이진(이분) 탐색
Binary Search
정렬되어 있는 리스트에서 탐색 범위를 절반씩 좁혀가며 데이터를 탐색하는 방법
변수 3개(start, end, mid)를 사용하여 탐색하며, 찾으려는 데이터와 중간점 위치에 있는 데이터를 반복적으로 비교해서 원하는 데이터를 찾는 것
접근 방법과 백준 10815 숫자 카드
Java로 만들어본 이진 탐색 알고리즘 코드
[반복문]
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static int[] arr_n;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr_n = new int[n];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr_n[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(arr_n);
int m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (binary_search(num)) bw.write("1 ");
else bw.write("0 ");
}
bw.flush();
br.close();
bw.close();
}
public static boolean binary_search(int num) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr_n.length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (num == arr_n[mid]) return true;
else if (num > arr_n[mid]) start = mid + 1;
else end = mid - 1;
}
return false;
}
}[재귀 함수]
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static int[] arr_n;
static boolean result;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr_n = new int[n];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr_n[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(arr_n);
int m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (binary_search(num, 0, n-1)) bw.write("1 ");
else bw.write("0 ");
}
bw.flush();
br.close();
bw.close();
}
public static boolean binary_search(int num, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) return false;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (num == arr_n[mid]) return true;
else if (num > arr_n[mid]) return binary_search(num, mid + 1, end);
else return binary_search(num, start, mid - 1);
}
}풀이
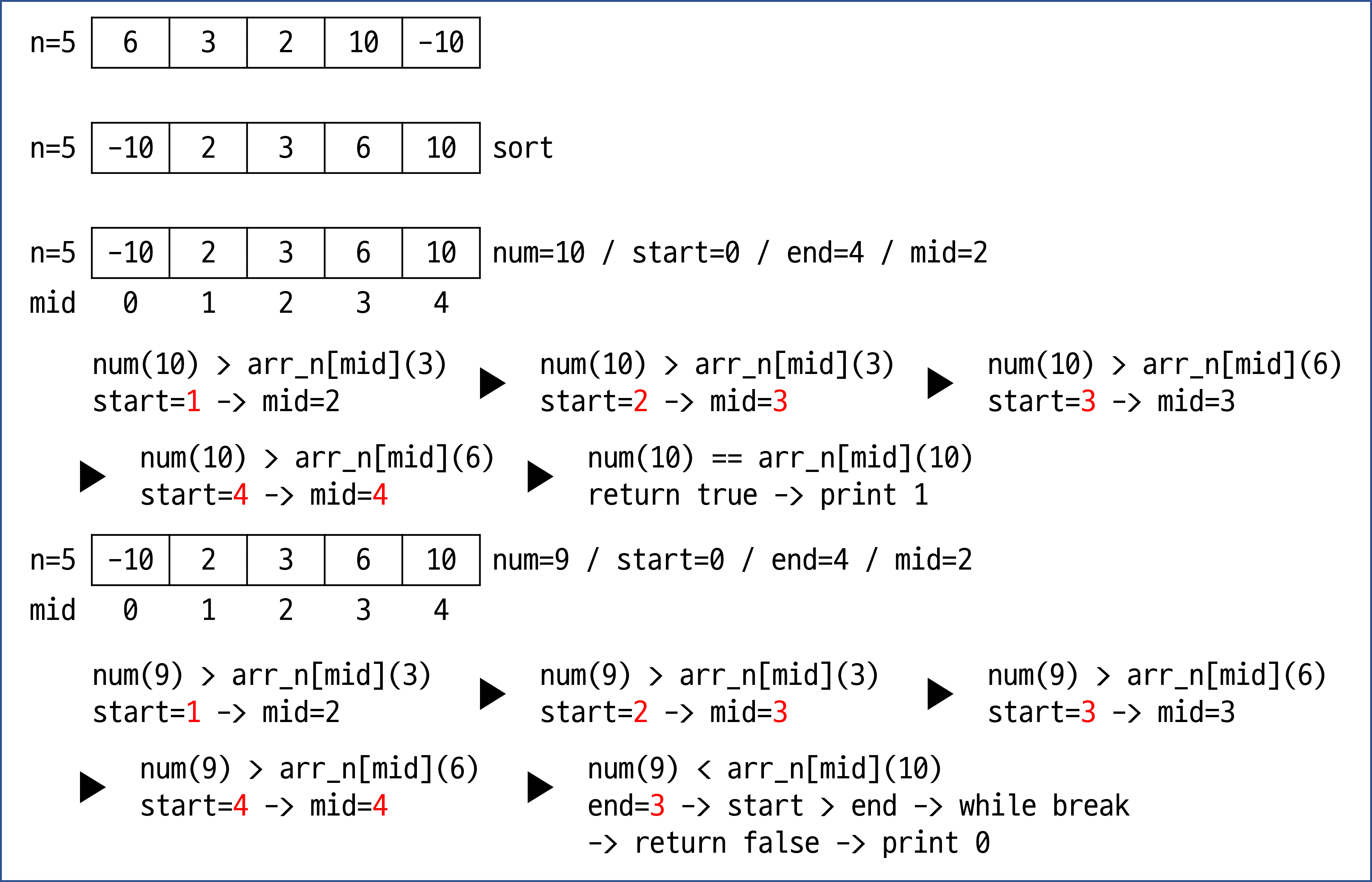
이진 탐색은 mid 값을 구하여 mid 인덱스의 arr 값과 타겟을 비교하는 방법임.
만약 arr 값이 더 크다면 end 값을 하나 줄이고, 타겟이 더 크다면 start 값을 하나 올리는 형식으로 진행하며, 이는 start가 end를 넘으면 break됨. → 자동으로 false 출력
arr 값과 타겟이 같다면 배열 안에 타겟이 있는 것으로 판단하여 true 출력
후기
나중에 자료구조 알고리즘에서 배웠던 정렬도 다 자바로 코드짜봐야겠다.
