서론
이진 분류는 머신러닝에서 가장 기본적이며 널리 사용되는 문제 유형 중 하나로, 주어진 입력 데이터가 두 개의 클래스 중 하나에 속하는지를 판단하는 과정이다.
로지스틱 회귀는 이진 분류 문제를 해결하기 위한 대표적인 기법으로, 확률적 접근 방식을 통해 클래스 레이블을 예측한다.
본 포스팅에서는 이진 분류의 개념부터 시작하여, 데이터 전처리, 모델 학습, 그리고 평가 방법까지 단계별로 살펴보겠다.
로지스틱 회귀
- 트레이닝 데이터의 특성과 분포를 바탕으로 데이터 구분을 위한 최적의 선형 결정 경계 탐색
- 시그모이드 함수를 통해 선형 결정 경계를 비선형 결정 경계로 변환
- 이를 바탕으로 모델 학습, 테스트 데이터의 결과를 레이블로 예측
데이터 전처리
- 특징 변수() - PetalLengthCm
- 목표 변수() - Species
사용 데이터셋: Iris Dataset
저작권 정보: CC0 1.0 Universal
데이터 로드
# Donwload dataset from kaggle
!kaggle datasets download -d uciml/iris
# unzip zip file
!unzip iris.zipimport pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("Iris.csv", sep = ",", header = 0)[["PetalLengthCm", "Species"]]
filtered_df = df[df['Species'].isin(['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor'])] # 필요 데이터만 추출목표 변수를 이산형 레이블로 매핑
filtered_df.loc[:, 'Species'] = filtered_df['Species'].map({'Iris-setosa': 0, 'Iris-versicolor': 1})특징 변수와 목표 변수 분리
x = filtered_df[['PetalLengthCm']].values
t = filtered_df['Species'].values.astype(int)데이터 분할
- 트레이닝 데이터: 모델 학습에 사용되는 데이터 (가중치, 바이어스 최적화)
- 테스트 데이터: 최종 모델의 성능 평가에 사용되는 데이터
- 검증 데이터: 모델의 학습 과정 중 사용되는 데이터 (모델의 에폭마다 과적합 확인)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, t_train, t_test = train_test_split(x, t, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)데이터 표준화
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)Tensor로 변환
# 배치 처리 및 일관된 데이터 형태를 위해 목표 변수를 2차원 Tensor로 변환
x_train = torch.tensor(x_train, dtype=torch.float32)
x_test = torch.tensor(x_test, dtype=torch.float32)
t_train = torch.tensor(t_train, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
t_test = torch.tensor(t_test, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)배치(Batch)
ML/DL에서 데이터를 처리하는 묶음의 단위
미니배치 경사하강법
- 확률적 경사하강법은 계산이 빠르고 메모리 측면에서 효율적
- 하지만, 계산 과정에서 노이즈가 많고 학습 과정이 불안정
- 경사하강법과 확률적 경사하강법의 단점을 보완한 알고리즘
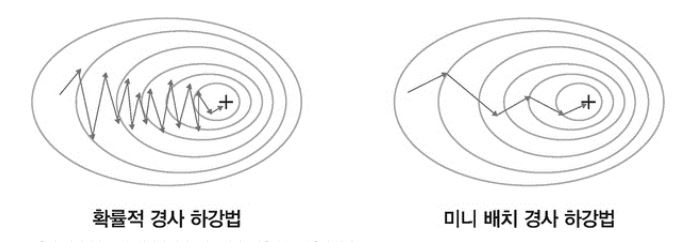 출처: 서지영(2022). 딥러닝 파이토치 교과서. 서울; (주) 도서출판 길벗.
출처: 서지영(2022). 딥러닝 파이토치 교과서. 서울; (주) 도서출판 길벗.
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
class IrisDataset(Dataset): # CustomDataset 클래스
def __init__(self, features, labels):
self.features = features # 특징 변수
self.labels = labels # 목표 변수
def __len__(self):
return len(self.features)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.features[idx], self.labels[idx]train_dataset = IrisDataset(x_train, t_train)
test_dataset = IrisDataset(x_test, t_test)
batch_size = 4
# 모델 훈련 시 데이터 순서에 따른 편향을 줄이기 위해 shuffle
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
# 모델 성능 평가 시 데이터 순서 유지
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)모델 학습
- 트레이닝 데이터의 특성과 분포를 바탕으로 데이터를 잘 구분할 수 있는 선형 결정 경계(직선) 탐색
- 직선:
- 최적의 (가중치)와 (바이어스) 탐색
- 시그모이드 함수를 통해 선형 결정 경계를 비선형 결정 경계(최적의 경계)로 변환
- 경계:
- 이를 바탕으로 모델 학습, 테스트 데이터의 결과를 레이블로 예측
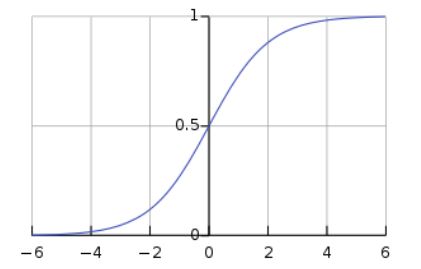
시그모이드 함수
- 비선형 함수
- 입력 값을 0과 1사이의 값으로 변환
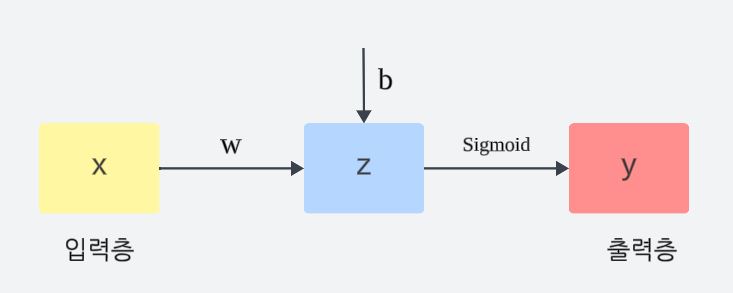
이진 분류 모델 (by 신경망)
- 입력층: 특징 변수들()
- 출력층: 예측 변수()
import torch.nn as nn
class BinaryClassificationModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BinaryClassificationModel, self).__init__()
self.layer_1 = nn.Linear(1, 1) # 입력 차원과 출력 차원을 1로 설정
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
z = self.layer_1(x)
y = self.sigmoid(z)
return y
model = BinaryClassificationModel()손실함수
BCE (Binary Cross Entropy)
이진 분류 문제에서 모델의 예측 변수와 목표 변수 간의 차이를 측정하기 위해 사용되는 손실 함수
- nn.BCELoss()
- BCE 손실함수
import torch.optim as optim
loss_function = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)num_epochs = 500
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train()
epoch_loss = 0
for batch_features, batch_labels in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(batch_features)
loss = loss_function(outputs, batch_labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
loss_list.append(epoch_loss / len(train_loader))
if (epoch+1) % 100 == 0:
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {loss.item()}')import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure()
plt.plot(loss_list, label='Train Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.title('Loss Trend')
plt.show()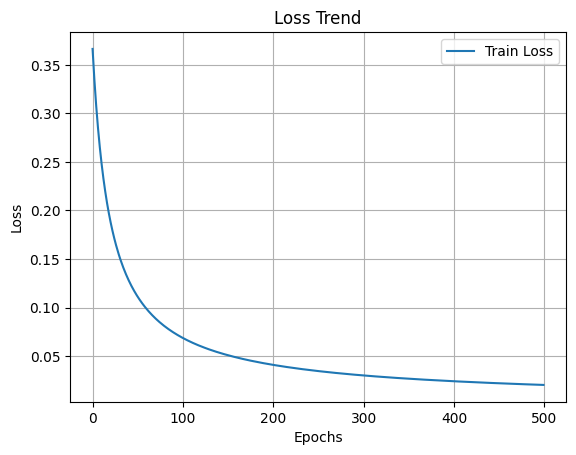
테스트
학습된 모델을 통해 테스트 데이터의 결과 예측
import numpy as np
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = model(x_test)
predicted_labels = (predictions > 0.5).float()
# 예측 결과와 실제 라벨을 출력하는 코드 표현 실습
actual_labels = t_test.numpy()
predicted_labels = predicted_labels.numpy()
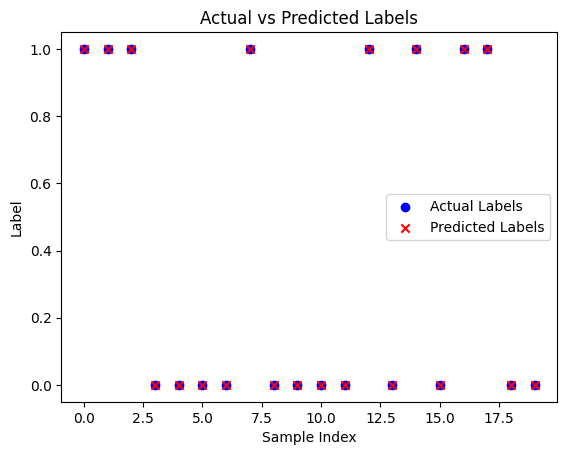
print("Predictions:", predicted_labels.flatten())
print("Actual Labels:", actual_labels.flatten())Predictions: [1. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0.]
Actual Labels: [1. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0.]
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(range(len(actual_labels)), actual_labels, color='blue', label='Actual Labels')
plt.scatter(range(len(predicted_labels)), predicted_labels, color='red', marker='x', label='Predicted Labels')
plt.xlabel('Sample Index')
plt.ylabel('Label')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted Labels')
plt.show()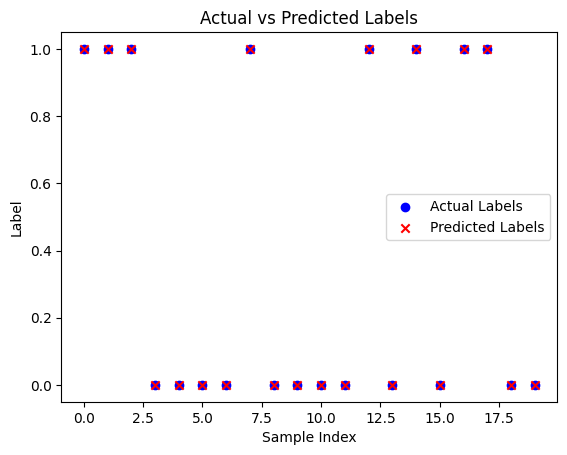
결론
이진 분류는 다양한 분야에서 중요한 역할을 하며, 로지스틱 회귀와 신경망 기반 모델을 통해 효과적으로 구현될 수 있다.
본 포스팅을 통해 데이터 전처리, 모델 학습, 손실 함수 및 경사 하강법의 개념을 이해하고, 실제로 모델을 구현하는 과정까지 경험하였다.
이러한 지식은 단순한 이진 분류 모델을 넘어, 다중 분류 모델 등 더 복잡한 머신러닝 기법으로 나아가는 토대를 마련해 줄 것이다.