
Graph ML Tasks
Node classification: Predict a property of a node
ex) Categorize online users / items
Link prediction: Predict whether there are missing links between two nodes
ex) Knowledge graph completion
Graph classification: Categorize different graphs
ex) Molecule property prediction
Others: Graph generation: Drug discovery/Graph evolution: Physical simulation
Node-level ML Tasks
Classify/Assign labels for each node
Example: Protein Folding
A protein chain acquires its native 3D structure
amino acids - alpha helix+pleated sheet - proteins
computationally predict a protein's 3D structure based solely on its amino acid sequence
- AlphaFold: Solving Protein Folding
Spatial graph
• Nodes: Amino acids in a protein sequence
• Edges: Proximity between amino acids (residues)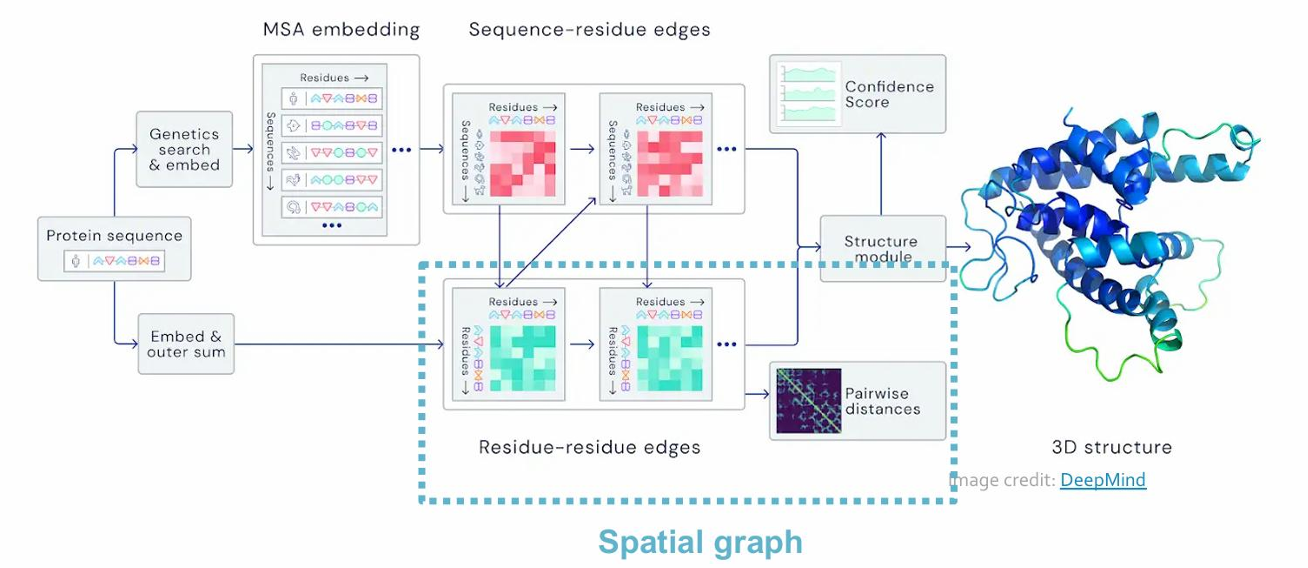 Edge-level ML Tasks
Edge-level ML Tasks
The task is to predict new links based on existing links
all node pairs are ranked, top K
Example: Recommendation
Users interacts wih items
• Watch movies, buy merchandise, listen to music
• Nodes: Users and items
• Edges: User-item interactions
Graph-level ML Tasks
Generates outputs from the features that characterize the structure of an entire graph
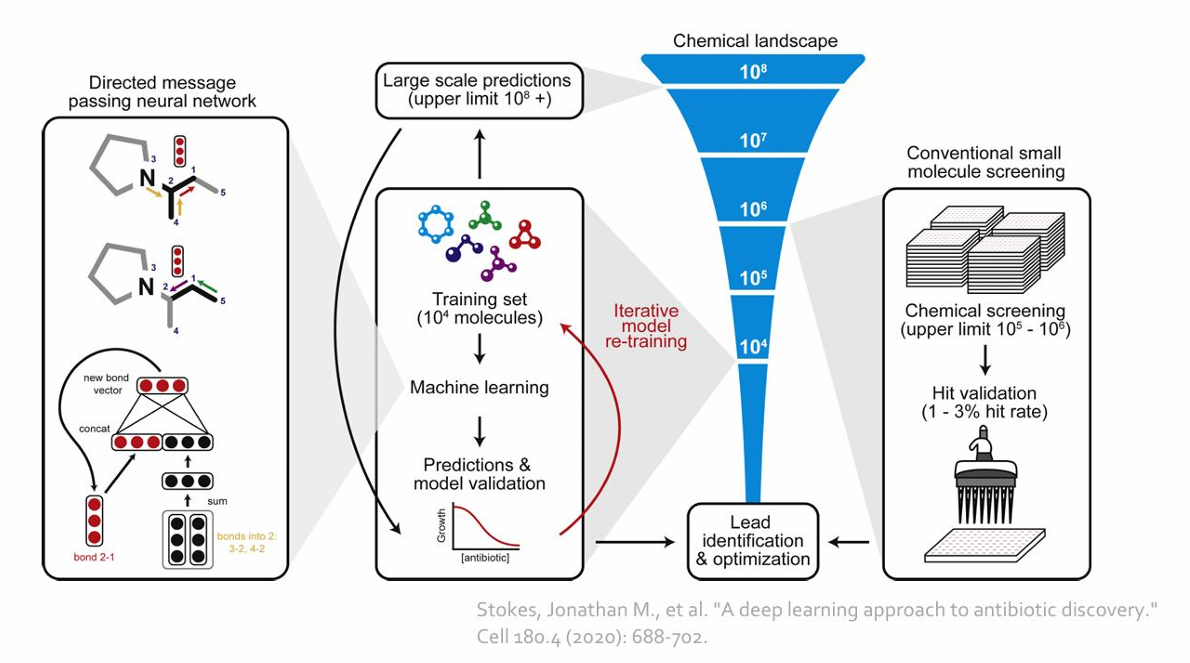
Example: Drug Discovery
Antibiotics are small molecular graphs
• Nodes: Atoms
• Edges: Chemical bonds
분자 구조 그래프 바꿈
Graph classification tasks by GNN: predict promising molecules
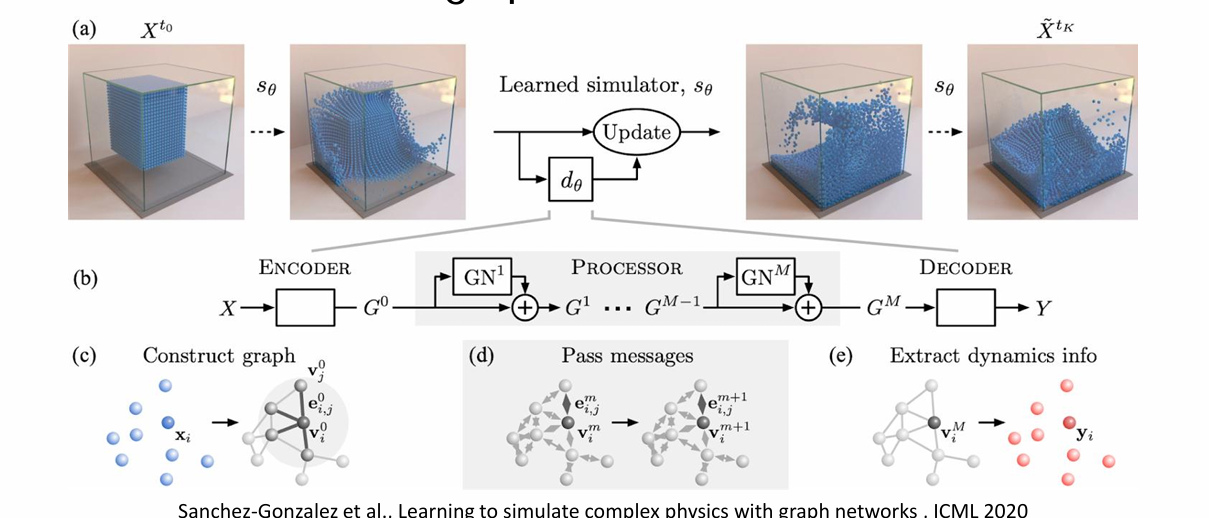
Example: Physics Simulation
• Nodes: Particles
• Edges: Interaction between particles
Tasks: Predict how a graph will evolve over
3. Graph ML: Traditional Approach
Traditional Pipeline for Graph ML
• Design features for nodes/links/graphs
• Obtain features for all training data
Train on ML model: Random Forest, SVM, Neural Network, etc.
Apply the ML model: given a new node/link/graph, obtain its features and make a prediction
ML in Graphs
Goal: Make prediction for a set of objects
Design choices:
features: d-dimensional vectors
objects: Nodes, edges, sets of nodes, entire graphs
Objective function:?
How to Design Features from a Given Graph
Using effective features for good test performance
ML uses hand-designed features- 뒤에서 알아보자
focus on undirected graphs
4. Node-level Tasks: Traditional Approaches
Goal: Characterize the structure and position of a node in
the network
Node Features: recap
- clustering coefficient
- Graphlet Degree Vector(GDV)
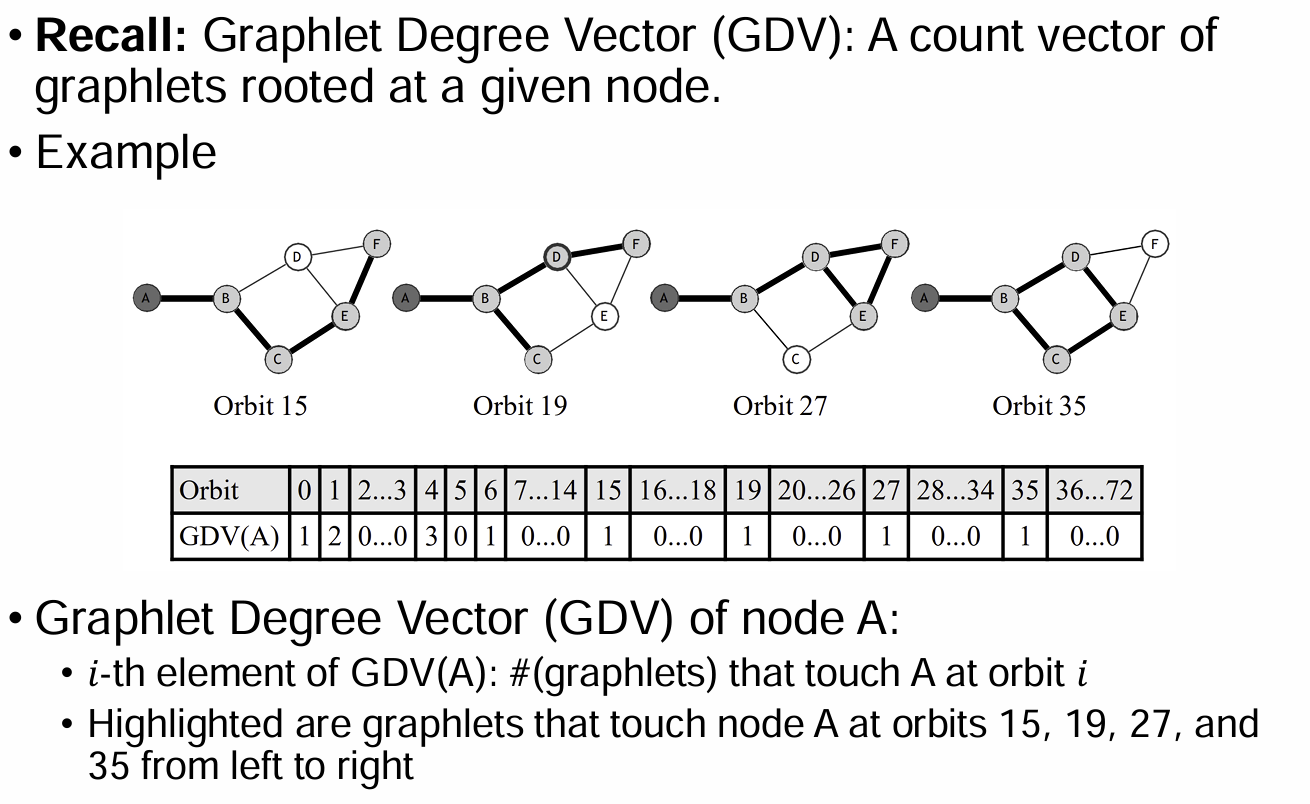
- Structural Roles (by RoIX)
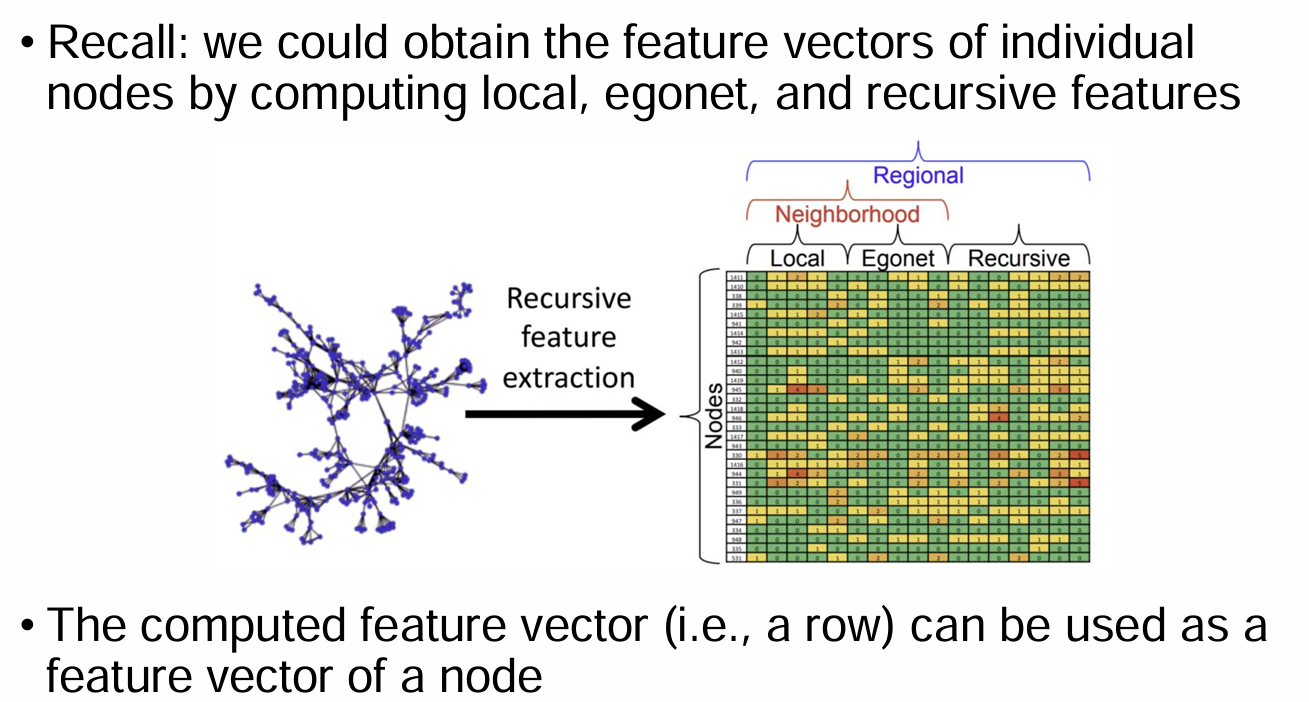
Summary
-
importance-based features: capture the importance of a
node is in a graph
node degree, node centrality
-> predict influential nodes in a graph -
structure-based features: Capture topological properties
of local neighborhood around a node.
Node degree, clustering coefficient, structural roles
-> predict a particular role a node plays in a graph
5. Edge-level Tasks: Traditional Approaches
- recall
predict new links
all node pairs are ranked, top k are predicted
design features for a pair of nodes
Link Prediction as a Task
two formulations
- links missing at random: remove random set of links
- links over time: G time t, output ranked list L predicted to appear at G
evaluation: n = # new edges that appear during the test period , take n elements of L and count correct edges
Link-Level Features:
1) Distance-based Features
: Shortest-path distance between two nodes
not capture the degree of neighborhood overlap 겹이웃 수 모름
2) Local Neighborhood Overlap
: Captures # neighboring nodes shared between two nodes
neighbor 교집합, /합집합, : degree?
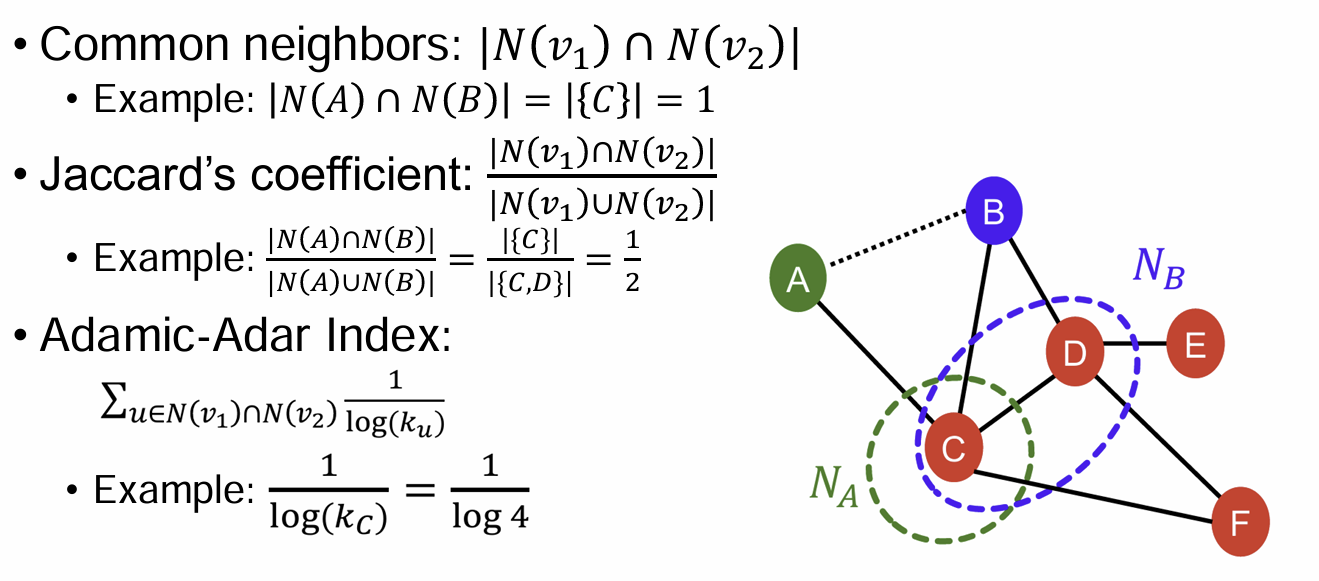
겹치는 이웃 없으면 0 -> 뒤에 해결
3) Global neighborhood overlap
Katz index: count # paths between two nodes
- Power of adjacency matrix: # paths of length k
u가 v의 neighbor 이면 1
# paths of length 1 between u and v =
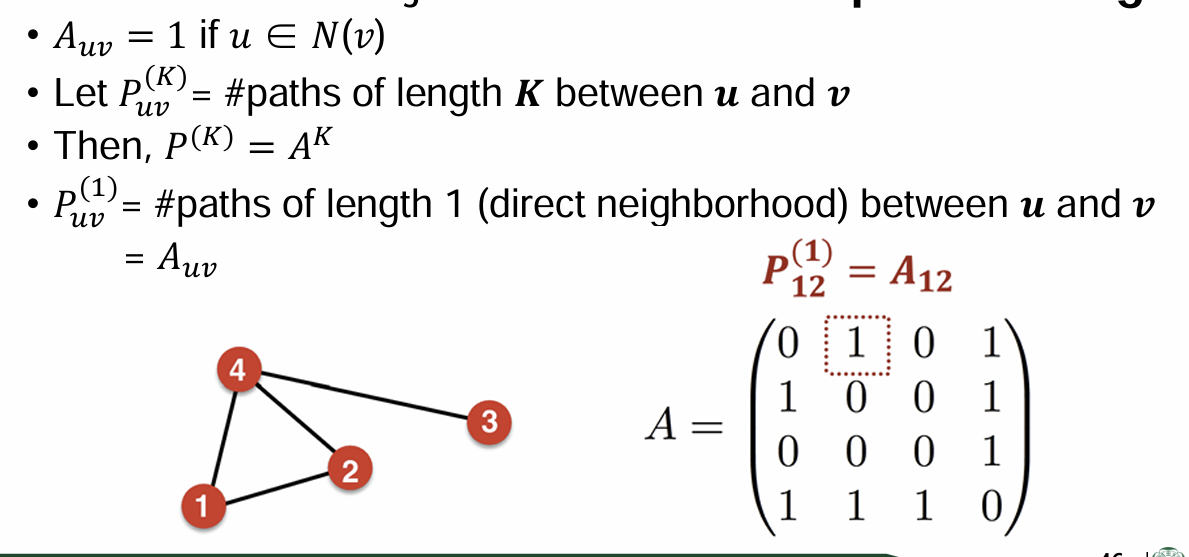
Computing
step 1: Compute #paths of length 1 between each of 𝒖’s neighbor and v
Step 2: Sum up these #paths across u’s neighbors
제곱
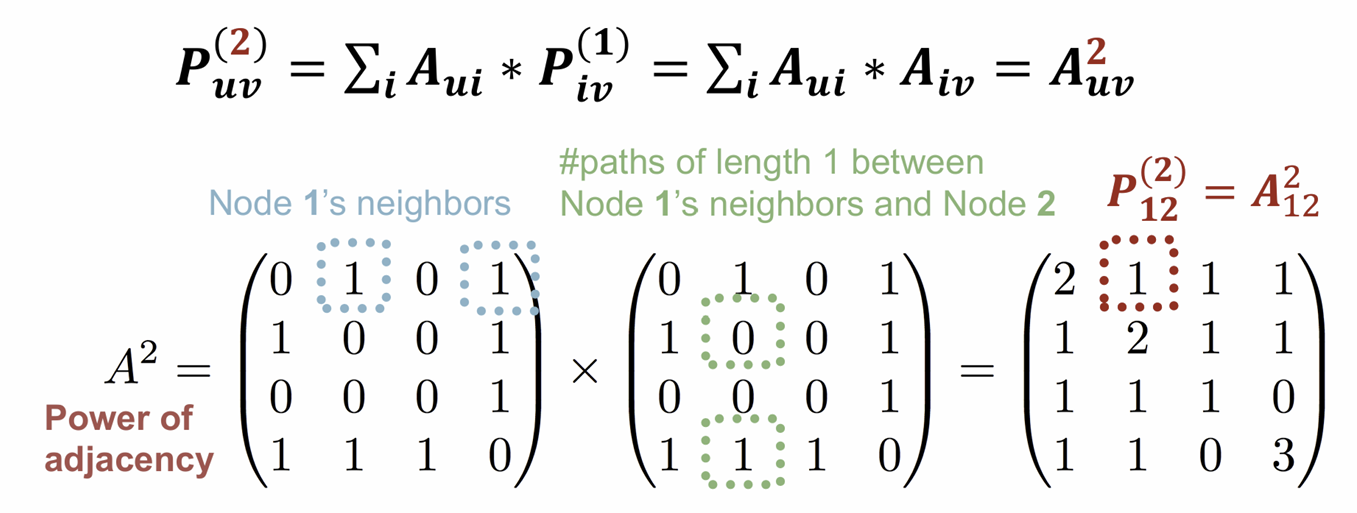
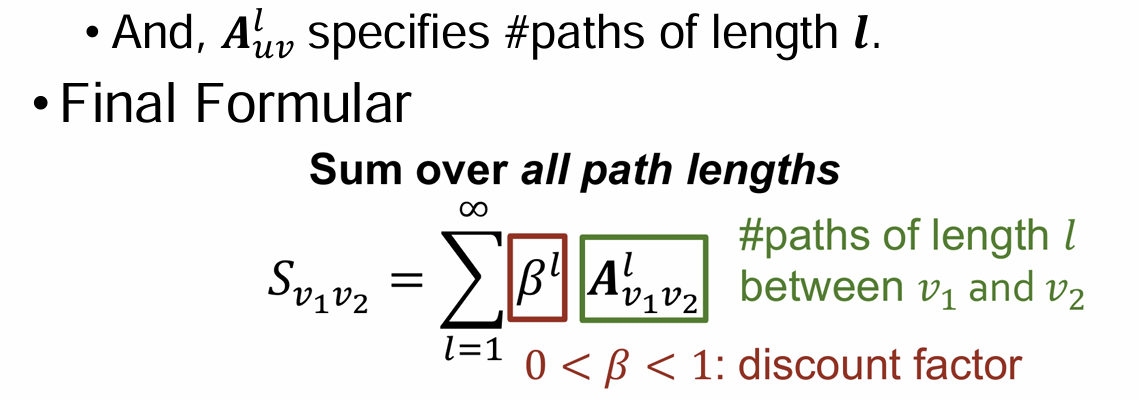
- Generalization -> Katz Index
: count # paths between two nodes(recap)
#paths of lenght 1 + length 2 + ...
6. Graph-level Tasks: Traditional Approaches
- recall: characterize the structure of an entire graph
Graph Features: Degree Distribution
Bag of node degrees: node degrees counts as features for graph (no ordering considered)
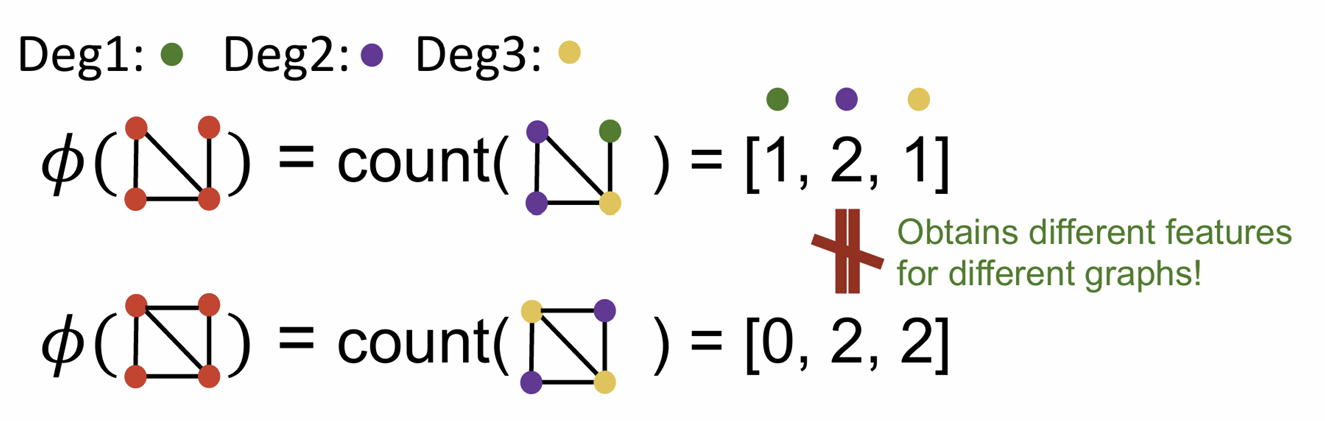
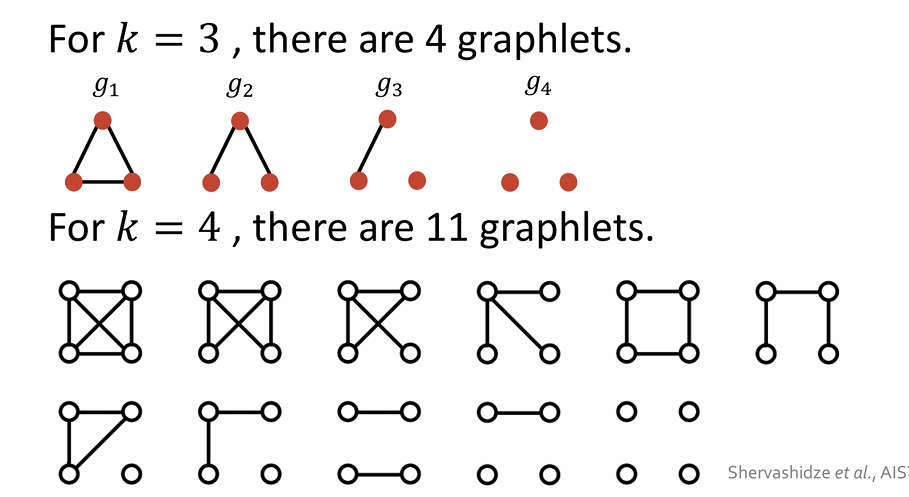
Graph Features: Graphlet
Key idea: Count #different graphlets in a graph
allow isolated nodes, not rooted (different from node-level features)
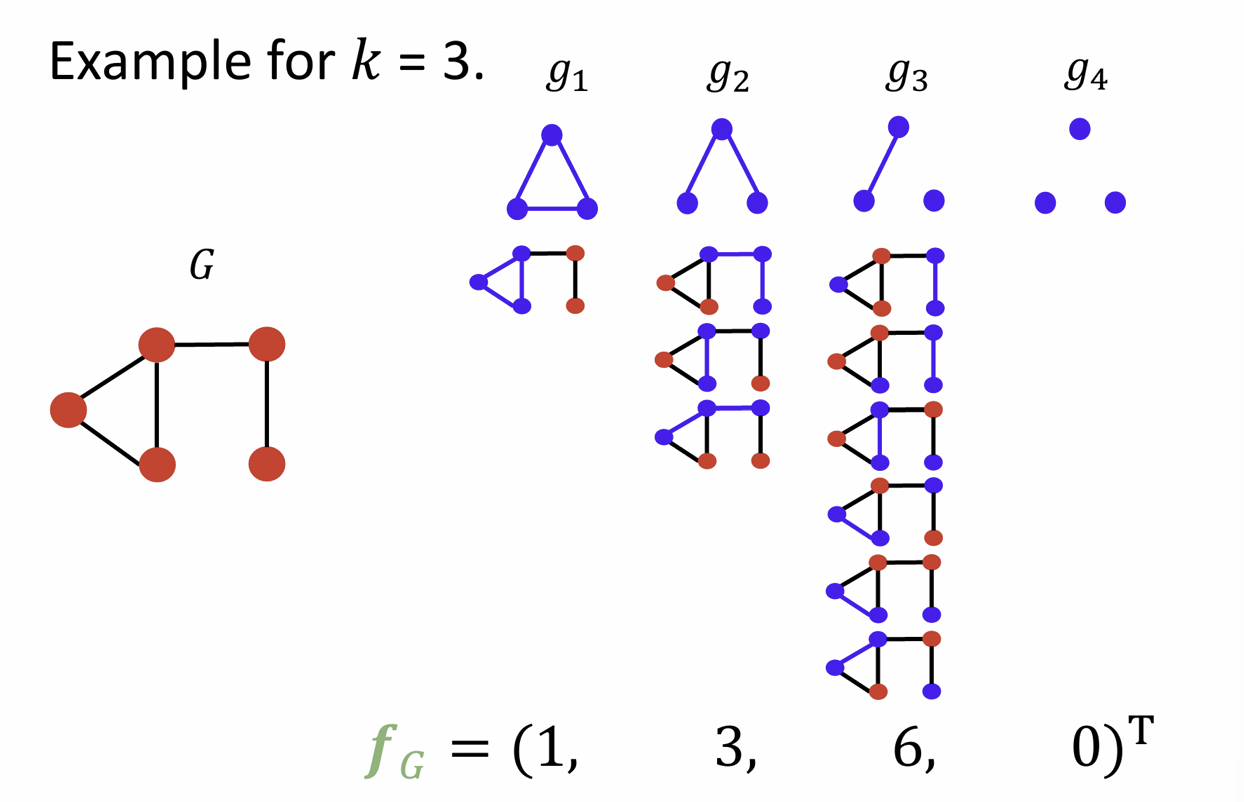
Advanced: Graph Kernel
Kernels: use “similarity-like mechanism” for computing features
ex) inner product
Graph Kernels: Measure similarity between two graphs
Graphlet Kernel, Weisfeiler-Lehman Kernel,...
