- python3
Problem
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), return the number of islands.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
Output: 1Example 2:
Input: grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
Output: 3Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 300
- grid[i][j] is '0' or '1'.
Plan Solution
BFS
- Initialize the Visited Set:
- Create a hash set named visited to keep track of the positions that have already been visited to avoid processing the same position multiple times.
- Enqueue Initial Positions:
- Traverse each position in the grid.
- For every position containing '1' (representing land) that has not been visited, enqueue the position and mark it as visited.
- This marks the start of a new island.
- Process the Queue:
- While the queue is not empty, dequeue a position and check all four possible movements (up, down, left, right).
- For each valid movement to an adjacent land position that has not been visited, enqueue the new position and mark it as visited.
- Continue this process until the queue is empty, indicating that the entire island has been traversed.
- Count the Islands:
- Increment the island count each time a new starting position is processed, and return the total count after all positions in the grid have been checked.
DFS
- While traversing the grid, if a '1' is found, start a DFS.
- The DFS visits the current cell and changes '1' to '#'.
- The DFS makes recursive calls in the order: down, up, right, and left to visit all connected '1's.
- The visited cells are marked as '#' to ensure they are not visited again.
- Once all connected '1's are visited, the DFS call ends, and the island count is incremented by 1.
- Continue traversing all cells in the grid to count the number of islands.
- Finally, return the total number of islands.
Code
BFS
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
count = 0
visited = set()
for i in range(rows):
for j in range (cols):
if grid[i][j] == '1' and (i,j) not in visited:
count+=1
self.bfs(grid, visited, i, j)
return count
def bfs(self, grid: List[List[str]], visited:set, i:int, j:int):
queue = deque([(i, j)])
visited.add((i,j))
while queue:
row, col = queue.popleft()
directions = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]
for dr, dc in directions:
nr, nc = row + dr, col + dc
if 0 <= nr < len(grid) and 0<= nc <len(grid[0]) and grid[nr][nc] == '1' and (nr, nc) not in visited:
visited.add((nr,nc))
queue.append((nr,nc))DFS
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
def dfs(i, j):
if i < 0 or j < 0 or i >= len(grid) or j >= len(grid[0]) or grid[i][j] != '1':
return
grid[i][j] = '#'
dfs(i + 1, j) # 아래로
dfs(i - 1, j) # 위로
dfs(i, j + 1) # 오른쪽으로
dfs(i, j - 1) # 왼쪽으로
count = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == '1':
dfs(i, j)
count += 1
return countResult
BFS
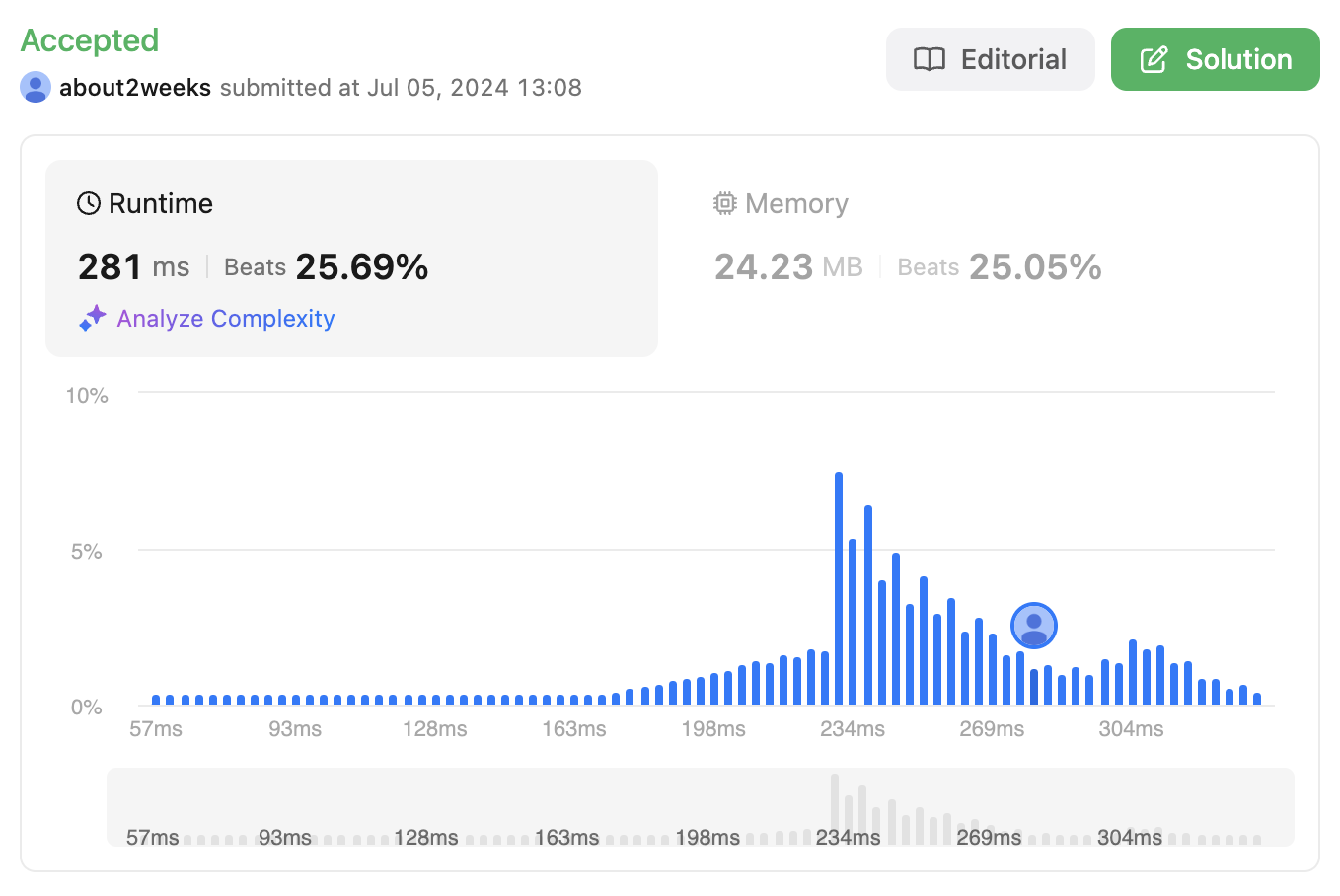
- Time Complexity : O(m*n)
- Space Complexity : O(m*n)
DFS
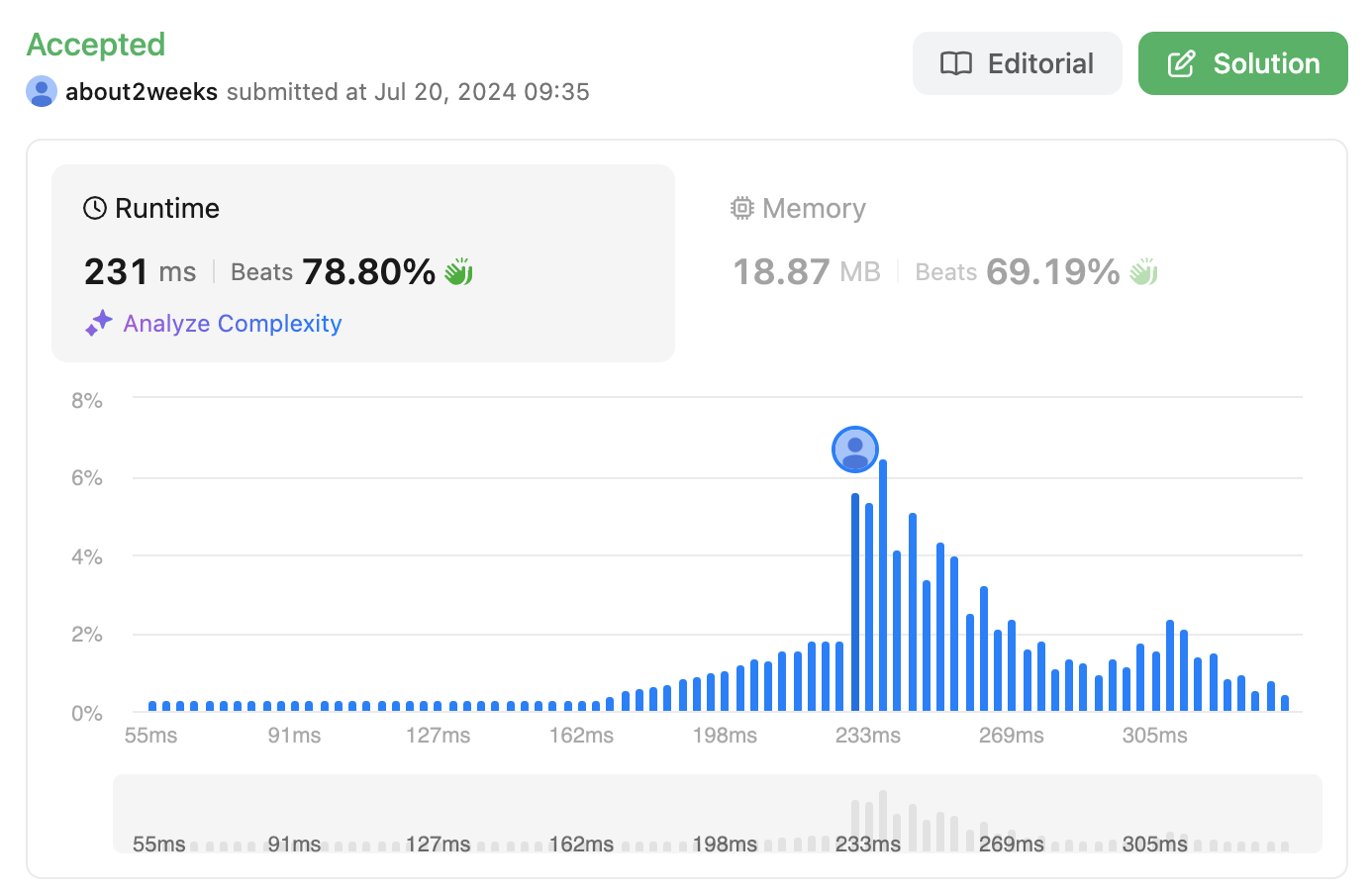
- Time Complexity : O(m*n)
- Space Complexity : O(m*n)
